In a healthcare setting, safety shoes are crucial for protecting professionals from a range of often-underestimated workplace hazards. While not as obvious as a construction site, environments like hospitals, clinics, and laboratories present significant risks from sharp objects, hazardous fluids, slippery surfaces, and heavy rolling equipment. Standard footwear simply does not offer the necessary protection against these daily threats.
The core reason healthcare professionals need safety shoes is to mitigate specific, environment-related risks that go beyond simple comfort. These shoes are a critical piece of personal protective equipment (PPE) designed to prevent puncture wounds, chemical burns, slips, and impact injuries.

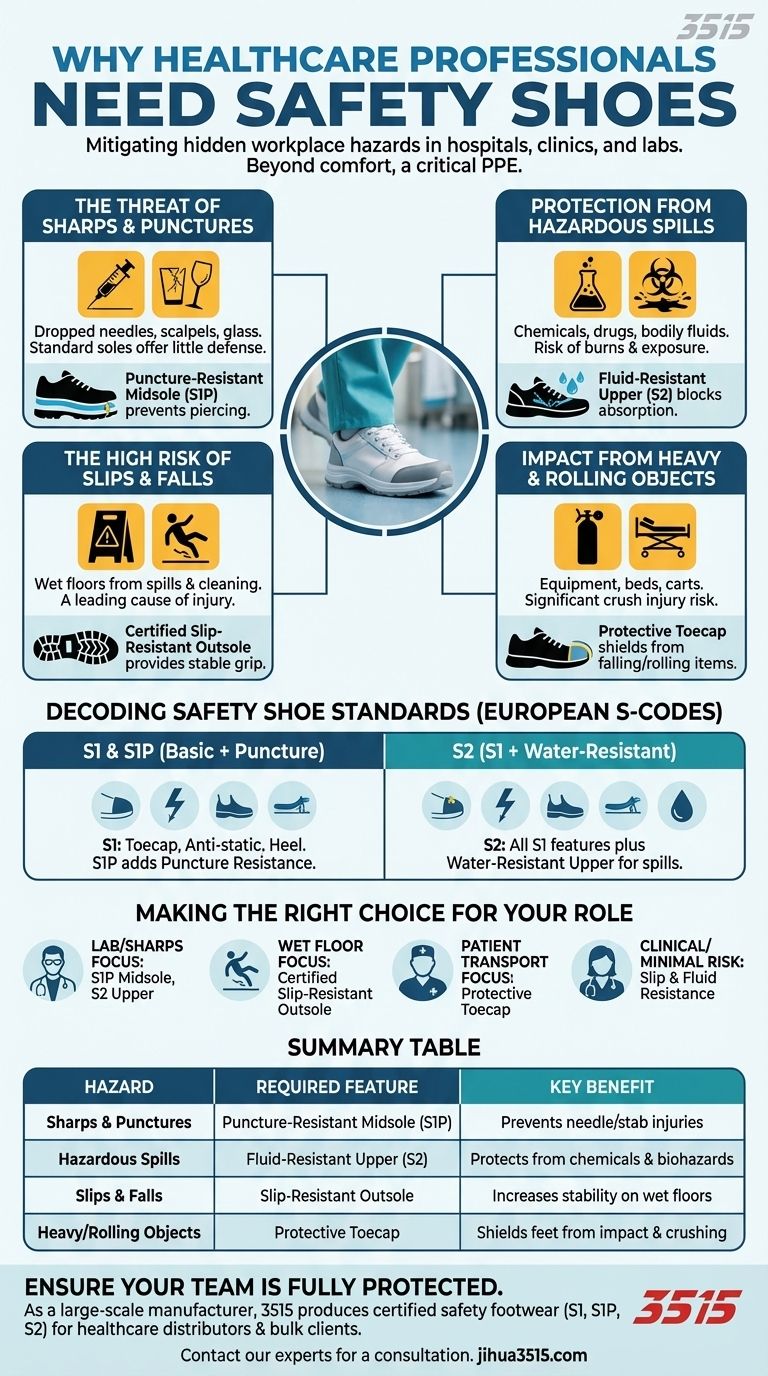
Unpacking the Hidden Hazards in Healthcare
The perception of healthcare footwear often centers on comfort for long shifts. However, for many roles, specific safety features are non-negotiable to address the unique dangers present in a clinical or laboratory environment.
The Threat of Sharps and Punctures
One of the most immediate dangers is from dropped sharps. This includes hypodermic needles, scalpels, and broken glass from vials or lab equipment.
A standard shoe offers little to no defense against a sharp object piercing the sole, which can lead to injury and potential exposure to infectious agents. Puncture-resistant safety shoes have a specialized midsole plate to prevent these objects from reaching the foot.
Protection from Hazardous Spills
Healthcare workers are routinely exposed to a variety of fluids. These can range from water and cleaning agents to corrosive chemicals, chemotherapy drugs, blood, and other bio-hazardous materials.
Fluid-resistant uppers, a key feature of certain safety shoe classifications, prevent these substances from seeping through to the skin, protecting against chemical burns and pathogenic exposure.
The High Risk of Slips and Falls
Floors in healthcare facilities are frequently wet from spills or constant cleaning. Slips, trips, and falls are among the most common causes of injury for healthcare workers.
Safety footwear with certified, high-traction, slip-resistant outsoles provides a stable grip on these unpredictable surfaces, drastically reducing the risk of a fall.
Impact from Heavy and Rolling Objects
While not often considered, the risk of impact and compression injuries is significant. This danger comes from portable medical equipment, rolling patient beds and gurneys, heavy oxygen canisters, and other movable devices.
A protective toecap, made from steel, composite, or alloy, shields the foot from falling objects or from being crushed by rolling equipment.
Decoding Safety Shoe Standards
Understanding the classification system for safety shoes helps in selecting the appropriate level of protection. While there are several global standards, the European "S-codes" are a common reference.
What 'S1' and 'S2' Ratings Mean
For healthcare and lab environments, the most relevant ratings are typically S1 and S2.
S1 rated shoes offer a basic level of protection, including a safety toecap, anti-static properties, and an enclosed heel. An S1P shoe adds a puncture-resistant midsole to this base.
S2 rated shoes include all the features of S1 but add a water-resistant upper, making them ideal for environments where spills are a primary concern.
Key Features to Prioritize
The specific hazards of your role dictate the features you need. The most critical for healthcare are puncture resistance, fluid resistance, and slip resistance. A protective toecap is essential for those handling heavy equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing safety footwear involves balancing protection with the practical demands of the job. It's important to approach this as a calculated decision about risk management.
Comfort vs. Protection
Proper safety shoes may feel heavier or less flexible than traditional clogs or athletic shoes. However, this is a direct trade-off for essential features like puncture-proof soles and impact-resistant toecaps that prevent serious injury.
Cost and Maintenance
Certified safety footwear is an investment in your personal safety. Like any critical tool, it requires proper care to maintain its protective qualities. Neglecting them can cause materials to degrade, compromising their integrity and putting you at risk.
Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
The level of protection needed varies by role. A surgeon in an operating room has different footwear needs than a lab technician handling chemicals or a porter transporting patients. A thorough risk assessment of your specific duties is the best way to determine the required level of PPE.
Making the Right Choice for Your Role
Selecting the correct footwear depends entirely on the specific risks you face daily.
- If your primary focus is working with sharps or in a lab: Prioritize a shoe with certified puncture resistance (S1P) and fluid-resistant uppers (S2).
- If your primary focus is navigating frequently wet or polished floors: Your non-negotiable feature is a certified slip-resistant outsole.
- If your primary focus is transporting patients or heavy equipment: A protective toecap is essential to guard against impact and compression injuries.
- If your primary focus is clinical work with minimal exposure to sharps or chemicals: A shoe with excellent slip resistance and fluid resistance may be sufficient.
Choosing the right footwear is a fundamental part of ensuring your own safety in a demanding professional environment.
Summary Table:
| Hazard | Required Safety Feature | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sharps & Punctures | Puncture-Resistant Midsole (S1P) | Prevents needle/stab injuries |
| Hazardous Spills | Fluid-Resistant Upper (S2) | Protects from chemicals & biohazards |
| Slips & Falls | Slip-Resistant Outsole | Increases stability on wet floors |
| Heavy/Rolling Objects | Protective Toecap | Shields feet from impact & crushing |
Ensure your team is fully protected. As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients in the healthcare sector. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots designed to meet S1, S1P, and S2 standards. Let us help you mitigate workplace risks with durable, purpose-built PPE. Contact our experts today for a consultation and to discuss your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Premium Lightweight Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Custom Safety Shoe Manufacturer for Wholesale & OEM Brands
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Breathable Training Shoes Custom Athletic Footwear Manufacturer
People Also Ask
- What protective functions do industrial safety shoes provide in petroleum environments? Secure Your Workers' Health
- Why are insulated protective shoes necessary? Essential Protection Against High-Voltage and Electrical Leakage Risks
- What is the significance of Functional Reach Test (FRT) benchmarks for balance risks in heavy boots and safety gear?
- How does the alignment of price and quality influence the perceived value of bulk-sourced safety shoes? | 3515 Insights
- How can the monitoring of safety shoe usage be utilized as a KPI? Drive Compliance & Strategic Safety Management
- Why is the Figure-of-8 obstacle walk test necessary? Essential Safety Shoe Performance Evaluation
- How do specialized safety shoes and tactical boots mitigate physical risks? Essential Protection for Industry Leaders
- Which is better, steel toe or composite toe boots? Match Your Job's Hazards for Optimal Safety



















