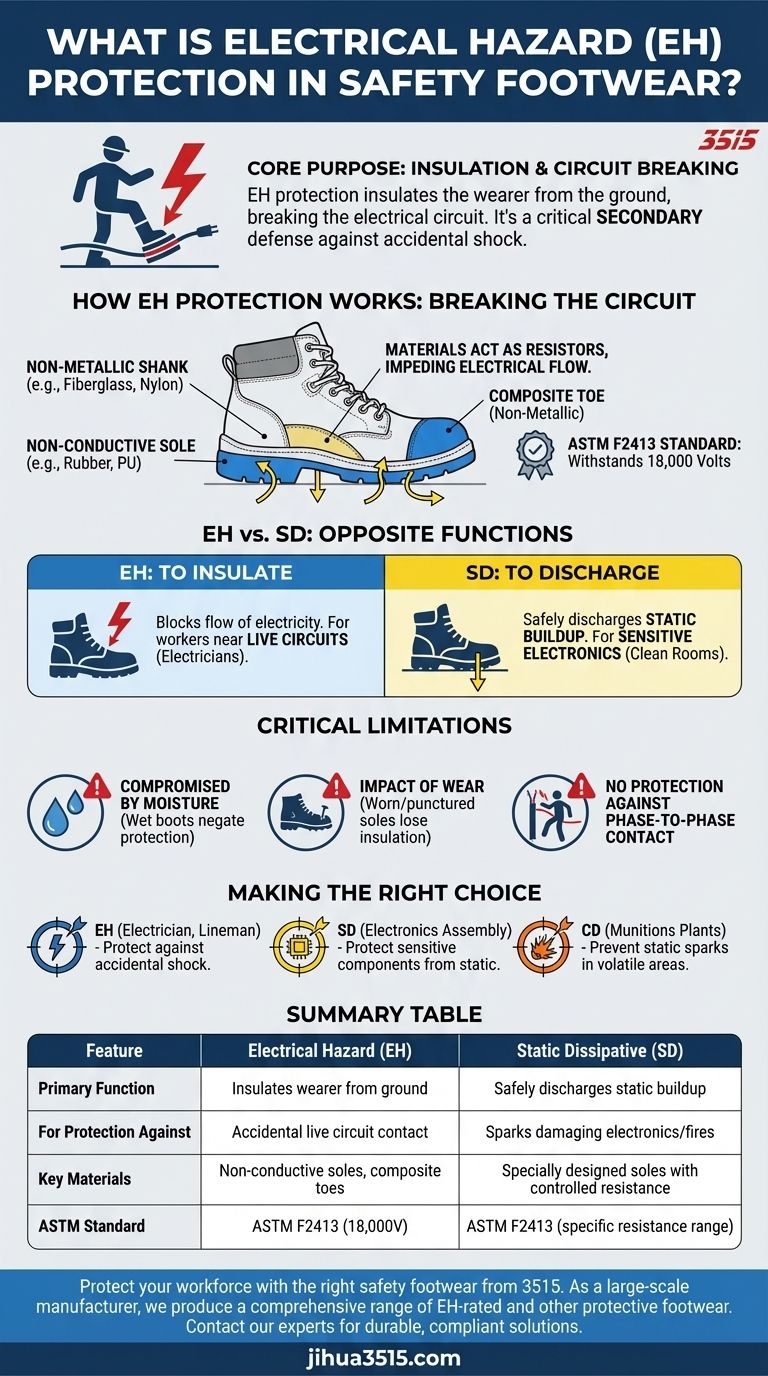
In simple terms, electrical hazard (EH) protection in safety footwear is a design feature that insulates you from the ground. The boot's non-conductive sole and heel are built to drastically reduce the chance of electricity flowing through your body if you accidentally step on a live electrical circuit. This feature serves as a critical secondary defense against electric shock.
The core purpose of Electrical Hazard (EH) rated footwear is to function as an insulator, breaking the electrical circuit between you and the ground. This design is fundamentally about protecting the wearer from accidental shock, not about managing static electricity.

How EH Protection Works: Breaking the Circuit
To understand EH footwear, it's essential to grasp the basic principle of an electrical circuit. For a person to receive a shock, their body must complete a path for electricity to flow from a power source to the ground. EH boots are engineered to interrupt this path.
The Principle of Insulation
EH-rated boots act as a resistor, a component that impedes the flow of electrical current. The materials used in the sole and heel are highly resistant to conducting electricity.
This insulation stops your body from becoming the "path of least resistance" for a current trying to reach the ground through your feet.
Key Construction Materials
The effectiveness of EH footwear comes down to its materials. The outsoles and heels are typically made from non-conductive compounds like rubber or specially formulated polyurethane.
These materials are chosen for their high dielectric strength, meaning they can withstand high voltage without breaking down and allowing current to pass through.
The Role of Non-Metallic Components
To ensure no conductive paths exist, EH boots are designed with non-metallic parts wherever possible. This is why composite safety toes are strongly preferred over steel toes in these environments.
While a steel toe boot can achieve an EH rating if constructed correctly, a non-metallic composite toe eliminates a potential conductor entirely, offering a more inherently insulating design. The shank, which provides arch support, will also be made of a non-conductive material like fiberglass or nylon instead of steel.
The ASTM Standard
Footwear claiming EH protection must meet a specific standard set by ASTM International (ASTM F2413). This standard requires a boot to withstand the application of 18,000 volts at 60 Hz for one minute with no dangerous current flow to the wearer.
Differentiating EH from Static Dissipative (SD) Footwear
A common and dangerous point of confusion is the difference between Electrical Hazard (EH) and Static Dissipative (SD) footwear. They serve opposite functions.
Electrical Hazard (EH): To Insulate
EH boots are designed to block the flow of electricity. They are for workers at risk of accidental contact with live electrical circuits, such as electricians or utility workers.
Static Dissipative (SD): To Release
SD footwear is designed to safely discharge the body's static electricity buildup into the floor. This prevents a static spark that could damage sensitive electronic components or ignite flammable materials. SD boots have a lower electrical resistance than regular shoes but a much higher resistance than fully conductive footwear.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
Trusting EH footwear requires understanding its limitations. It is a valuable tool, but it is not infallible.
Not a Primary Defense
EH boots are always considered a secondary source of protection. The primary safety measures in any electrical environment are de-energizing circuits, proper lockout/tagout procedures, and using insulated tools.
The Impact of Moisture and Wear
The insulating properties of EH footwear are severely compromised by water. If the boots are wet, or if the wearer is standing in water, the protective barrier is negated.
Furthermore, as the sole wears down or becomes punctured by conductive objects like metal shavings or nails, its insulating capability degrades and can be lost entirely.
Protection from the Ground Up Only
EH boots only offer protection from shock potentials that occur from the ground up. They provide no protection against phase-to-phase contact, such as touching two separate live conductors at the same time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Job
Selecting the appropriate footwear is a critical safety decision based entirely on the specific hazards of your environment.
- If your primary focus is working near live electrical circuits (electrician, lineman): Your non-negotiable is a clearly marked, ASTM-certified EH-rated boot to protect against accidental shock.
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive electronics from static discharge (clean rooms, circuit board assembly): You need Static Dissipative (SD) footwear to safely channel static buildup away from your body.
- If your primary focus is working in highly explosive or volatile environments (munitions plants): You may require Conductive (CD) footwear, which prevents any static buildup whatsoever by directly grounding you.
Choosing the correct safety footwear is not just about compliance; it's a critical decision that directly impacts your personal safety on the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electrical Hazard (EH) | Static Dissipative (SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Insulates the wearer from the ground | Safely discharges static buildup |
| For Protection Against | Accidental contact with live circuits | Sparks that could damage electronics or ignite fires |
| Key Materials | Non-conductive soles (rubber, PU), composite toes | Specially designed soles with controlled electrical resistance |
| ASTM Standard | ASTM F2413 (withstands 18,000 volts) | ASTM F2413 (specific resistance range) |
Protect your workforce with the right safety footwear from 3515.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of EH-rated and other protective footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots, ensuring your team has the critical secondary protection they need.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific safety requirements and explore our durable, compliant footwear solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Wholesale Durable Safety Boots | Custom Steel Toe & Puncture-Resistant Manufacturing
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
People Also Ask
- Why are puncture-resistant soles necessary for oilfield safety shoes? Prevent Severe Foot Injuries on the Job
- What are OSHA approved shoes? Understanding the Correct Standards for Workplace Safety
- Why is a waterproof membrane important in safety footwear? Essential for Worker Health & Performance
- What are the limitations of composite toe boots? A Guide to the Safety Trade-offs
- What are the different names for safety shoes? Choose the Right Protection for Your Job
- What factors should be considered when purchasing work shoes? A Guide to Safety, Comfort, and Durability
- What are the benefits of a waterproof lining in safety boots? Protect Your Feet and Your Gear
- What are the key performance benchmarks set by the EN ISO 20345 standard for safety boots? A Guide to Selecting the Right Protection



















