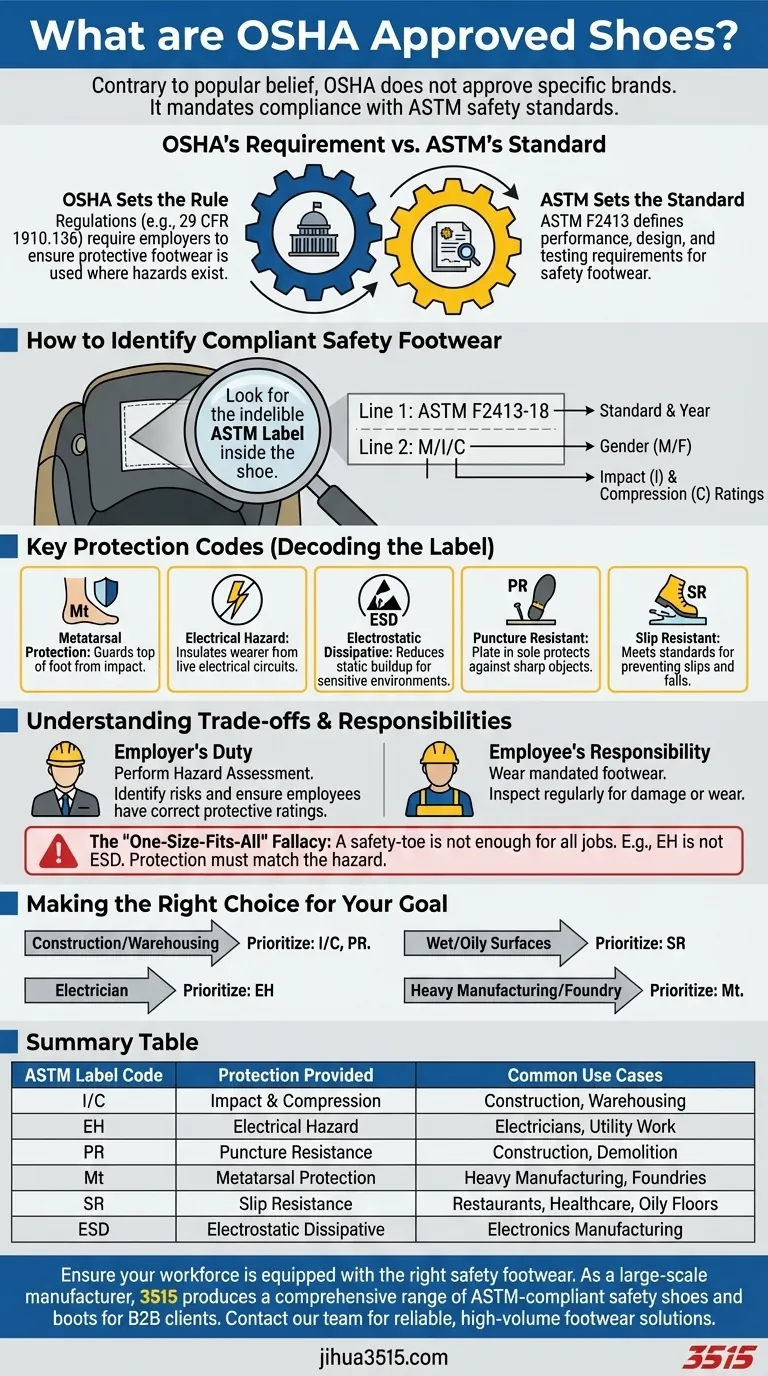
Contrary to a common misconception, OSHA does not approve, certify, or endorse specific brands or models of shoes. Instead, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires employers to ensure their workers use protective footwear that meets or exceeds specific safety standards, most notably those set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). A compliant shoe is identified not by an OSHA logo, but by an indelible label inside the shoe detailing the specific ASTM standard (e.g., ASTM F2413-18) it meets.
The critical point isn't finding an "OSHA Approved" sticker. It's about understanding that OSHA mandates the use of footwear that is tested and certified to specific ASTM standards to protect workers against identified workplace hazards like impact, compression, and electrical shock.
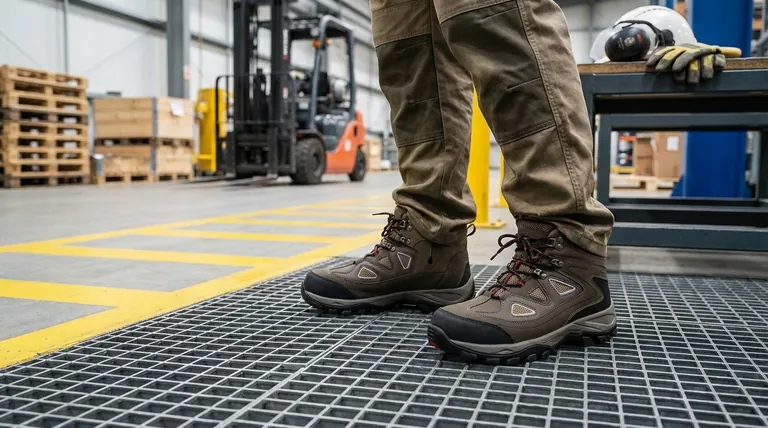

OSHA's Requirement vs. ASTM's Standard
To select the right footwear, you must understand the two key organizations involved and their distinct roles. One sets the rule, and the other defines the performance.
OSHA Sets the Rule
OSHA is the U.S. government agency responsible for ensuring safe and healthful working conditions.
Their regulations, such as 29 CFR 1910.136, state that employers must require employees to use protective footwear when they are working in areas where there is a danger of foot injury.
ASTM Sets the Standard
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) is an international standards organization that develops and publishes technical standards.
ASTM F2413 is the primary standard for protective footwear performance in the United States. It specifies the minimum requirements for design, performance, testing, and classification.
How to Identify Compliant Safety Footwear
The proof of a shoe's compliance is found on its label, typically stitched to the tongue or inside of the shoe. This information tells you exactly what hazards the shoe is designed to protect against.
Decoding the ASTM Label
A compliant label will have a specific format that is easy to read once you know what to look for. It is typically presented in a two-line format.
Line 1: ASTM F2413-18
This line confirms the shoe meets the performance requirements of the ASTM F2413 standard and indicates the year of the standard it was tested against (in this case, 2018).
Line 2: M/I/C
This line identifies the gender (M/Male or F/Female) the shoe is for, followed by the ratings for Impact (I) and Compression (C) resistance, which are foundational for all safety-toe footwear.
Key Protection Codes
Following the primary I/C rating, additional codes denote protection against specific hazards.
- Mt (Metatarsal): Protects the top of the foot (the metatarsal bones) from impact.
- EH (Electrical Hazard): Insulates the wearer from the ground, protecting against accidental contact with live electrical circuits.
- ESD (Electrostatic Dissipative): Reduces the buildup of static electricity, crucial for work in sensitive electronics manufacturing or certain volatile environments.
- PR (Puncture Resistant): Includes a puncture-resistant plate in the sole to protect against sharp objects from below.
- SR (Slip Resistant): Indicates the shoe meets specific standards for slip resistance, a critical factor in preventing workplace falls.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Responsibilities
Choosing the right shoe is a shared responsibility, and focusing on only one type of protection can create new risks.
The Employer's Duty
The employer must first perform a hazard assessment of the workplace. This process identifies the specific foot-related dangers present, such as falling objects, rolling equipment, sharp materials, or electrical wires.
Based on this assessment, the employer is responsible for ensuring employees are using footwear with the correct protective ratings.
The Employee's Responsibility
The employee is responsible for wearing the protective footwear mandated by their employer.
They must also inspect the footwear regularly for damage or excessive wear, as compromised shoes may no longer provide the required level of protection.
The "One-Size-Fits-All" Fallacy
A common mistake is assuming any safety-toe shoe is sufficient for any job.
A shoe rated for Electrical Hazard (EH) protection is fundamentally different from an Electrostatic Dissipative (ESD) shoe. Likewise, a shoe with impact resistance offers no protection from a nail puncturing the sole unless it is also rated for Puncture Resistance (PR).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct footwear is about matching the shoe's certified protections to your specific workplace hazards.
- If your primary focus is construction or warehousing: Prioritize footwear with high ratings for Impact (I), Compression (C), and Puncture Resistance (PR).
- If your primary focus is working as an electrician: You must have footwear specifically rated for Electrical Hazard (EH) protection.
- If your primary focus is working on wet or oily surfaces: Ensure your shoes are certified as Slip Resistant (SR) to prevent falls.
- If your primary focus is heavy manufacturing or foundry work: Consider Metatarsal (Mt) protection for added safety against objects dropping on the top of your foot.
Ultimately, a compliant safety shoe is not just a piece of equipment; it's a critical tool precisely chosen to mitigate the specific risks of your job.
Summary Table:
| ASTM Label Code | Protection Provided | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| I/C | Impact & Compression Resistance | Construction, Warehousing |
| EH | Electrical Hazard Protection | Electricians, Utility Work |
| PR | Puncture Resistance | Construction, Demolition |
| Mt | Metatarsal Protection | Heavy Manufacturing, Foundries |
| SR | Slip Resistance | Restaurants, Healthcare, Oily Floors |
| ESD | Electrostatic Dissipative | Electronics Manufacturing |
Ensure your workforce is equipped with the right safety footwear.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of ASTM-compliant safety shoes and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We can help you source the precise footwear rated for your specific workplace hazards—from impact and compression to electrical hazard and slip resistance.
Contact our team today for a consultation on reliable, high-volume footwear solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
- Premium Sport Style Safety Boots for Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- Do snake bite boots work? Your Ultimate Guide to Effective Snake Bite Protection
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture
- Is safety-toe as good as steel toe? Choose the Right Protection for Your Job
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management



















