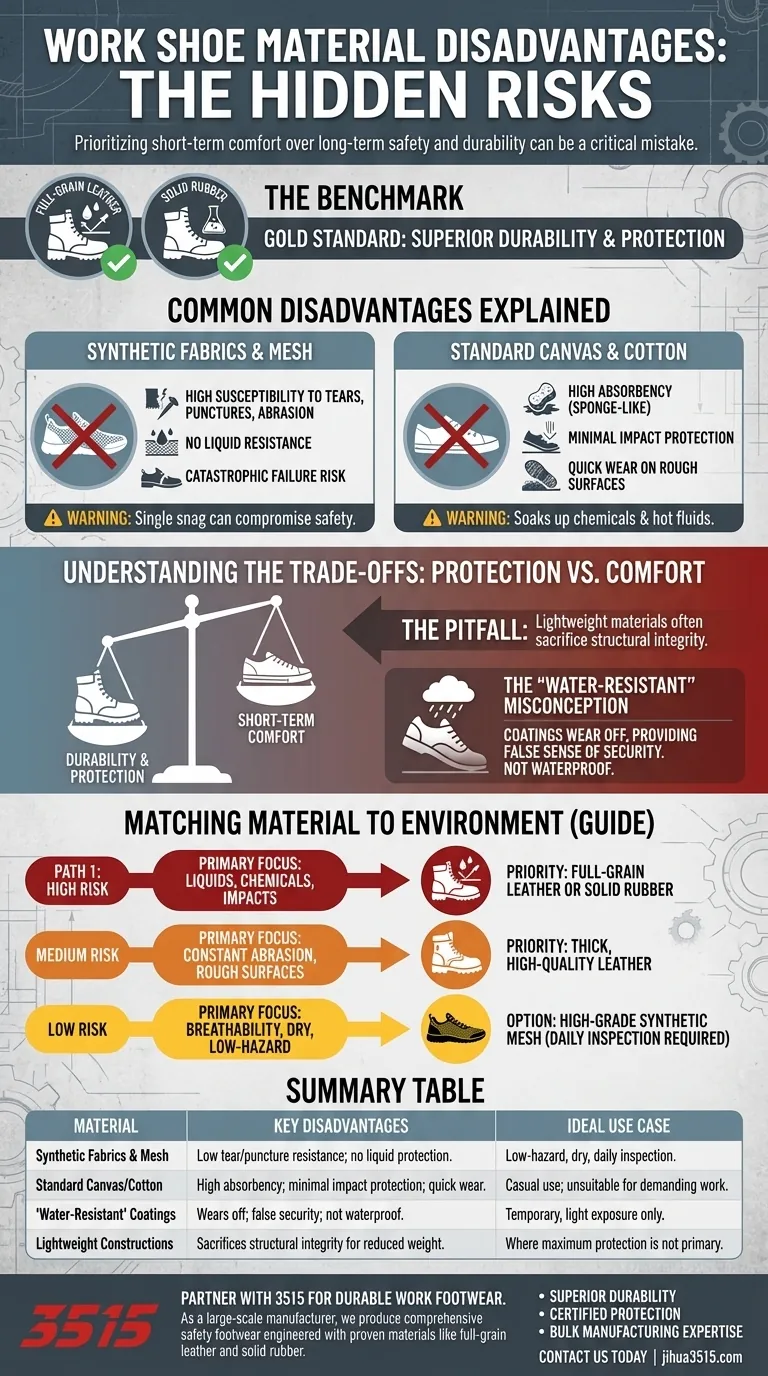
Ultimately, the key disadvantages of certain work shoe materials are a severe lack of durability and an inability to protect you from workplace hazards. Materials like basic synthetic mesh or canvas often fail to provide the necessary resistance to liquids, abrasion, and impacts, creating a significant safety risk compared to proven materials like leather and rubber.
Choosing a work shoe based on comfort alone can be a critical mistake. Many modern, lightweight materials sacrifice the fundamental durability and protection required in demanding environments, leading to premature failure and potential injury.

A Framework for Evaluating Work Shoe Materials
Before diving into specific disadvantages, it's crucial to understand the context. The "best" material is entirely dependent on the hazards of your specific job. A material that is a disadvantage in a machine shop could be an advantage in a dry warehouse.
The Benchmark: Leather and Rubber
For decades, full-grain leather and solid rubber have been the gold standard for work footwear for a reason. They offer a superior combination of durability, puncture resistance, and protection from liquids and chemicals. Most other materials are measured against this high standard.
Common Material Disadvantages Explained
While newer materials offer benefits like reduced weight and increased breathability, these advantages often come with significant downsides in a work context.
Synthetic Fabrics & Mesh
Many modern work shoes incorporate nylon or polyester mesh panels for ventilation and flexibility. However, this is their primary weakness.
These materials are highly susceptible to tears, punctures, and abrasion. A single snag on a sharp corner can create a catastrophic failure in the shoe's upper.
Furthermore, mesh and standard synthetic fabrics offer virtually no resistance to liquids. Spills, chemicals, or even morning dew can easily penetrate the material, compromising your safety and comfort.
Standard Canvas and Cotton
Canvas is a durable fabric for casual use but is generally unsuitable for demanding work environments.
Its main disadvantage is its high absorbency. Canvas acts like a sponge, soaking up any liquid it contacts, which poses a serious risk with chemical or hot fluid spills.
It also provides minimal protection from impacts or compression and wears out very quickly when exposed to rough surfaces like concrete or gravel.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Protection vs. Comfort
The most common mistake is prioritizing short-term comfort over long-term safety and durability. The disadvantages of a poor material choice often become apparent only after a safety incident occurs.
The Pitfall of Lightweight Construction
The appeal of a lightweight, sneaker-like work shoe is understandable. However, this weight reduction is often achieved by using less durable materials.
These materials may not have the structural integrity to protect your foot from a falling object or the crushing force of heavy equipment, even if the shoe has a safety toe.
The "Water-Resistant" Misconception
Many synthetic materials are treated with a coating to make them "water-resistant." This is not the same as being waterproof.
These coatings wear off over time, especially with exposure to dirt and chemicals. They provide a false sense of security and will inevitably fail, unlike the inherent liquid resistance of high-quality rubber or properly treated leather.
Durability Under Daily Stress
The core point is that materials not specifically engineered for occupational stress will break down. Seams will rip, fabrics will tear, and the shoe will lose its supportive structure far sooner than a purpose-built leather or rubber boot. This not only costs more in frequent replacements but creates a constant risk of failure.
Matching the Material to Your Work Environment
Use the demands of your job as the ultimate guide for selecting a shoe material.
- If your primary focus is protection from liquids, chemicals, or impacts: Prioritize full-grain leather or seamless rubber constructions.
- If your primary focus is durability against constant abrasion and rough surfaces: A thick, high-quality leather is the most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is breathability in a dry, low-hazard environment: A shoe with panels made from high-grade, tear-resistant synthetic mesh may be an acceptable option, but inspect it for wear daily.
By understanding these material limitations, you can make an informed choice that prioritizes your safety and well-being on the job.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Disadvantages | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Synthetic Fabrics & Mesh | Low tear/puncture resistance; no liquid protection; prone to catastrophic failure. | Low-hazard, dry environments with daily inspection. |
| Standard Canvas/Cotton | High absorbency (sponge-like); minimal impact protection; quick wear on rough surfaces. | Casual use; unsuitable for most demanding work. |
| 'Water-Resistant' Coatings | Wears off over time; provides a false sense of security; not permanently waterproof. | Temporary, light exposure only. |
| Lightweight Constructions | Often sacrifices structural integrity and protective qualities for reduced weight. | Where maximum protection is not the primary concern. |
Don't Compromise on Safety – Partner with 3515 for Durable Work Footwear
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of durable shoes and boots, engineered with proven materials like full-grain leather and solid rubber to overcome the common disadvantages of inferior materials.
We provide:
- Superior Durability: Footwear built to withstand daily occupational stress, reducing replacement costs.
- Certified Protection: Reliable safety features for hazards like impacts, punctures, and liquids.
- Bulk Manufacturing Expertise: Consistent quality and reliable supply for your business needs.
Let's discuss your requirements and ensure your workforce is properly protected.
Contact 3515 today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Factory-Direct Wholesale Canvas Boots with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- How are safety shoes classified under the EN ISO 20345 standard? A Guide to SB, S1, S1P, S2, S3, S4, and S5 Ratings
- Why is high-breathability inner lining material critical for diabetic protective footwear? Ensure Superior Skin Health
- Why use breathable, protective safety shoes for high-heat labor? Protect Physical Health and Renal Function
- What are the advantages of using fabrics in safety shoe uppers? Enhance Comfort & Style for Indoor Work
- What is the function of eco-labeling? Drive B2B Growth with Transparent Green Data for Safety & Training Shoes
- Where are composite toe shoes typically used? Essential for Electrical & Security Work
- In what way do assistive devices like crutches and protective footwear synergize during early-stage load management?
- What is the purpose of front hardeners in safety shoes? Essential Protection for Construction & Welding



















