Choosing the right safety shoe is a critical decision based on the specific hazards of your work environment. For industrial or construction sites, steel-toe boots are essential for protection against heavy falling objects, while slip-resistant shoes are non-negotiable for kitchens or food processing plants with wet surfaces. For electricians, Electrical Hazard (EH) rated shoes are required to protect against shock, and those working with chemicals need specifically resistant footwear.
The most effective way to select safety footwear is not by job title, but by conducting a simple risk assessment of your environment. Identify the primary hazards—impact, puncture, slipping, or electrical—and choose the shoe with the specific features designed to mitigate those exact risks.

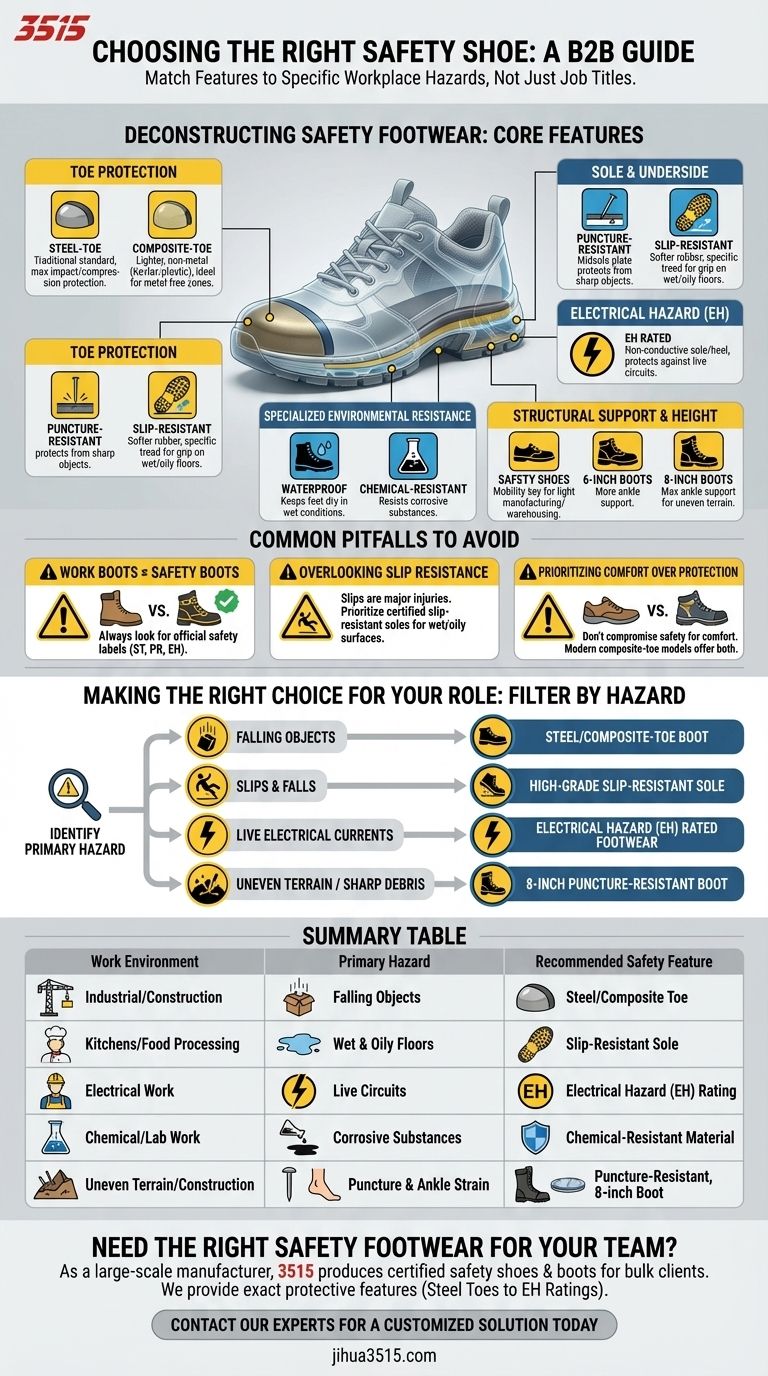
Deconstructing Safety Footwear: The Core Features
To make an informed choice, you must first understand the distinct protective components that define a safety shoe. Each feature is engineered to counter a specific type of workplace hazard.
Toe Protection: Steel vs. Composite
The most recognized safety feature is the protective toe cap. Steel-toe caps are the traditional standard, offering maximum protection against impact and compression from heavy objects.
Composite-toe caps are made from non-metal materials like Kevlar, carbon fiber, or plastic. They provide a lighter-weight alternative and are ideal for environments where metal-free footwear is required.
Sole and Underside Protection
The sole of the shoe provides two key forms of protection. Puncture-resistant soles contain a flexible steel or composite plate in the midsole to protect your feet from sharp objects like nails or scrap metal.
Slip-resistant outsoles are made from softer rubber compounds and feature specific tread patterns designed to channel away liquids, providing superior grip on wet, oily, or slick surfaces.
Electrical Hazard (EH) Protection
Electrical Hazard (EH) rated footwear is designed with non-conductive, shock-resistant soles and heels. This feature provides a secondary source of protection against accidental contact with live electrical circuits. It is absolutely essential for electricians and utility workers.
Specialized Environmental Resistance
For work in wet conditions or with corrosive materials, specialized protection is required. Waterproof boots are essential for roles in agriculture, fisheries, and mining to keep feet dry and prevent discomfort.
Chemical-resistant shoes are constructed from materials that can withstand degradation from specific corrosive substances, crucial for lab workers or those in chemical manufacturing.
Structural Support and Height
The height of the footwear often corresponds to the level of support and protection needed. Safety shoes are ideal for environments like warehousing or light manufacturing where mobility is key.
6-inch and 8-inch boots offer progressively more ankle support and protection, making them better suited for agriculture, general construction, and work on uneven terrain like asphalt paving.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Choosing the wrong footwear can create new risks. Understanding the trade-offs between different features is crucial for making a truly safe and effective decision.
Mistaking "Work Boots" for "Safety Boots"
A rugged-looking boot is not necessarily a safety boot. True safety footwear is rated and certified to meet specific protection standards. Always look for official labels indicating features like steel toe (ST), puncture resistance (PR), or electrical hazard (EH).
Overlooking Slip Resistance
Impact protection is often the primary focus, but slips, trips, and falls are among the most common workplace injuries. For any environment with water, oil, or smooth floor surfaces, a certified slip-resistant sole is a top priority.
Prioritizing Comfort Over Protection
While comfort is important for reducing fatigue, it should never come at the expense of necessary safety features. The primary factor in your decision must be the hazards of your environment. Modern safety shoes, especially composite-toe models, offer excellent protection without the weight of older designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Role
Filter your options based on the most significant and frequent hazards you face daily.
- If your primary focus is protection from falling objects: Your non-negotiable starting point is a certified steel-toe or composite-toe boot.
- If your primary focus is preventing slips and falls: Prioritize footwear with a high-grade, certified slip-resistant outsole designed for wet or oily surfaces.
- If your primary focus is working near live electrical currents: You must select footwear with a clear Electrical Hazard (EH) rating to ensure your safety.
- If your primary focus is navigating uneven terrain or sharp ground debris: An 8-inch, puncture-resistant boot offers the best combination of ankle support and underfoot protection.
Ultimately, the right safety shoe is a crucial piece of personal protective equipment tailored specifically to your daily risks.
Summary Table:
| Work Environment | Primary Hazard | Recommended Safety Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial/Construction | Falling Objects | Steel/Composite Toe |
| Kitchens/Food Processing | Wet & Oily Floors | Slip-Resistant Sole |
| Electrical Work | Live Circuits | Electrical Hazard (EH) Rating |
| Chemical/Lab Work | Corrosive Substances | Chemical-Resistant Material |
| Uneven Terrain/Construction | Puncture & Ankle Strain | Puncture-Resistant, 8-inch Boot |
Need the right safety footwear for your team? As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety shoes and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We can provide the exact protective features—from steel toes to EH ratings—your workforce requires. Contact our experts today for a customized solution that meets your safety standards and volume needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
People Also Ask
- What type of footwear is needed for those working in a foundry? Essential Protection for Extreme Heat & Metal Splash
- Why might mobile workers prefer composite toe boots? Lighter, Safer, and More Comfortable for All-Day Wear
- What are some key factors to consider for the fit of safety footwear? Ensure Optimal Protection and Comfort
- What is the significance of integrating inertial sensor-based classification technology into smart safety shoes?
- What is the primary function of standardized safety shoes? Essential Protection & Automated Compliance for Labs
- What is the key difference between work shoes and safety shoes? The Critical Feature You Need to Know
- What are the properties of rubber outsoles in safety shoes? Unmatched Durability & Slip Resistance
- Why might composite-toe boots be a better choice for passing through metal detectors? Ensure Security Checkpoint Efficiency



















