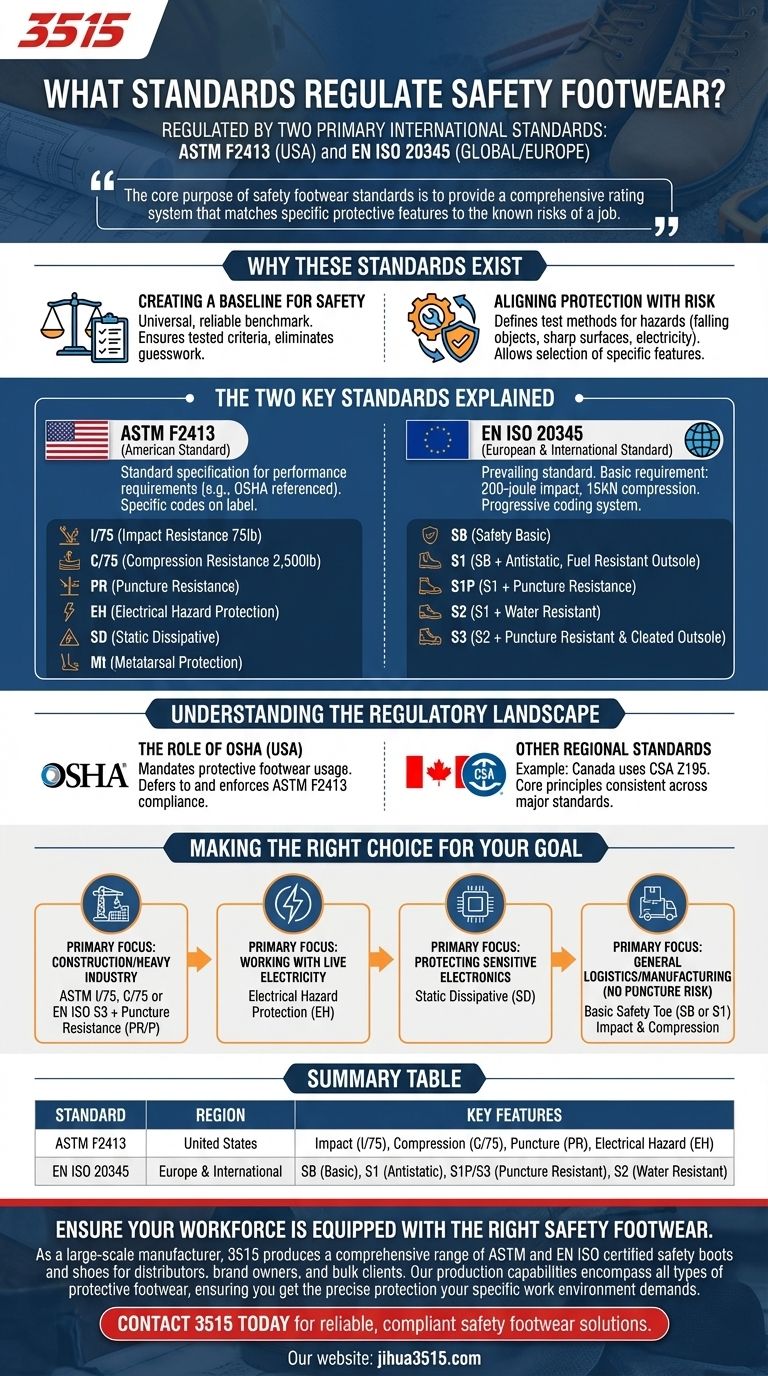
In short, safety footwear is regulated by two primary international standards: ASTM F2413 in the United States and EN ISO 20345, which is the European standard and a global benchmark. These standards define the minimum performance requirements for protecting feet against specific workplace hazards like impact, compression, and punctures.
The core purpose of safety footwear standards is not just to certify a "steel toe cap," but to provide a comprehensive rating system that matches specific protective features to the known risks of a job. Understanding these ratings is the key to ensuring true workplace safety.

Why These Standards Exist
Creating a Baseline for Safety
Safety footwear standards create a universal, reliable benchmark for performance. They ensure that a boot marketed as "protective" has been tested against a consistent set of criteria.
This eliminates guesswork for employers and workers, providing a clear language for identifying the protection offered.
Aligning Protection with Risk
The standards are designed to answer critical questions about performance. They define test methods and requirements for hazards like falling objects, sharp surfaces on the ground, and electrical contact.
This allows you to select footwear with features specifically designed to mitigate the actual risks present in your work environment.
The Two Key Standards Explained
ASTM F2413 (The American Standard)
ASTM F2413 is the standard specification for performance requirements for protective (safety) toe cap footwear in the United States. It is the standard referenced by regulatory bodies like OSHA.
The standard establishes minimum requirements for footwear to protect against a variety of hazards. Each requirement is denoted by a specific code on the shoe's label.
Key ASTM ratings include:
- I/75 (Impact Resistance): The toe cap can withstand a 75-pound impact.
- C/75 (Compression Resistance): The toe cap can withstand a compressive load of 2,500 pounds.
- PR (Puncture Resistance)
- EH (Electrical Hazard Protection)
- SD (Static Dissipative)
- Mt (Metatarsal Protection)
EN ISO 20345 (The European & International Standard)
EN ISO 20345 is the prevailing standard across Europe and is widely recognized internationally. It specifies that all safety footwear must have a toe cap capable of resisting a 200-joule impact and a 15 kilonewton (KN) compression test.
Footwear meeting this basic requirement is marked SB (Safety Basic). Additional protections are indicated by a progressive coding system:
- S1: SB requirements plus anti-static properties and a fuel-resistant outsole.
- S1P: All S1 requirements plus puncture resistance.
- S2: All S1 requirements plus resistance to water penetration and absorption.
- S3: All S2 requirements plus puncture resistance and a cleated outsole.
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape
The Role of OSHA
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates that employers ensure their employees use protective footwear when working in areas with foot injury hazards.
OSHA does not create its own footwear standard. Instead, it defers to and enforces compliance with ASTM F2413. This means that for a workplace to be OSHA-compliant, the safety footwear must meet the ASTM performance criteria.
Other Regional Standards
While ASTM and EN ISO are the most dominant, other countries and regions have their own standards. For example, Canada uses the CSA Z195 standard.
Though the testing methods may vary slightly, the core principles of protecting against impact, compression, and other specific hazards remain consistent across all major international standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate footwear, you must first conduct a risk assessment of your work environment. Once the specific hazards are identified, you can match them to the corresponding standard ratings.
- If your primary focus is construction or heavy industry: You need footwear with top-tier impact and compression ratings (ASTM I/75, C/75 or EN ISO S3) and mandatory puncture resistance (PR or P).
- If your primary focus is working with live electricity: You must select footwear specifically rated for Electrical Hazard protection (EH).
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive electronics: You need Static Dissipative (SD) footwear to prevent the buildup of static electricity that can damage components.
- If your primary focus is general logistics or manufacturing with no puncture risk: A basic safety toe (SB or S1) that meets impact and compression standards is often sufficient.
Ultimately, choosing the right safety footwear is an exercise in matching the certified protections of the shoe to the specific dangers of your job.
Summary Table:
| Standard | Region | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM F2413 | United States | Impact (I/75), Compression (C/75), Puncture (PR), Electrical Hazard (EH) |
| EN ISO 20345 | Europe & International | SB (Basic), S1 (Antistatic), S1P/S3 (Puncture Resistant), S2 (Water Resistant) |
Ensure your workforce is equipped with the right safety footwear.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of ASTM and EN ISO certified safety boots and shoes for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of protective footwear, ensuring you get the precise protection your specific work environment demands.
Contact 3515 today for reliable, compliant safety footwear solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Leather Safety Boots with Customizable Protective Toe
- Wholesale Durable Breathable Safety Boots Custom OEM Manufacturer
- Custom Safety Shoe Manufacturer for Wholesale & OEM Brands
People Also Ask
- Which standards does OSHA reference for safety footwear? Ensure Full Compliance with ASTM F2413
- How does a Reliability Block Diagram (RBD) enhance footwear stability? Engineering High-Performance Shoe Systems
- What are the primary protective functions of industrial safety boots in oil palm plantations? Master Rough Terrain Safety
- What materials are commonly used in external metatarsal guards? A Guide to Protection & Flexibility
- What features of safety shoes help withstand impact and compression hazards? Essential Protection for Your Workforce
- What is security guard safety boots risk assessment? A Guide to On-Site Hazard Analysis
- Why is the mechanical fatigue resistance of conductive yarns core to smart safety shoes? Ensure Data Reliability
- How do professional-grade safety shoes prevent nursing low back pain? Expert Solutions for Spinal Health



















