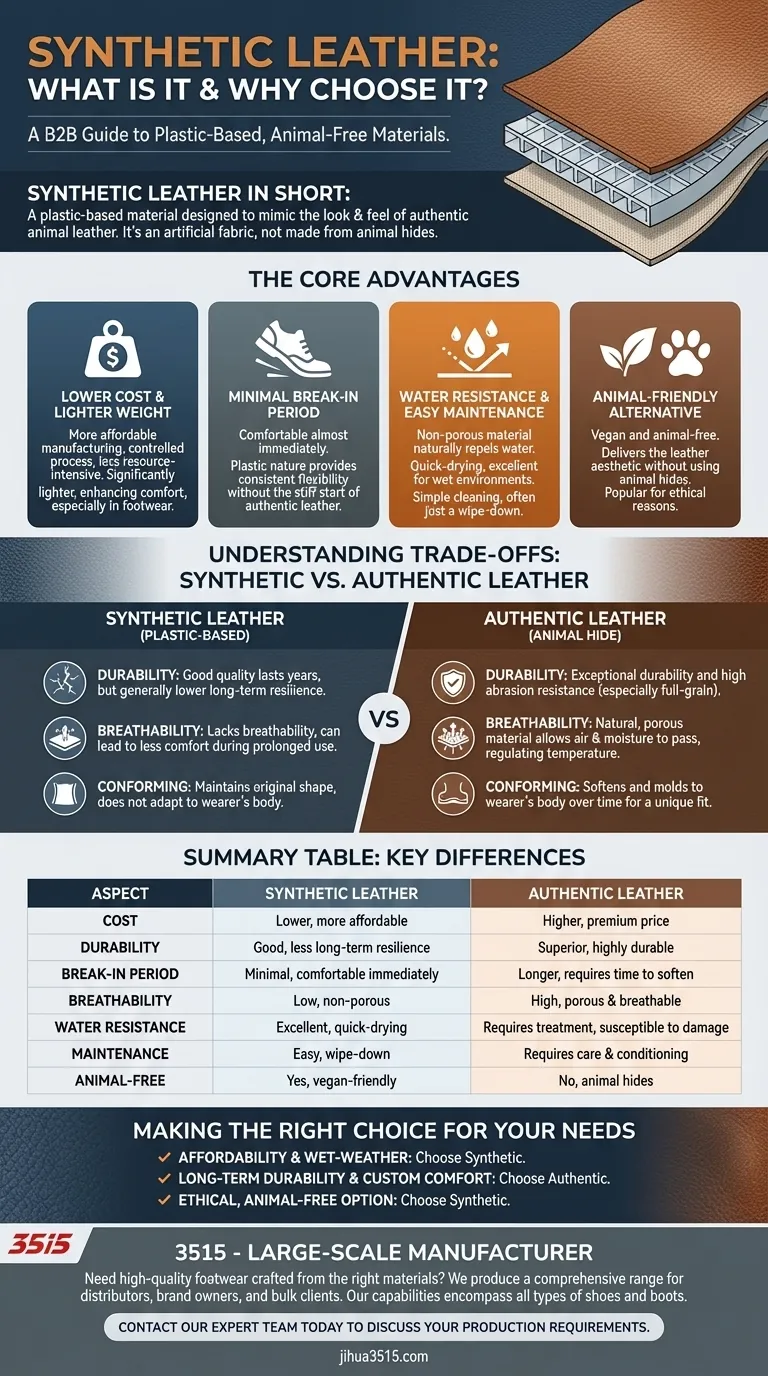
In short, synthetic leather is a plastic-based material designed to mimic the look and feel of authentic animal leather. It is fundamentally an artificial fabric, offering key advantages such as a lower cost, a much shorter break-in period, and being an entirely animal-free product.
The central decision between synthetic and authentic leather is not about which is universally "better," but which is better suited for a specific purpose. Synthetic leather excels in affordability and water resistance, while authentic leather offers superior long-term durability and breathability.

The Core Advantages of Synthetic Leather
Synthetic materials provide a distinct set of benefits rooted in their man-made origins. These characteristics make them a practical choice for specific applications and user priorities.
Lower Cost and Lighter Weight
Synthetic leather is almost always more affordable than its authentic counterpart. The manufacturing process is more controlled and less resource-intensive. This also results in a lighter material, which can significantly enhance comfort, especially in footwear.
Minimal Break-in Period
Unlike authentic leather, which can be stiff and requires time to soften and conform to your shape, synthetic leather is comfortable almost immediately. Its plastic nature provides consistent flexibility right from the start.
Water Resistance and Easy Maintenance
Because it is a non-porous plastic material, synthetic leather naturally repels water. This makes it an excellent choice for use in wet environments, as it is quick-drying and less prone to water damage. Cleaning is also simpler, often requiring just a wipe-down.
An Animal-Friendly Alternative
For those seeking vegan or animal-free products, synthetic leather provides a convincing alternative. It delivers the aesthetic of leather without using any animal hides, making it a popular choice for ethical reasons.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Synthetic vs. Authentic Leather
To make an informed choice, it's critical to understand where synthetic leather compromises compared to the real thing. These trade-offs define the ideal use case for each material.
Durability and Longevity
Authentic leather, particularly full-grain, is known for its exceptional durability and high resistance to abrasion. While good-quality synthetic leather can last for years, it generally does not possess the same long-term resilience as real leather.
Breathability and Comfort
Authentic leather is a natural, porous material that allows air and moisture to pass through, a property known as "breathing." This helps regulate temperature and reduce sweat. Synthetic leather is essentially plastic and lacks this breathability, which can lead to less comfort during prolonged use.
Conforming to Your Shape
Over time, real leather softens and molds itself to the wearer's body, creating a unique, custom fit. Synthetic materials do not share this quality; they maintain their original shape and do not adapt in the same way.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Your final decision should be guided by your primary goal and the environment in which you'll use the product.
- If your primary focus is affordability and wet-weather performance: Synthetic leather is the logical choice for its lower cost and excellent water resistance.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability and custom comfort: Authentic leather is the superior investment, as it will last longer and mold perfectly to your shape.
- If your primary focus is an ethical, animal-free option: Synthetic leather delivers the desired aesthetic without relying on animal products.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the material that truly serves your needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Synthetic Leather | Authentic Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower, more affordable | Higher, premium price |
| Durability | Good, but less long-term resilience | Superior, highly durable (especially full-grain) |
| Break-in Period | Minimal, comfortable immediately | Longer, requires time to soften |
| Breathability | Low, non-porous | High, porous and breathable |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, quick-drying | Requires treatment, can be damaged by water |
| Maintenance | Easy, often just a wipe-down | Requires more care and conditioning |
| Animal-Free | Yes, vegan-friendly | No, made from animal hides |
Need high-quality footwear crafted from the right materials for your market?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether your customers demand the long-term value of authentic leather or the practical benefits of synthetic materials, our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots to meet your specific needs.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your production requirements and discover how we can add value to your supply chain.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Factory Direct Wholesale Leather Comfort Shoes with Dial Closure
- Wholesale Leather Business Casual Shoes with Dial Closure - Manufacturer of Comfort Dress Sneakers
- Classic Leather Derby Dress Shoes Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Wholesale Leather Derby Shoes Manufacturer | Customizable Business & Dress Footwear
- Wholesale Classic Leather Lace-Up Ankle Boots for Brand Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- How easy is it to maintain suede shoes? Simple Steps for Long-Lasting Style
- Why is the use of high-performance footwear necessary during the biomechanical adjustment and dynamic capture process?
- How should footwear manufacturers address perceived contamination risks? Design Safe Recycled Lining & Components
- What is the primary function of shoe-worn motion sensors? Powering Real-Time Parkinson’s Gait Intervention
- How does Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) technology facilitate footwear production transitions? Boost Efficiency!
- What makes the three-layer support system in shoes unique? A Synergistic Approach to Foot Comfort
- What role do dynamic balance testing systems play in LOS for footwear users? Measuring Stability for Better Design
- What is the therapeutic function of medical footwear for diabetic ulcers? Learn How to Prevent & Heal Chronic Foot Wounds



















