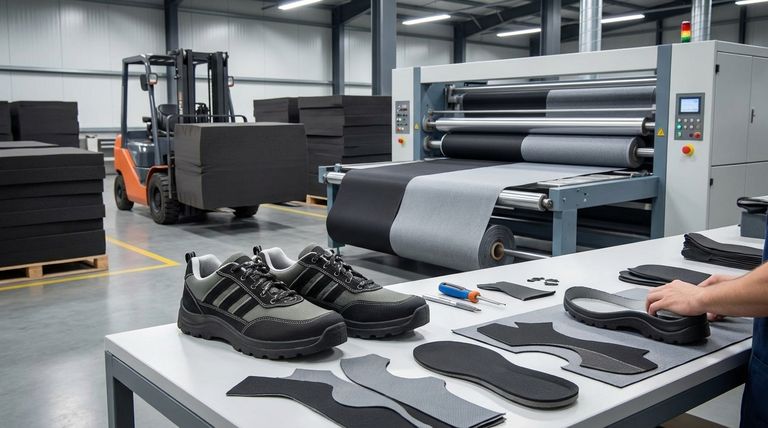
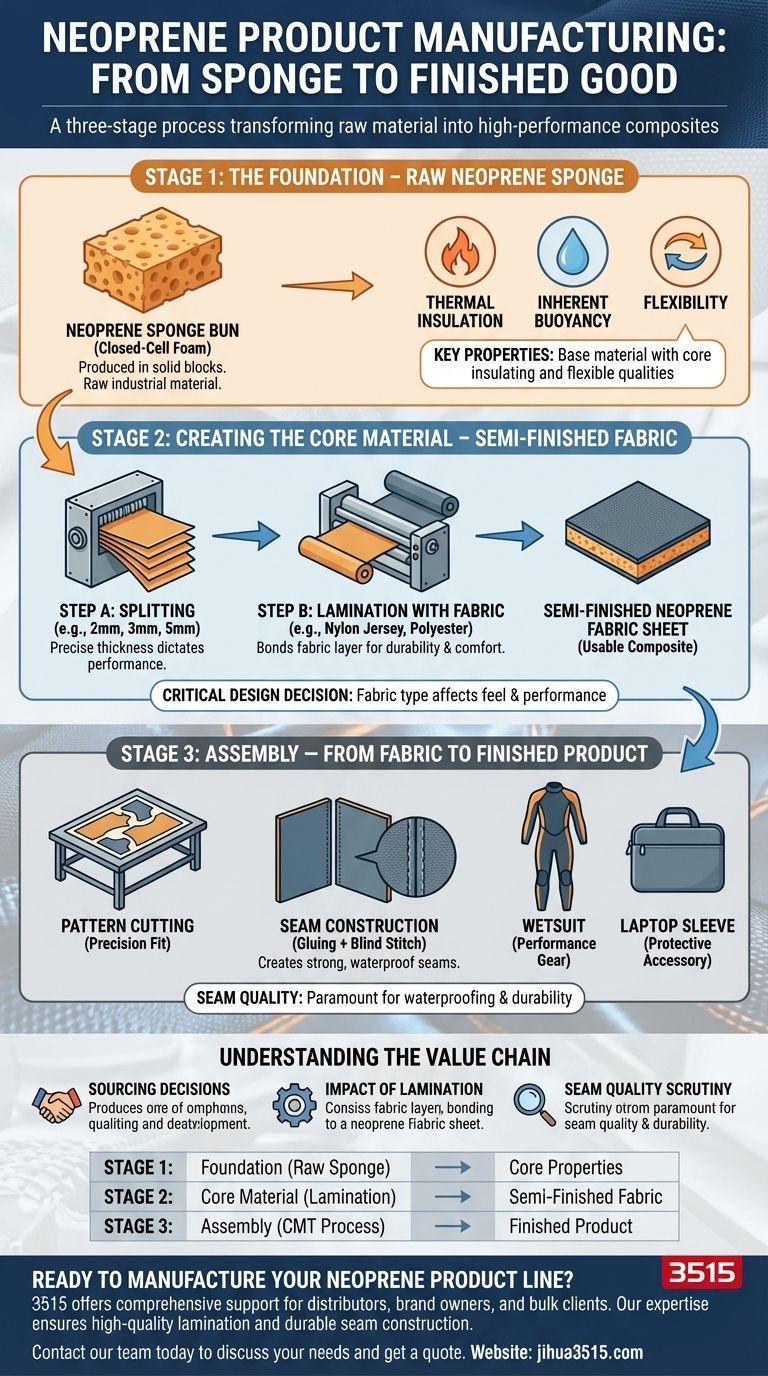
The manufacturing of a neoprene product is a distinct, three-stage process. It begins with the raw neoprene sponge, which is then converted into a semi-finished, usable fabric through lamination, and finally assembled into a finished item like a wetsuit or laptop sleeve. Each stage adds specific functional characteristics to the final product.
Understanding the neoprene manufacturing process is about recognizing how a simple raw material is transformed into a high-performance composite. The key value is added not just in the final assembly, but in the intermediate step of creating the laminated fabric itself.

Stage 1: The Foundation – Raw Neoprene Sponge
What is a Neoprene Sponge?
The process begins with the base material, known as a neoprene sponge or foam. This is a synthetic rubber (polychloroprene) that has been expanded into a closed-cell foam structure.
It is typically produced and shipped in large, solid blocks or "buns." At this stage, it is a raw industrial material, not yet suitable for direct use in most consumer products.
Key Properties at this Stage
The raw sponge possesses the core properties that make neoprene so valuable: excellent thermal insulation, inherent buoyancy, and flexibility. The specific chemical composition determines its initial stretchiness and density.
Stage 2: Creating the Core Material – Semi-Finished Fabric
This is the most critical stage, where the raw sponge is transformed into the versatile material designers and manufacturers work with. This semi-finished product is often sold on its own.
Step A: Splitting the Sponge
The large neoprene buns are sliced, or "split," into sheets of a precise, uniform thickness. This thickness (e.g., 2mm, 3mm, 5mm) is one of the most important specifications, as it directly dictates the final product's insulation and flexibility.
Step B: Lamination with Fabric
The raw, split sheets of neoprene are then laminated by bonding a fabric layer to one or both sides. This is crucial for durability, comfort against the skin, and appearance.
Commonly used fabrics include nylon jersey for stretch and durability or polyester for UV resistance and color vibrancy. The type of fabric used dramatically affects the final product's feel and performance.
The Result: A Usable Composite
The outcome of this stage is a composite sheet material—the neoprene fabric. It combines the insulating core of the rubber with the protective and aesthetic qualities of the laminated textile.
Stage 3: Assembly – From Fabric to Finished Product
The final stage involves turning the laminated neoprene fabric into a specific product. This is often referred to as the Cut, Make, and Trim (CMT) process.
Pattern Cutting and Layout
The laminated sheets are laid out and cut into specific panel shapes according to the product's design pattern. Precision here is key to ensuring a proper fit.
Seam Construction
The cut panels are joined together. For performance products like wetsuits, this involves a combination of gluing the edges together first, followed by a special blind stitch that does not fully puncture the neoprene. This technique creates a strong, waterproof seam.
Final Finishing Touches
Finally, components like zippers, seals, cuffs, and printed logos are added to complete the product. Quality control checks ensure the seams are secure and the product meets all specifications.
Understanding the Value Chain
Sourcing Sponge vs. Fabric
A manufacturer can choose to source raw neoprene sponge and manage the splitting and lamination in-house. This offers maximum control but requires significant investment in machinery.
More commonly, companies purchase the semi-finished laminated fabric from specialized suppliers, allowing them to focus solely on the final product assembly.
The Impact of Lamination
The choice of laminated fabric is a critical design decision. A super-stretch jersey will create a flexible, high-performance wetsuit, while a more durable, abrasion-resistant fabric might be chosen for work boots or protective gear.
Why Seam Quality is Paramount
In the final assembly stage, the method of seam construction is where many products succeed or fail. A poorly glued or stitched seam will leak and compromise the insulating properties of the neoprene, rendering a product like a wetsuit ineffective.
How This Impacts Your Design or Sourcing
- If your primary focus is product design: Concentrate on the semi-finished stage; the neoprene thickness and the type of laminated fabric will define your product's core performance and feel.
- If your primary focus is sourcing a finished product: Scrutinize the final assembly, especially the seam construction and finishing details, as this is the best indicator of manufacturing quality and durability.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing: Your key strategic decision is whether to buy raw sponge for full control or pre-laminated sheets to simplify your production line.
By understanding these distinct stages, you can make more informed decisions about material specification, supplier selection, and product quality.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Foundation | Production of neoprene sponge/foam | Raw material with core insulating properties |
| 2. Core Material | Splitting & lamination with fabric (e.g., nylon) | Semi-finished, versatile neoprene fabric sheet |
| 3. Assembly | Cutting, gluing, blind-stitching, adding components | Finished product (e.g., wetsuit, protective gear) |
Ready to manufacture your neoprene product line?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 offers comprehensive support through every stage of the neoprene manufacturing process. We produce a full range of footwear and are equipped to handle complex projects for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our expertise ensures high-quality lamination, precision cutting, and durable seam construction for superior final products.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Comfort Leather Business Shoes with Dial Lacing System
- Durable Canvas Work Shoes with Rubber Lug Sole | Wholesale Manufacturer
- Lightweight Breathable Sneakers with Wet-Traction Grip for Wholesale & Private Label
- Wholesale Perforated Comfort Dress Shoes | Custom Derby Shoe Manufacturer
People Also Ask
- How can you enhance the water resistance of boots? A Guide to Lasting Protection
- Why are wireless IMU sensors preferred in human biomechanical testing? Essential Tools for High-Precision Data
- What is the National Firefighter Registry for Cancer? A Critical Health Study for Firefighters
- What role do 3D CAD tools play in the design of depth shoe lasts for diabetic patients? Precision Digital Engineering
- How can sensor-integrated footwear components be designed for various shoe sizes? Master Modular VR Sensor Design
- What are polyurethane boots used for? Discover Unmatched Durability & Comfort
- What are the key factors to consider when selecting textiles for shoe design? Master Material Selection
- What role does personal protective equipment (PPE) play during excavation? Essential Gear for High-Risk Environments



















