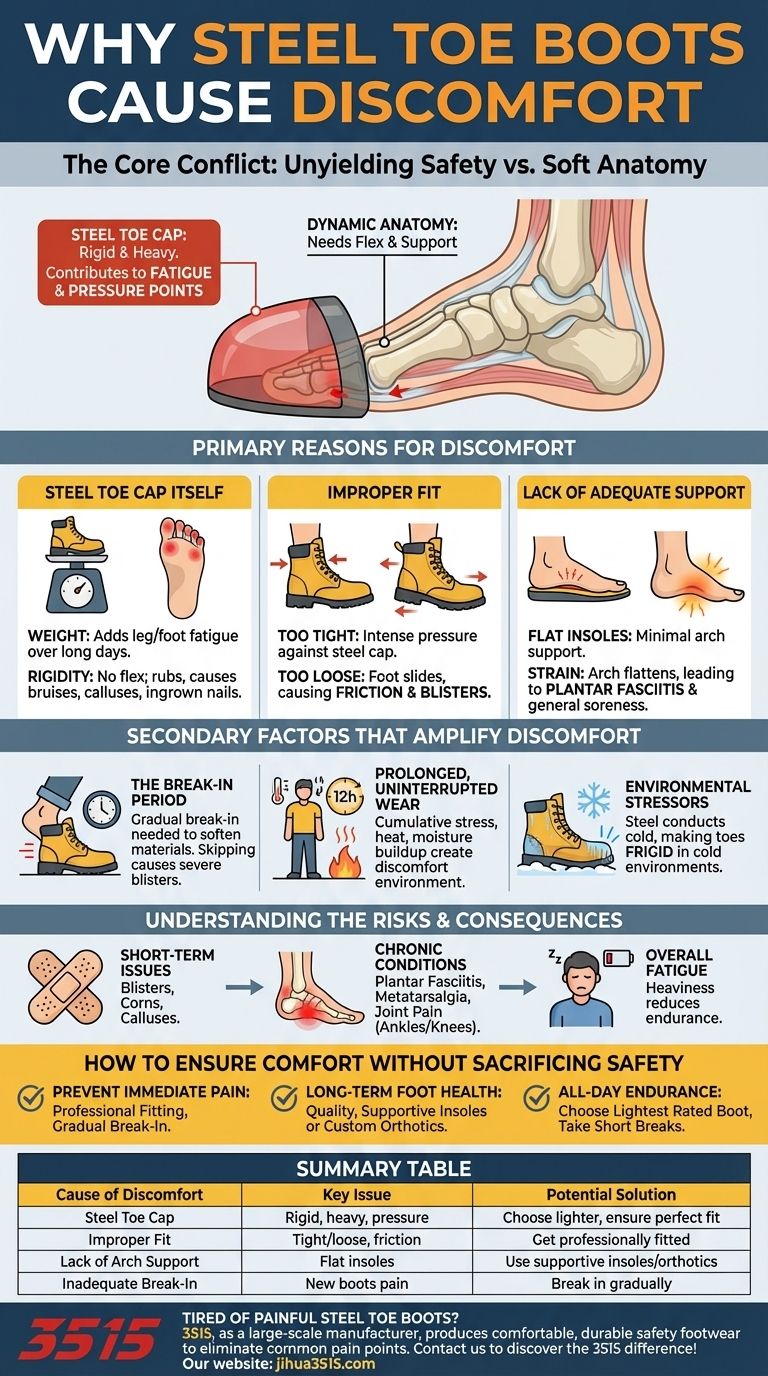
The primary reasons steel toe boots cause discomfort are the inherent weight and rigidity of the steel cap, an improper fit that creates pressure points, and inadequate internal support for your foot's natural arch. These factors combine to restrict movement and create friction, leading to pain and fatigue over a long workday.
The core issue is not that steel toe boots are inherently flawed, but that their rigid, protective structure often conflicts with the dynamic, unique anatomy of your foot. True comfort comes from bridging this gap with proper fit, support, and break-in time.

The Core Conflict: Rigidity vs. Anatomy
The fundamental source of pain is the battle between an unyielding safety boot and the soft tissues and bones of your feet. Understanding the specific points of failure is the first step to finding a solution.
The Steel Toe Cap Itself
The protective steel cap is non-negotiable for safety, but it's also the main culprit for discomfort. It adds significant weight, which contributes to leg and foot fatigue over the day.
More importantly, the cap is completely rigid. It doesn't flex or adapt to your foot's shape, which can cause rubbing and direct pressure on your toes, leading to bruises, calluses, or ingrown toenails.
The Critical Importance of Fit
An improper fit is the most common and solvable problem. A boot that is too tight will constrict your foot and create intense pressure points against the steel cap.
Conversely, a boot that is too loose allows your foot to slide, causing friction that results in painful blisters. Your heel may also lift with each step, creating instability and soreness.
Lack of Adequate Support
Most work boots come with basic, flat insoles that offer minimal arch support. Without proper support, the arch of your foot can flatten under strain, leading to a painful condition known as plantar fasciitis.
This lack of a supportive foundation also contributes to general foot soreness and can affect your ankles and knees over time.
Secondary Factors That Amplify Discomfort
Beyond the boot's construction, how you use and care for your footwear plays a significant role in your overall comfort level.
The Break-In Period
Rigid leather and synthetic materials need time to soften and conform to the unique shape of your foot. Skipping a gradual break-in period and immediately wearing new boots for a full shift is a common cause of severe blisters and pain.
Prolonged, Uninterrupted Wear
Standing or walking for 8-12 hours without rest puts immense, cumulative stress on your feet. The constant pressure, combined with heat and moisture buildup inside the boot, creates a perfect environment for discomfort and skin issues.
Environmental Stressors
Steel is an excellent thermal conductor. In cold environments, the steel cap can draw heat away from your toes, leaving them feeling frigid and uncomfortable. This is a distinct disadvantage compared to composite-toe alternatives.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While essential for safety, the design of steel toe boots introduces specific comfort and health risks that you must manage.
From Blisters to Chronic Conditions
Short-term issues like blisters, corns, and calluses are common results of friction and pressure.
If the root causes aren't addressed, these can escalate into chronic conditions like plantar fasciitis (heel pain), metatarsalgia (pain in the ball of the foot), or persistent joint pain in the ankles and knees.
The Impact of Weight on Fatigue
The heaviness of traditional steel toe boots requires more energy with every step. This doesn't just make your feet tired; it contributes to overall body fatigue, reducing your endurance throughout the workday.
Potential Hazards
Unless specifically rated for it, the steel cap can conduct electricity, posing a risk in certain environments. While this is a safety issue more than a comfort one, it is a critical trade-off to be aware of when selecting footwear.
How to Ensure Comfort Without Sacrificing Safety
Making the right choices about your boots and how you wear them is key to preventing pain. Use your primary goal to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is preventing immediate pain: Prioritize getting a professional fitting to ensure the size and width are perfect, and commit to breaking the boots in gradually over several days.
- If your primary focus is long-term foot health: Invest in high-quality, supportive insoles or custom orthotics that match your arch type.
- If your primary focus is all-day endurance: Choose the lightest weight boot that meets your worksite's safety standards and make a point to take short breaks to rest your feet.
By understanding these factors, you can effectively select and manage your safety footwear for both protection and comfort.
Summary Table:
| Cause of Discomfort | Key Issue | Potential Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Toe Cap | Rigid, heavy, causes pressure | Choose lighter materials or ensure perfect fit |
| Improper Fit | Too tight or loose, causing friction/blisters | Get professionally fitted for correct size/width |
| Lack of Arch Support | Flat insoles lead to plantar fasciitis | Use supportive insoles or custom orthotics |
| Inadequate Break-In | New boots cause immediate pain | Break in gradually over several days |
Tired of painful steel toe boots? As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of comfortable, durable work boots designed to eliminate common pain points. Let us help you provide footwear that combines superior protection with all-day comfort. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover the 3515 difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Wholesale Mesh Steel Toe Safety Shoes with Dial Closure Factory Production
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
People Also Ask
- Are steel toe boots inherently bad for your feet? Debunking Myths for Workplace Safety
- Why is it important for organizations to prioritize the use of steel toe shoes? Boost Safety & Productivity
- What are the benefits of alloy-toe boots? Superior Protection with Lighter Weight
- What safety standards do steel toe boots comply with? Understanding ASTM F2413 and OSHA 1910.136
- How can one prevent blisters when wearing steel toe boots? A Complete Guide to Pain-Free Workdays
- What materials are used for toe protection in work boots? Steel vs. Composite Toe Cap Guide
- Is the myth about steel-toe boots being dangerous true? Debunking the 'Guillotine Effect' Myth
- How do steel toe shoes protect workers? The Ultimate Guide to Foot Safety



















