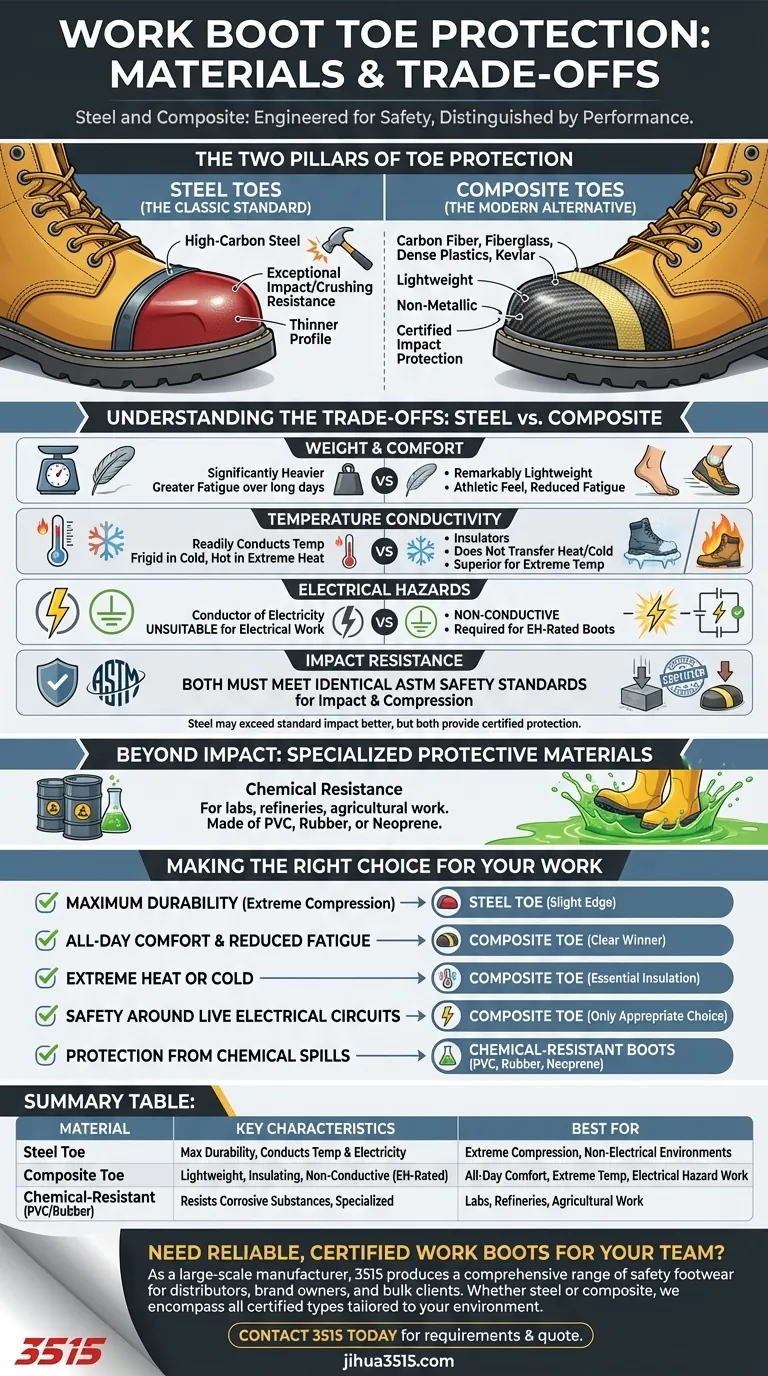
The primary materials used for toe protection in work boots are steel and advanced non-metal composites. Steel is the traditional choice, while composites include modern materials like carbon fiber, dense plastics, and Kevlar. Both are engineered to meet strict safety standards for impact and compression resistance, but they offer very different performance characteristics.
Your choice between a steel or composite toe is not about which is "stronger"—both must pass the same safety tests. The real decision hinges on secondary factors like weight, comfort in extreme temperatures, and suitability for specific electrical hazards.

The Two Pillars of Toe Protection
The safety toe is the cornerstone of a protective work boot. While many materials are used in boot construction, the protective cap itself is almost always made from one of two core material types: metal or non-metal composite.
Steel Toes: The Classic Standard
Steel has been the industry standard for decades for a reason. These protective caps are stamped from high-carbon steel, providing exceptional resistance to impact and crushing forces.
They are known for their ultimate strength and can be made with a thinner profile than composites, sometimes resulting in a less bulky boot.
Composite Toes: The Modern Alternative
Composite toes are engineered from a blend of non-metallic materials. This category includes everything from carbon fiber and fiberglass to specialized high-density plastics and Kevlar aramid fiber.
The goal of a composite toe is to provide the same certified level of impact protection as steel but without the associated weight and conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Steel vs. Composite
Choosing the right material requires understanding how each performs in a real-world work environment. The differences directly impact your comfort, safety, and daily fatigue.
Weight and Comfort
Steel is significantly heavier than composite materials. Over the course of a long workday, this extra weight can lead to greater fatigue and strain.
Composite toes are remarkably lightweight, making the boot feel more like an athletic shoe and reducing fatigue for those who are on their feet all day.
Temperature Conductivity
Because it's a metal, steel readily conducts temperature. In cold environments, the toe cap can become frigid, and in extreme heat, it can get uncomfortably warm.
Composites are insulators, meaning they do not transfer heat or cold. This makes them a far superior choice for anyone working in extreme temperature conditions.
Electrical Hazards
This is a critical safety distinction. Steel is a conductor of electricity, making steel-toe boots unsuitable for electricians or others working in environments with a high risk of electrical contact.
Composite materials do not conduct electricity, which is why they are the required choice for many Electrical Hazard (EH) rated boots.
Impact Resistance
It is a common misconception that one is inherently safer than the other. Both steel and composite toe caps must meet the exact same ASTM or other regional safety standards for impact and compression.
While steel may withstand an impact that exceeds the standard better than composite, both provide identical, certified protection for all rated hazards.
Beyond Impact: Specialized Protective Materials
For some jobs, the primary threat isn't a falling object but a hazardous substance. In these cases, the entire boot is constructed from specialized materials.
Chemical Resistance
Boots designed for labs, refineries, or agricultural work use materials specifically chosen to resist corrosive substances.
These are typically made of PVC, rubber, or neoprene. Some heavy-duty leather boots may also feature chemical-resistant properties through treatments and specialized components like Nitrile outsoles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Work
Selecting the correct toe protection is a crucial step in ensuring both your safety and your comfort on the job.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability under extreme compression: Steel toe boots offer a slight edge for impacts that go far beyond certified standards.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort and reduced fatigue: Composite toe boots are the clear winner due to their lightweight construction.
- If your primary focus is working in extreme heat or cold: Composite toes provide essential insulation that steel cannot match.
- If your primary focus is safety around live electrical circuits: Composite toe boots are the only appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is protection from chemical spills: Look for boots specifically constructed from PVC, rubber, or neoprene.
Choosing the right material for your environment is the foundation of daily workplace safety and comfort.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Toe | Maximum durability, conducts temperature, electrically conductive | Extreme compression, maximum durability, non-electrical environments |
| Composite Toe | Lightweight, temperature insulating, non-conductive (EH-rated) | All-day comfort, extreme temperatures, electrical hazard work |
| Chemical-Resistant (PVC/Rubber) | Resists corrosive substances, specialized construction | Labs, refineries, agricultural work with chemical exposure |
Need reliable, certified work boots for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether you require the classic durability of steel toes or the modern advantages of lightweight composite caps, our production capabilities encompass all types of certified safety shoes and boots tailored to your specific work environment.
Contact 3515 today to discuss your requirements and get a quote for high-quality, comfortable work boots that meet the highest safety standards.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Heavy-Duty Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Bulk Supply
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Durable Goodyear Welt Leather Work Boots for Wholesale & Private Label
People Also Ask
- How do steel toe shoes protect workers? The Ultimate Guide to Foot Safety
- What are key tips for fitting steel toe boots correctly? Ensure Safety and All-Day Comfort
- Why might steel toes be a valuable feature in motorcycle boots? Balancing Protection & Control
- How do steel toe work shoes compare to composite toe shoes? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job.
- What is the difference between safety toe and steel toe work boots? Choose the right protection for your job.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of steel toe boots? A Guide to Maximum Protection vs. Comfort
- How do weather conditions affect the choice between steel and non-steel safety toes? Choose the Right Toe for Extreme Temperatures
- Why choose composite toe boots over steel toe? Lighter, Non-Conductive & Metal Detector Safe



















