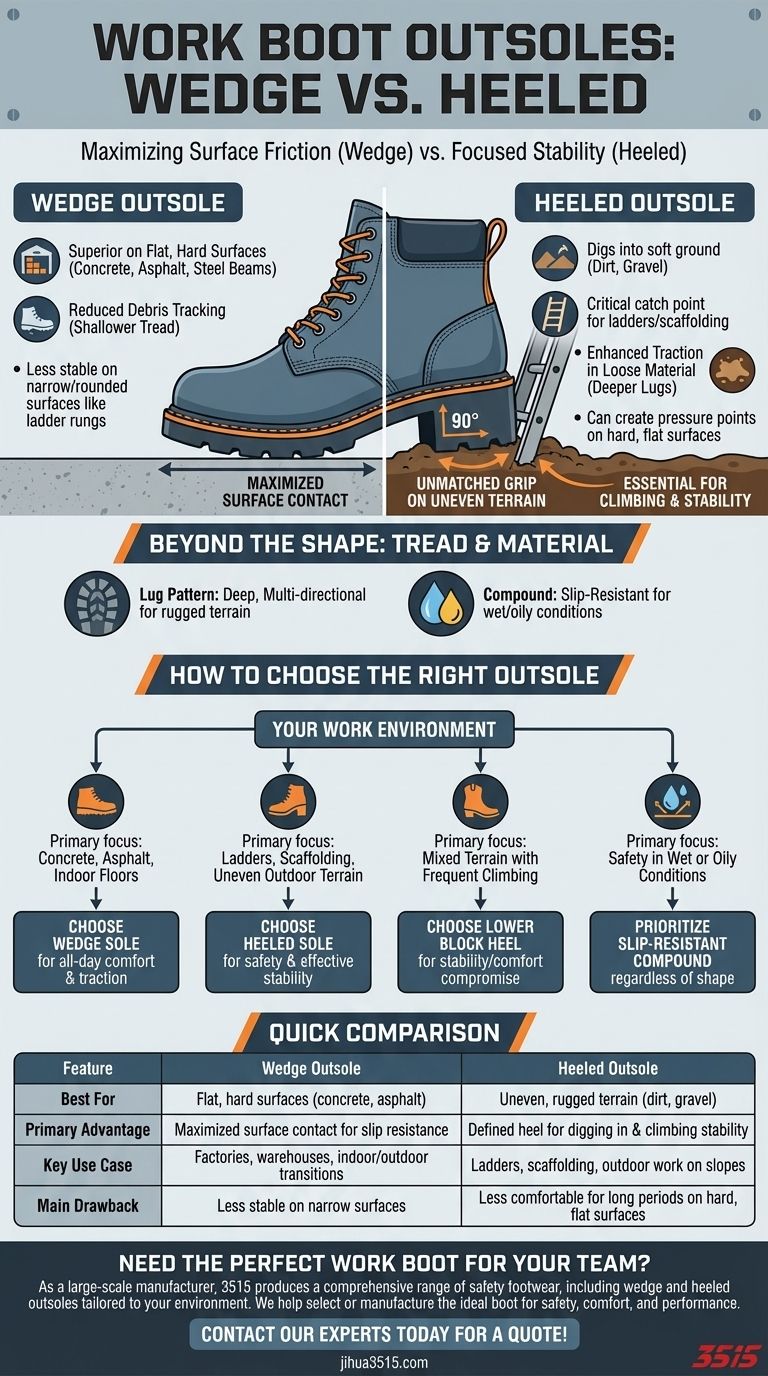
The fundamental difference between wedge and heeled outsoles lies in how they interact with the ground. A wedge outsole maximizes surface area contact for exceptional grip on flat, uniform surfaces, while a heeled outsole uses a defined heel to dig in and provide stability on uneven, rugged terrain and when climbing.
Your choice is not about which outsole is better overall, but which is the correct tool for your specific work environment. The decision hinges on a simple trade-off: maximized surface friction versus focused stability on variable ground.

The Case for the Wedge Outsole
A wedge sole runs the full length of the boot, maintaining a continuous, flat point of contact with the ground. This design is purpose-built for specific environments.
Maximized Surface Contact
The primary advantage of a wedge sole is its large, uninterrupted surface area. This distributes your weight evenly and creates significantly more friction on smooth surfaces.
Superior on Flat, Hard Surfaces
This design excels on concrete floors, asphalt, and steel beams. Workers in factories, warehouses, and construction sites with prepared surfaces benefit most from the stability and slip resistance a wedge sole provides.
Reduced Debris Tracking
Because they lack a deep, defined heel, wedge soles typically have shallower tread patterns. This means they are less likely to pick up mud, rocks, and other debris, making them ideal for transitioning between outdoor and indoor spaces.
The Advantage of the Heeled Outsole
A heeled outsole, often called a 90-degree heel, creates a distinct break between the heel and the main part of the sole. This feature is a critical safety and performance tool for many jobs.
Unmatched Grip on Uneven Terrain
The sharp angle of the heel acts like a hook. It allows you to dig into soft ground like dirt or gravel and lock onto uneven surfaces for superior stability where a flat sole might slip.
Essential for Climbing and Stability
For anyone working on ladders, scaffolding, or even just climbing onto equipment, the heel is non-negotiable. It provides a crucial catch point on rungs and edges, preventing your foot from sliding forward.
Enhanced Traction in Loose Material
Heeled boots typically feature deeper, more aggressive lug patterns. This, combined with the heel, allows the outsole to bite into loose terrain, providing reliable traction in conditions where a wedge sole would struggle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is perfect for every situation. Understanding their inherent limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Wedge Sole Limitations
While excellent on flat ground, a wedge sole can become less stable on narrow or rounded surfaces like a ladder rung, where its full surface area can't make contact. They also offer less purchase when navigating steep, loose inclines.
Heeled Sole Drawbacks
The defined heel can create a pressure point, which may lead to discomfort during long days spent standing on hard, flat concrete. The deeper treads common on heeled boots also track significantly more mud and debris.
Beyond the Shape: Tread and Material Matter
The shape of the outsole is only part of the equation. The materials and tread pattern are equally critical for performance and safety.
The Role of the Lug Pattern
Deep, multi-directional lugs, often found on heeled boots, are designed to channel water and grip terrain from multiple angles. This is essential for traction on rugged, outdoor surfaces.
The Importance of the Compound
Regardless of the shape, the rubber compound determines the sole's performance on specific hazards. Look for outsoles specifically rated as slip-resistant if you frequently work on wet, oily, or slick surfaces.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your daily tasks should be the deciding factor. Analyze your environment and choose the outsole that provides the greatest benefit for your most common challenges.
- If your primary focus is on concrete, asphalt, or indoor floors: A wedge sole will provide superior all-day comfort and traction.
- If your primary focus is on ladders, scaffolding, or uneven outdoor terrain: A heeled sole is the safer and more effective choice for stability.
- If your primary focus is on mixed terrain with frequent climbing: A lower, block-style Western work heel offers a good compromise between stability and comfort.
- If your primary focus is on safety in wet or oily conditions: Prioritize a certified slip-resistant rubber compound, regardless of the outsole's shape.
Choosing the right outsole is about matching the tool to the task, ensuring your safety and performance from the ground up.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Wedge Outsole | Heeled Outsole |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Flat, hard surfaces (concrete, asphalt) | Uneven, rugged terrain (dirt, gravel) |
| Primary Advantage | Maximized surface contact for slip resistance | Defined heel for digging in and climbing stability |
| Key Use Case | Factories, warehouses, indoor/outdoor transitions | Ladders, scaffolding, outdoor work on slopes |
| Main Drawback | Less stable on narrow surfaces like ladder rungs | Can be less comfortable for long periods on hard, flat surfaces |
Need the Perfect Work Boot for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, including both wedge and heeled outsoles tailored to your specific work environments.
We can help you select or manufacture the ideal boot to ensure your team's safety, comfort, and performance from the ground up.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
People Also Ask
- What role do professional work boots play in protecting hotel staff during heavy lifting? Safety & Support Essentials
- Why are pull-on boots not suitable for wildland firefighting? The Critical Safety Flaw Explained
- What advancements have been made in soft-toe boot design? From Durability to All-Day Comfort
- What are the two main types of cowboy boot heels? Roper vs. Riding Heels Explained
- What do the symbols M, F, I, and C represent on safety toe boots? Decode ASTM F2413 for Maximum Protection
- What are the main benefits of composite toe work boots? Lighter, Safer, and More Comfortable
- What are the consequences of using poorly made wildland firefighter boots? Protect Your Safety and Performance
- What should be considered regarding the width of boots? Achieve Ultimate Comfort & Performance



















