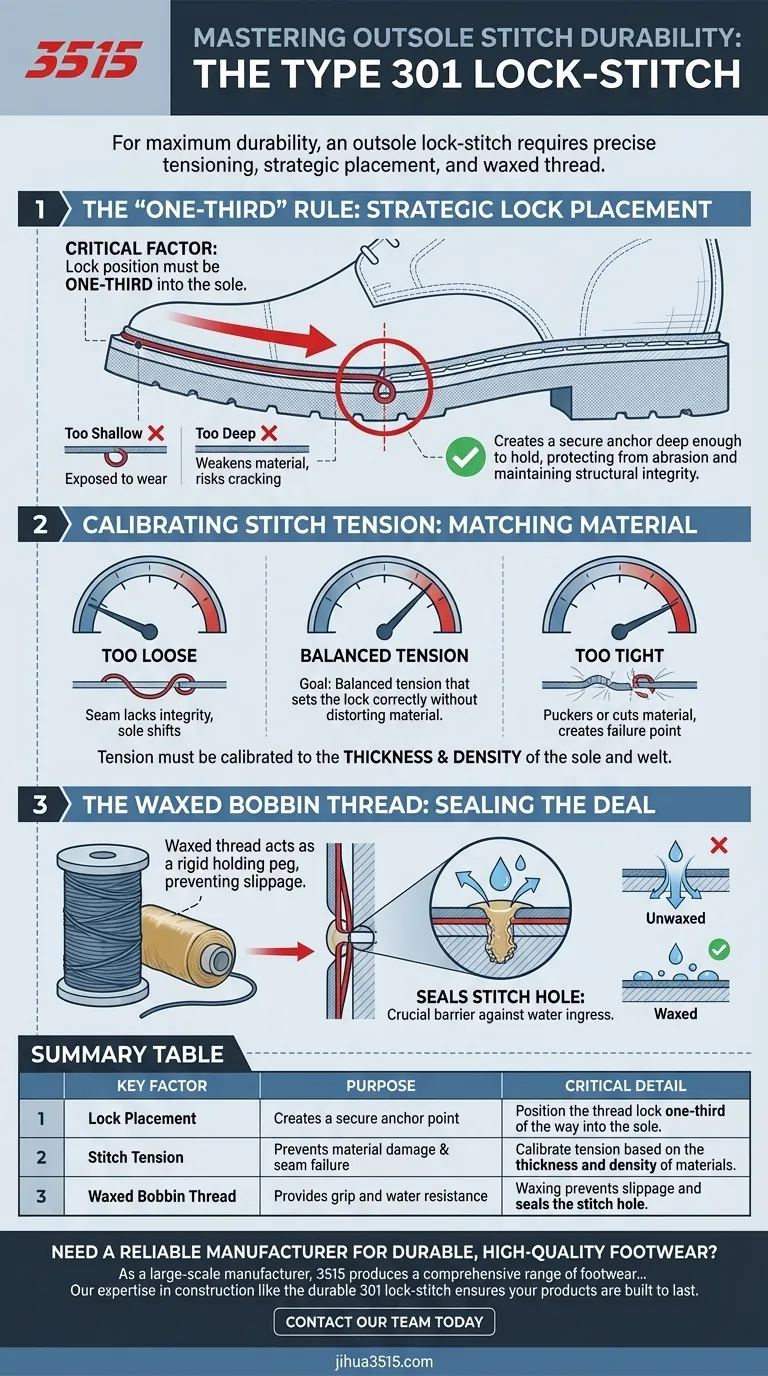
For maximum durability, an outsole lock-stitch requires precise tensioning, strategic placement of the thread lock, and proper treatment of the bobbin thread. You must set the stitch tension according to the specific thickness of the sole and welt materials. The lock itself should be positioned exactly one-third of the way into the sole from the welt, creating a secure anchor. Finally, waxing the bobbin thread is essential for both grip and water resistance.
The key to a durable outsole stitch is not simply tightness, but creating a perfectly placed, water-resistant anchor point within the sole material itself, protecting the seam from both mechanical stress and environmental damage.

The Mechanics of a Bulletproof Outsole Seam
A Type 301 lock-stitch is the standard for high-quality footwear construction because it creates an independent, non-raveling seam. Understanding how to execute it perfectly is the difference between a product that lasts for years and one that fails prematurely.
The "One-Third" Rule for Lock Placement
The single most critical factor for durability is the lock position. This is the point where the top thread and bobbin thread interlock.
This lock must be formed one-third of the way into the sole from the welt-sole interface.
Placing the lock at this specific depth protects the stitch from surface abrasion while maintaining the structural integrity of the outsole. It creates a secure anchor deep enough to hold, but not so deep that it weakens the material.
Setting Correct Stitch Tension
Stitch tension must be calibrated to the thickness and density of the materials being joined.
If tension is too loose, the seam will lack integrity and allow the sole to shift. If it is too tight, it can pucker the material or even cut through the leather or rubber over time, creating a point of failure.
The goal is a balanced tension that pulls the lock to the correct one-third depth without distorting the sole or welt.
The Role of the Waxed Bobbin Thread
The bobbin thread, which runs along the bottom of the sole, plays a unique role. It must be treated with wax.
This treatment transforms the thread into a rigid holding peg. The wax allows the top thread to lock around it securely, preventing any possibility of slippage or the sole detaching under load.
Furthermore, the wax effectively seals the stitch hole, providing a crucial barrier against water ingress, which can degrade the sole and welt materials over time.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even with the right equipment, small errors in technique can compromise the entire construction. Understanding these common mistakes is crucial for consistent quality control.
Misplacing the Lock
A lock positioned too shallow (less than one-third deep) is exposed to excessive surface wear and can easily be abraded, causing the entire seam to fail.
A lock positioned too deep (more than one-third deep) can compromise the sole's integrity, creating an internal weak point that can lead to cracking or splitting under flex.
Ignoring Material Variations
Assuming one tension setting works for all materials is a frequent error. A thick leather sole requires significantly different tension settings than a more flexible composite or rubber sole.
Always perform a test run on scrap material to dial in the perfect tension and verify the lock position before starting on the final product.
Skipping the Wax Treatment
An unwaxed bobbin thread will not provide the necessary grip for the top thread. This can lead to stitch slippage and eventual sole detachment, especially in high-stress areas like the toe flex point. It also leaves the stitch holes open to moisture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving a perfect outsole stitch requires balancing these three core principles. Your specific priority will determine where you focus the most attention.
- If your primary focus is sheer mechanical strength: Prioritize the one-third lock placement above all else, as this is the fundamental anchor for the entire seam.
- If your primary focus is all-weather durability: Emphasize the waxed bobbin thread to ensure every stitch hole is sealed against water damage.
- If you are working with a variety of materials: Focus on rigorously calibrating stitch tension for each unique combination of sole and welt to prevent material damage.
Mastering these details ensures you are not just attaching a sole, but engineering a foundation built to last.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Purpose | Critical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Lock Placement | Creates a secure anchor point | Position the thread lock one-third of the way into the sole from the welt. |
| Stitch Tension | Prevents material damage & seam failure | Calibrate tension based on the thickness and density of the sole and welt materials. |
| Waxed Bobbin Thread | Provides grip and water resistance | Waxing the thread prevents slippage and seals the stitch hole against moisture. |
Need a reliable manufacturer for durable, high-quality footwear?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, and our expertise in construction techniques like the durable 301 lock-stitch ensures your products are built to last.
Contact our team today to discuss your production needs and benefit from our quality-driven manufacturing process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Leather Work Boots with Customizable Wedge Sole for Brands
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Premium Wholesale Tactical Style Safety Shoes Boots with Quick Lacing
- Wholesale Mesh Steel Toe Safety Shoes with Dial Closure Factory Production
- Heavy-Duty Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Bulk Supply
People Also Ask
- What type of boots are suitable for challenging weather conditions in a business setting? | Durable & Professional Footwear
- What are the best practices for storing leather work boots? Preserve Your Investment for Years
- What maintenance tips are recommended for leather safety footwear? Extend Lifespan & Preserve Safety
- What protection do leather work boots need? A Complete Guide to Material Care and Worker Safety
- How does cleaning your work boots help in their maintenance? Extend Lifespan & Boost Safety



















