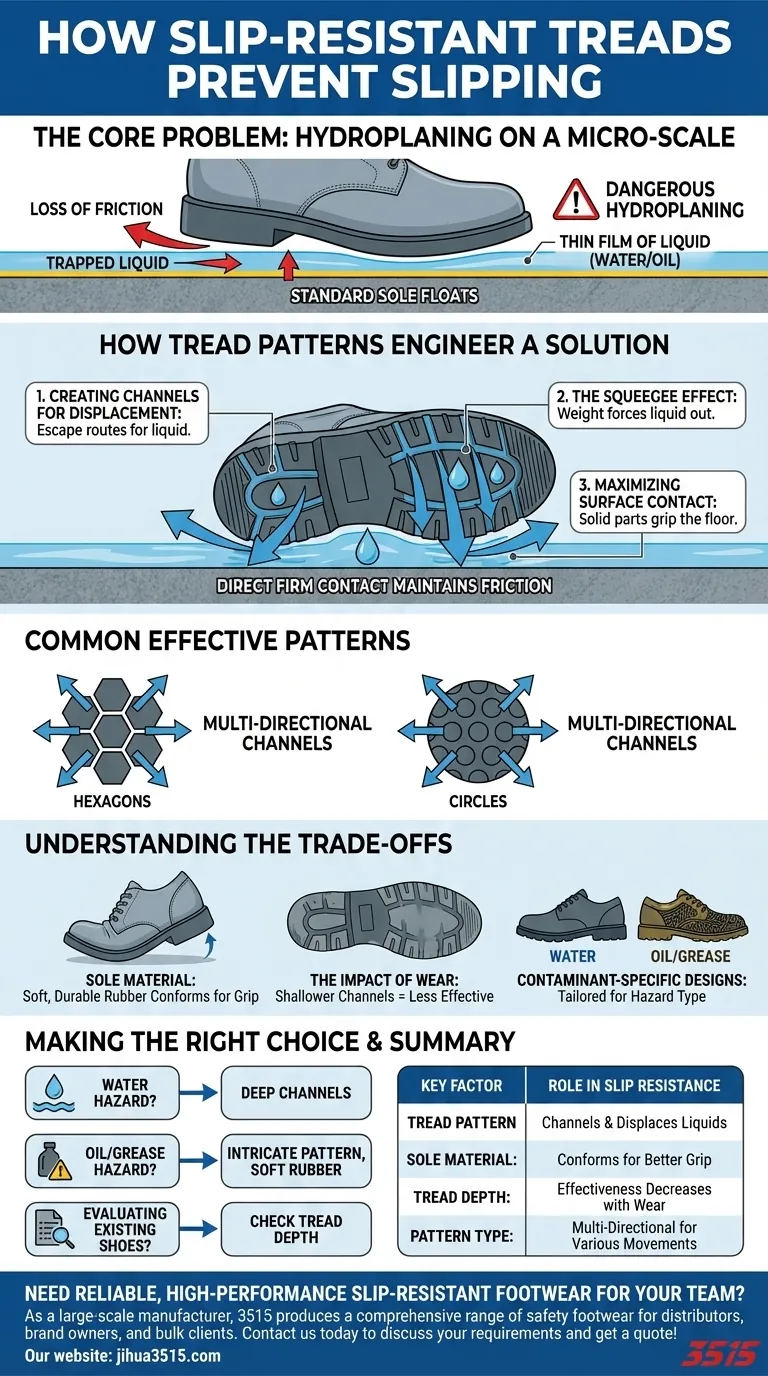
The tread pattern on slip-resistant shoes prevents slipping by acting as a sophisticated drainage system that channels liquids out from underneath the sole. Instead of trapping a thin film of water or oil—which causes a dangerous hydroplaning effect—the grooves force the liquid away. This allows the solid parts of the tread to make direct, firm contact with the floor, maintaining the friction necessary for a secure grip.
The core principle of slip-resistance is not about creating a "stickier" shoe, but about efficiently clearing a path through contaminants. The tread pattern's primary job is to displace liquid, ensuring the sole can actually touch the ground.
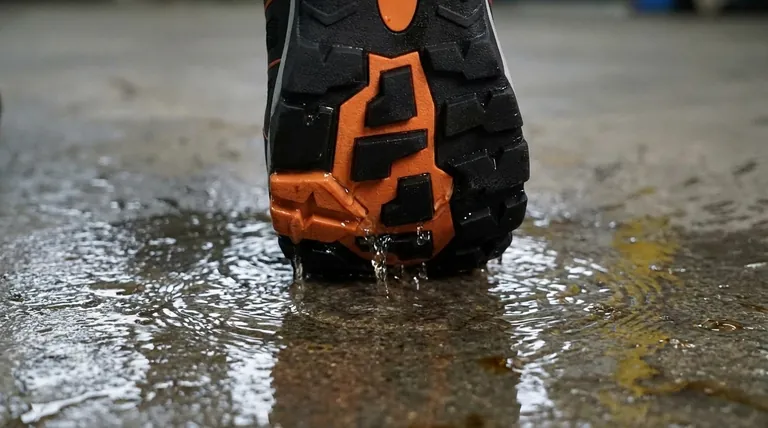

The Core Problem: Hydroplaning on a Micro-Scale
A Thin Film of Liquid
Even a barely visible layer of water, oil, or grease on a smooth floor creates a significant hazard. This liquid acts as a barrier between your shoe's sole and the floor surface.
The Loss of Friction
When a standard, flat-soled shoe steps on this liquid, the fluid gets trapped underneath. The shoe effectively floats on this thin film, eliminating the direct contact required for friction and causing a slip.
Why a Standard Sole Fails
This phenomenon is essentially hydroplaning, just on a much smaller scale than with a car's tires. A smooth sole has no way to displace the trapped liquid, making it inherently unstable on wet or greasy surfaces.
How Tread Patterns Engineer a Solution
Creating Channels for Displacement
The grooves and channels in a slip-resistant tread pattern are designed specifically to combat this problem. They create an escape route for any liquid under the shoe.
The Squeegee Effect
When you put your weight on the shoe, the liquid is squeezed out from under the flat, solid parts of the tread. It is immediately forced into the surrounding channels and pushed away from the center of the sole.
Maximizing Surface Contact
With the liquid successfully displaced, the solid surfaces of the tread can make direct contact with the floor. This re-establishes the friction needed to prevent a fall.
Common Effective Patterns
Tread patterns are often composed of many small shapes, like hexagons or circles. These create multi-directional channels that effectively disperse liquid no matter which way your foot moves or pressure is applied.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It's Not Just the Pattern
A great tread pattern is only effective when paired with the right material. The sole itself must be made of a soft but durable rubber compound that can conform to microscopic imperfections in the floor for a better grip.
The Impact of Wear
The effectiveness of a tread pattern is directly related to its depth. As a shoe wears down, these channels become shallower and less capable of displacing liquid, significantly reducing their slip-resistant properties.
Contaminant-Specific Designs
A pattern that works well for water may be less effective against more viscous liquids like oil or grease. The size and complexity of the channels must be suited to the type of hazard you most frequently encounter.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Choosing the correct shoe requires matching its design to your specific workplace hazards.
- If your primary hazard is water on smooth floors: Look for a pattern with deep, clear channels that can displace a higher volume of liquid quickly.
- If you work with oil or grease: Prioritize shoes with smaller, more intricate tread patterns and a soft rubber sole to maximize surface contact.
- If you are evaluating existing shoes for safety: Check the tread depth. If the patterns are worn nearly smooth, the shoe no longer offers reliable protection and must be replaced.
By understanding how a tread pattern works, you can better assess whether a shoe is truly equipped to keep you safe.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Slip Resistance |
|---|---|
| Tread Pattern | Channels and displaces liquids (water, oil) from under the sole. |
| Sole Material | Soft, durable rubber conforms to floor imperfections for better grip. |
| Tread Depth | Deeper channels displace more liquid; effectiveness decreases with wear. |
| Pattern Type | Multi-directional designs (e.g., hexagons) work for various movements. |
Need reliable, high-performance slip-resistant footwear for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, engineered with advanced tread patterns and durable materials to protect your workforce in any environment.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
- Wholesale Anti-Smash & Puncture-Proof Safety Shoes Custom Manufacturing for Brands
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Heavy-Duty Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Bulk Supply
People Also Ask
- What special requirements should work shoes for all-day wear meet? Key Features for All-Day Comfort & Safety
- What are the requirements for a genuine slip-resistant shoe? Key Features for Ultimate Safety
- What are non-slip shoes? Essential Safety Footwear for High-Risk Workplaces
- What is the primary role of industrial-grade 3D printing in shoe last & insole research? Enhance Your Slip-Resistance
- What material should the sole of a non-slip shoe be made of? The Key to Maximum Traction
- How does a whole-shoe portable bio-simulated mechanical slip tester provide superior performance characterization?
- Why is the sole material of shoes important for slip resistance? It's the Foundation of Your Safety
- What is the benefit of angled or rounded sole designs in non-slip shoes? Prevent Hydroplaning for Superior Grip



















