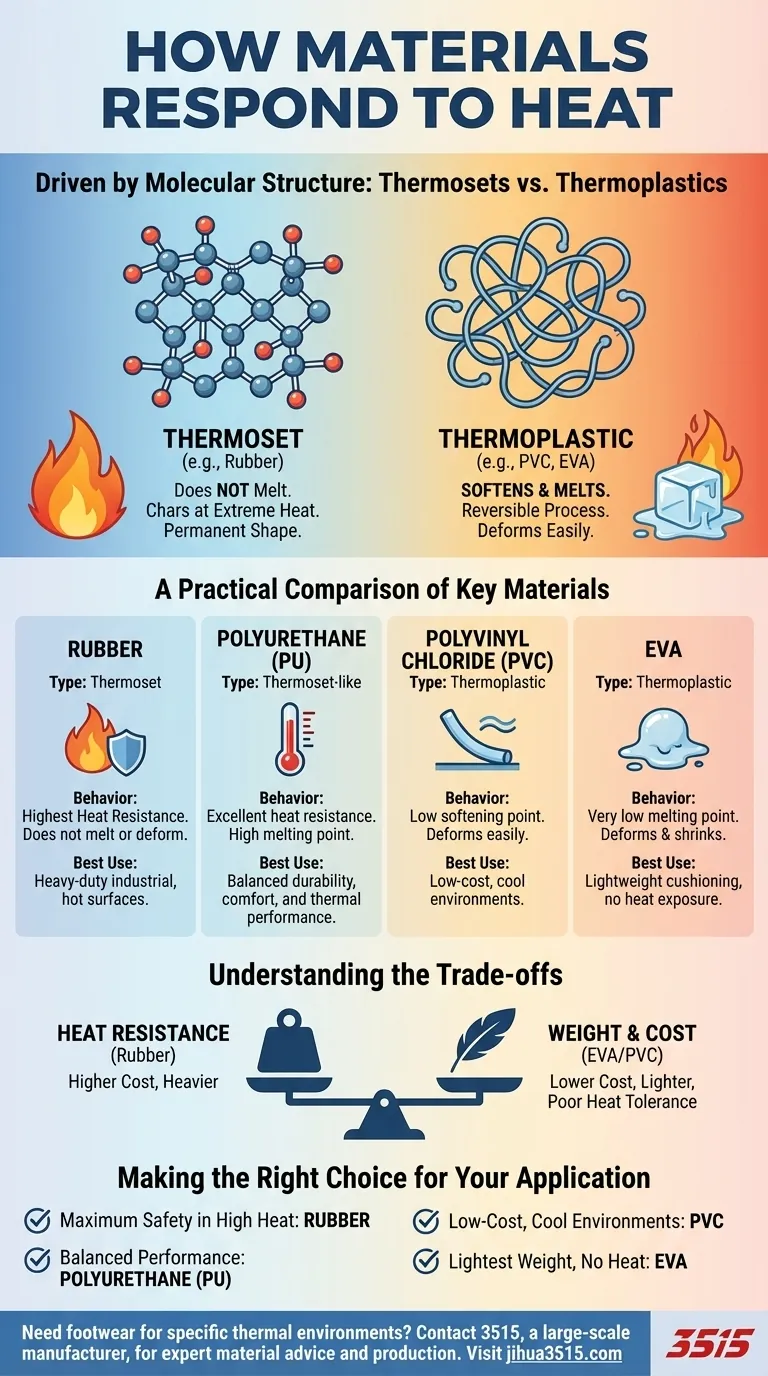
At a fundamental level, materials respond to heat based on their molecular structure. For common polymers used in applications like footwear, rubber and polyurethane (PU) offer superior heat resistance, maintaining their form at high temperatures. In contrast, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) are prone to softening and deforming when exposed to significant heat.
The critical difference lies in whether a material is a thermoset or a thermoplastic. Thermoset polymers (like rubber) are set into a permanent shape, while thermoplastics (like PVC and EVA) can be repeatedly softened by heat.

The Core Principle: Molecular Structure and Heat
A material's reaction to heat is not a random property; it is dictated by the chemical bonds holding its polymer chains together. This creates two primary categories of polymers with vastly different thermal behaviors.
Understanding Thermosets (e.g., Rubber)
Thermoset polymers have strong, cross-linked chemical bonds between their molecular chains. This creates a rigid, three-dimensional network.
Once cured, these materials cannot be re-melted. When exposed to extreme heat, they will eventually char and degrade rather than soften and lose their shape, giving them excellent thermal stability.
Understanding Thermoplastics (e.g., PVC & EVA)
Thermoplastic polymers have weaker forces between their molecular chains, with no cross-linking.
When heated, these chains can slide past one another, causing the material to soften, become pliable, and eventually melt. This process is reversible, as the material will harden again upon cooling, but any deformation that occurs while soft will be permanent.
The Special Case of Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer that can be formulated as either a thermoset or a high-performance thermoplastic elastomer.
In durable applications like high-quality boots, it is engineered to have strong intermolecular bonds, giving it a high melting point and excellent resistance to heat-induced deformation, behaving more like a thermoset.
A Practical Comparison of Key Materials
Applying this principle allows us to predict how each material will perform in a real-world scenario involving heat.
Rubber: The Benchmark for Heat Resistance
As a classic thermoset material (specifically, vulcanized rubber), it offers the highest resistance to heat. It will not melt or deform, making it the standard for heavy-duty industrial environments where contact with hot surfaces or high ambient temperatures is a concern.
Polyurethane (PU): The Balanced Performer
PU provides excellent resistance to deformation from heat, far surpassing standard thermoplastics like PVC and EVA. It combines this thermal stability with being lighter and more flexible than traditional rubber.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Low Thermal Tolerance
PVC is a cost-effective thermoplastic with a relatively low softening point. It will lose its structural integrity and deform easily in high-heat conditions, making it unsuitable for demanding thermal environments.
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA): Highly Sensitive to Heat
EVA is prized for being extremely lightweight and providing excellent cushioning, often as a foam. However, as a thermoplastic with a very low melting point, it deforms and can even shrink under moderate heat exposure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is never just about a single property. Heat resistance must be weighed against other critical factors.
Heat Resistance vs. Weight and Cost
There is a direct trade-off between thermal performance, weight, and price. Rubber offers maximum heat resistance but is heavy. EVA is extremely light and inexpensive but has poor heat tolerance. PVC is a low-cost baseline, while PU offers a superior balance of properties at a higher cost.
Deformation Is Not the Only Failure
A material might not deform but could still transfer heat rapidly, posing a burn risk. The insulating properties of the material are a separate but equally important consideration for safety and comfort in hot environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the primary demands of your specific environment and task.
- If your primary focus is maximum safety in high-heat industrial settings: Rubber is the most reliable choice due to its inability to melt.
- If your primary focus is a balance of durability, comfort, and good heat resistance: Polyurethane (PU) offers the best all-around performance.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, general-purpose use in cool environments: PVC is a suitable and economical option.
- If your primary focus is achieving the lightest possible weight where heat is not a factor: EVA provides superior cushioning and minimal weight.
Ultimately, understanding a material's fundamental structure is the key to predicting its performance under thermal stress.
Summary Table:
| Material | Type | Key Thermal Behavior | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Thermoset | Does not melt; chars at extreme heat | Maximum safety in high-heat industrial settings |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Thermoset-like | High melting point; excellent heat resistance | Balanced durability, comfort, and thermal performance |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Thermoplastic | Low softening point; deforms easily | Low-cost, general-purpose use in cool environments |
| EVA | Thermoplastic | Very low melting point; deforms and shrinks | Lightweight cushioning where heat is not a factor |
Need footwear that can withstand your specific thermal environment?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our expertise in material science ensures your products are built with the right polymer—whether it's heat-resistant rubber for industrial safety or high-performance PU for balanced durability—to meet your exact demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and leverage our full production capabilities for all types of shoes and boots.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Factory-Direct Wholesale Canvas Boots with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Factory Direct Wholesale Rain Boots Durable Waterproof & Fully Customizable
- Durable Leather Work Boots Wholesale Manufacturer & Custom Factory
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Durable Goodyear Welt Leather Work Boots for Wholesale & Private Label
People Also Ask
- Why are rubber soles beneficial in cold-weather boots? Superior Traction & Waterproofing
- Why is rubber commonly used for non-slip soles? The Science of Superior Grip
- What types of rubber are typically employed in non-slip footwear soles? Your Guide to Maximum Grip and Safety
- What types of work environments are hiker-style rubber outsoles best for? Ideal for Outdoor & Industrial Safety
- What factors determine the slip resistance of rubber-soled shoes? Tread, Compound & Design Explained



















