To properly evaluate footwear, the most effective resources are standards organizations like ASTM International and reputable footwear manufacturers. These provide the objective data and specialized knowledge needed to compare features against the specific hazards of a workplace.
The most reliable method for evaluating footwear isn't about finding the "best shoe," but about conducting a thorough hazard assessment of the job environment first. The right resources are then used to match a shoe's specific safety features to those identified risks.
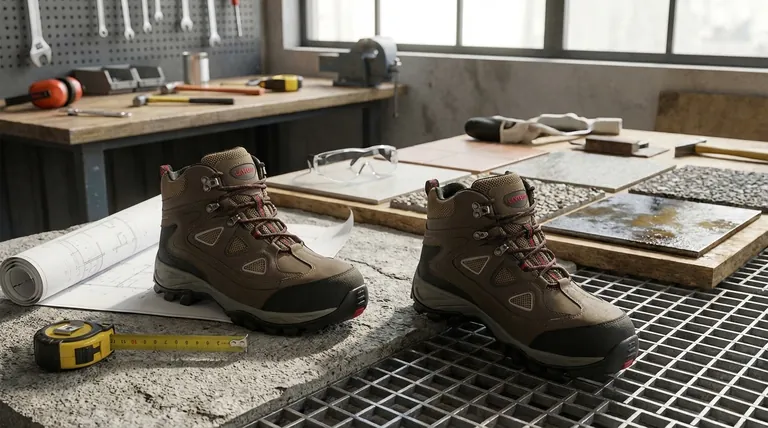

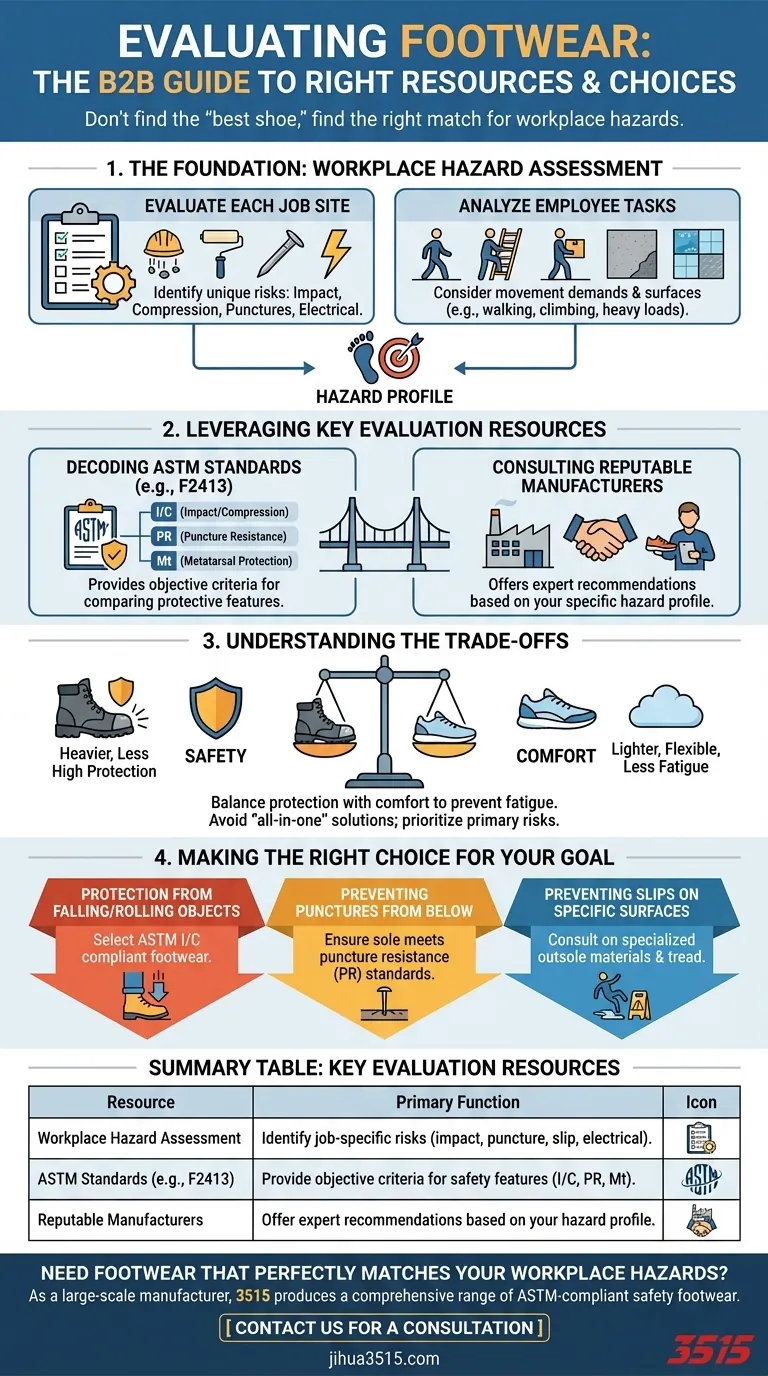
The Foundation: The Workplace Hazard Assessment
Before you can evaluate any piece of footwear, you must first understand the environment where it will be used. This foundational step dictates all subsequent choices.
Evaluate Each Job Site
Every location has a unique risk profile. You must systematically identify potential dangers to the feet.
This includes risks of impact from falling objects, compression from rolling equipment, punctures from sharp objects on the floor, or exposure to electrical hazards.
Analyze Each Employee's Tasks
The specific duties an employee performs are just as important as the location. A static job has different footwear needs than one requiring constant walking, climbing, or carrying heavy loads.
Consider the surfaces they walk on (e.g., concrete, slick tile, uneven ground) and the physical demands of their movements.
Leveraging Key Evaluation Resources
Once you have a clear picture of the hazards, you can use external resources to find footwear with the appropriate protective features.
Decoding ASTM International Standards
ASTM International (formerly the American Society for Testing and Materials) develops and publishes technical standards for a wide range of products, including safety footwear.
These standards, such as ASTM F2413, provide a common language and set of requirements for features like impact resistance (I), compression resistance (C), and metatarsal protection (Mt).
Using these labels allows you to make an objective, apples-to-apples comparison of the protective capabilities of different shoes.
Consulting with Reputable Manufacturers
Experienced footwear manufacturers are a critical resource. They possess deep knowledge about which shoe constructions and materials are best suited for specific tasks and industries.
By providing them with your detailed hazard assessment, they can recommend footwear designed and tested for the exact conditions your employees face.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting footwear often involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single shoe that is perfect for every task and every environment.
Safety vs. Comfort
Often, the most protective footwear—with features like steel toes and thick puncture-resistant soles—can be heavier and less flexible. This can lead to fatigue over a long shift.
It is crucial to find the right balance where the necessary level of protection is achieved without creating undue discomfort that could lead to other issues.
Specificity vs. Versatility
A shoe designed for one specific hazard, like electrical work, may not offer the best slip resistance on an oily surface.
Be wary of "all-in-one" solutions. The most effective approach is to select footwear with the specific features required for the primary risks identified in your assessment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your hazard assessment will guide your final selection. Prioritize the features that mitigate the most significant risks in your specific environment.
- If your primary focus is protection from falling or rolling objects: Select footwear that explicitly meets ASTM standards for impact (I) and compression (C).
- If your primary focus is preventing punctures from below: Ensure the shoe has a sole that meets puncture resistance (PR) standards.
- If your primary focus is preventing slips on specific surfaces: Consult with manufacturers about outsole materials and tread patterns proven to perform on those surfaces.
Ultimately, a systematic evaluation process ensures your footwear choice is based on objective needs, not just brand or style.
Summary Table:
| Key Evaluation Resource | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Workplace Hazard Assessment | Identify job-specific risks (impact, puncture, slip, electrical). |
| ASTM Standards (e.g., F2413) | Provide objective criteria for safety features (I/C, PR, Mt). |
| Reputable Manufacturers | Offer expert recommendations based on your hazard profile. |
Need footwear that perfectly matches your workplace hazards?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of protective shoes and boots, designed to meet and exceed ASTM standards.
Let our experts help you select the ideal footwear based on your specific hazard assessment. Contact us today for a consultation and get the right protection for your team.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Premium Suede Metatarsal Guard Safety Boots Work Shoes
People Also Ask
- What are some extra features that can be found in safety shoes? Beyond Basic Steel Toe Protection
- What are the OSHA requirements for safety footwear? A Guide to Compliance & ASTM Standards
- What is the process for evaluating job dangers related to footwear? A Guide to Systematic Hazard Assessment
- What are the primary protective functions of industrial-grade safety shoes? Essential Occupational Safety Guide
- Why is placing retro-reflective markers on limbs more effective? Boost Safety with Biological Motion on Safety Shoes
- What primary protective functions do industrial safety shoes provide for personnel working on an airport apron?
- How does functional protective footwear improve the work environment? Combat Fatigue with Shock-Absorbing Technology
- What comfort features are included in oilfield safety shoes? Reduce Fatigue & Enhance On-Site Safety



















