The primary OSHA requirement for safety footwear is that it must meet or be equivalent to the standards developed by ASTM International, a recognized consensus-standards organization. OSHA's regulation 29 CFR 1910.136 mandates that employers ensure employees use protective footwear in hazardous environments, and it points to ASTM F2413 as the defining standard for footwear performance and testing.
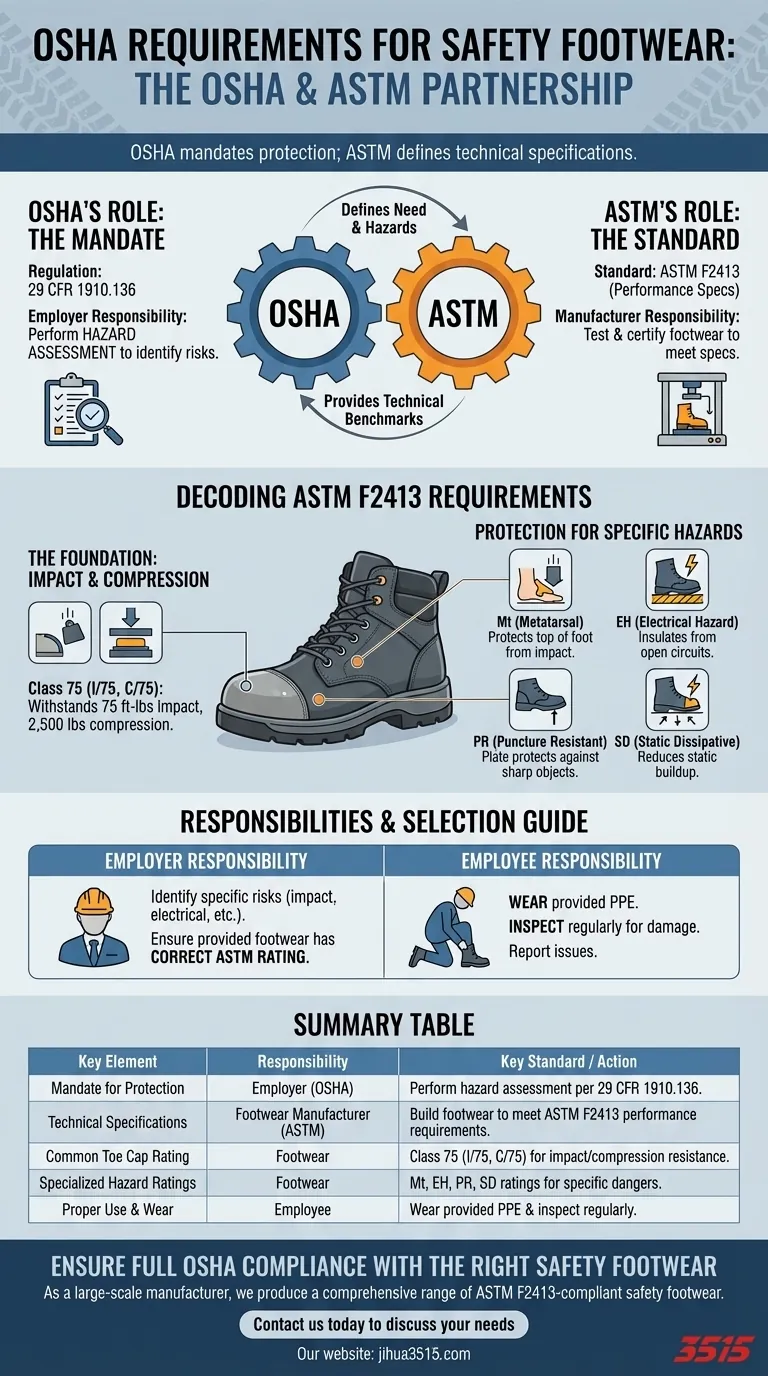
The critical takeaway is that OSHA defines the need for protective footwear based on a workplace hazard assessment, but ASTM defines the technical specifications for the footwear itself. Your responsibility is to match the correct ASTM-rated shoe to the specific hazards of your job.
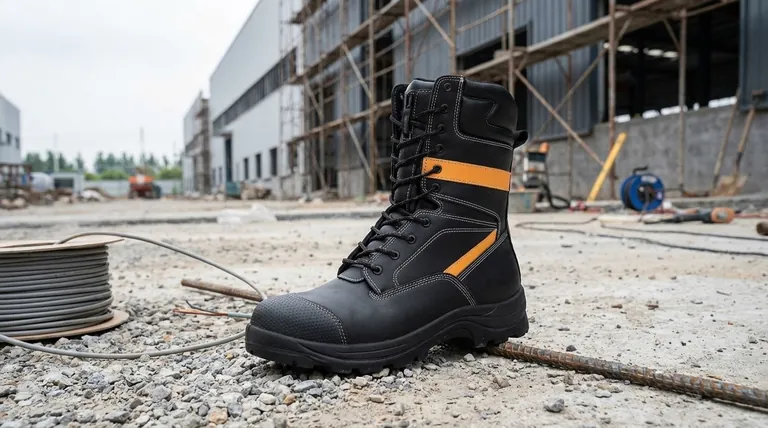

The OSHA and ASTM Partnership: Who Requires What?
To understand safety footwear compliance, you must understand the distinct roles of these two organizations. They work in tandem to ensure worker safety.
OSHA's Role: The Mandate for Protection
OSHA does not publish its own detailed design specifications for safety boots. Instead, it places a general duty on employers to protect workers from known hazards.
The key regulation, 29 CFR 1910.136(a), requires employers to ensure employees use protective footwear when working in areas where there is a danger of foot injury. This includes dangers from falling or rolling objects, objects piercing the sole, or electrical hazards.
The employer's first responsibility is to perform a hazard assessment to identify these specific risks.
ASTM's Role: The Technical Standard
ASTM International provides the technical benchmarks that footwear must meet. The current governing standard is ASTM F2413, "Standard Specification for Performance Requirements for Protective (Safety) Toe Cap Footwear."
This standard establishes the minimum requirements for the design, performance, testing, and classification of safety footwear. If a boot is labeled as ASTM F2413 compliant, it has been tested according to the methods in ASTM F2412.
Decoding Key ASTM F2413 Requirements
An ASTM-compliant safety shoe always starts with the toe cap, but various ratings exist for specialized hazards. The boot's label will indicate which standards it meets.
The Foundation: Impact and Compression Resistance
This is the most fundamental requirement for any footwear to be considered "safety toe."
All ASTM F2413 footwear must have a built-in toe cap that meets specific resistance ratings for impact (I) and compression (C). The highest and most common rating is Class 75, meaning the toe box can withstand 75 foot-pounds of impact and 2,500 pounds of compression.
Protection for Specific Hazards
Beyond the toe cap, ASTM specifies codes for footwear designed to protect against other dangers.
- Metatarsal (Mt): Protects the top of the foot (the metatarsal bones) from impact.
- Electrical Hazard (EH): Insulates the wearer from the ground to protect against open electrical circuits.
- Puncture Resistant (PR): Includes a puncture-resistant plate in the sole to protect against sharp objects from below.
- Static Dissipative (SD): Reduces the buildup of static electricity by conducting it to the ground.
Essential Protective Features
While not tied to a specific ASTM code, features like slip-resistant soles and durable upper materials (such as leather) are critical components of any effective safety shoe. They provide the stability and durability needed in hazardous environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Responsibilities
Compliance is not just about buying the right boot; it's about implementing a complete safety strategy.
The Employer's Critical Responsibility
The most common point of failure is an improper hazard assessment. The employer is legally responsible for identifying the specific risks in their workplace—be they impact, puncture, electrical, or otherwise—and ensuring the provided footwear carries the correct ASTM rating for those hazards.
An expensive boot with an I/75 and C/75 rating is non-compliant and unsafe if the primary risk to the employee is an electrical hazard and the boot isn't EH-rated.
The Employee's Role
Employees have a responsibility to wear the personal protective equipment (PPE) provided by their employer. They should also inspect their footwear regularly for damage and communicate with their supervisor if they feel the equipment is inadequate or has been compromised.
Beyond Compliance: Fit and Comfort
While OSHA and ASTM do not regulate comfort, it is a critical safety factor. Footwear that is ill-fitting or uncomfortable is less likely to be worn correctly, if at all. Discomfort can also serve as a major distraction, increasing the risk of other types of accidents.
Selecting the Right Footwear for Your Hazard
Use your workplace's hazard assessment to determine which features are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is working around heavy, rolling, or falling objects: Your footwear must, at minimum, have a Class 75 rating for impact (I/75) and compression (C/75).
- If your primary focus is protection from nails or sharp debris on the ground: You must have a boot with a Puncture Resistant (PR) rating.
- If your primary focus is working near live electrical currents: The only acceptable choice is footwear with an Electrical Hazard (EH) rating.
- If your primary focus is preventing static discharge in a sensitive environment: You need footwear rated for Static Dissipative (SD) performance.
Ultimately, workplace safety is achieved by matching footwear certified to the correct ASTM standard against the specific risks identified in your work environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Element | Responsibility | Key Standard / Action |
|---|---|---|
| Mandate for Protection | Employer (OSHA) | Perform a hazard assessment per 29 CFR 1910.136. |
| Technical Specifications | Footwear Manufacturer (ASTM) | Build footwear to meet ASTM F2413 performance requirements. |
| Common Toe Cap Rating | Footwear | Class 75 (I/75, C/75) for impact/compression resistance. |
| Specialized Hazard Ratings | Footwear | Mt (Metatarsal), EH (Electrical Hazard), PR (Puncture Resistant), SD (Static Dissipative). |
| Proper Use & Wear | Employee | Wear provided PPE and inspect it regularly for damage. |
Ensure Full OSHA Compliance with the Right Safety Footwear
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of ASTM F2413-compliant safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots, from basic impact-resistant models to specialized footwear for electrical hazards, puncture resistance, and metatarsal protection.
We help you mitigate risk and protect your workforce by providing durable, comfortable, and fully compliant footwear tailored to the specific hazards identified in your assessment.
Contact us today to discuss your safety footwear needs and request a quote. Get in Touch via Our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium Waterproof High-Cut Industrial Safety Boots for Wholesale and Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a standardized 30x21x21cm load box in labor tests? Optimize Safety with Data.
- What is the impact of composite toe boots on metal detectors? A Guide for Secure Facilities
- What are the benefits of wearing firefighter boots? Essential Protection for Extreme Conditions
- What are the advantages of using plastic toe caps in safety footwear? Lightweight & Metal-Free Protection
- What role does closed-cell resin material play in functional footwear? Unlock Adaptive Comfort and Safety
- What issues can arise if a safety toe boot is too tight? Avoid Pain and Compromised Safety
- How should safety footwear be cared for? A Practical Guide to Extend Boot Life & Safety
- What are the key material performance requirements for safety footwear? Guide to ASTM F2413 & OSHA Compliance



















