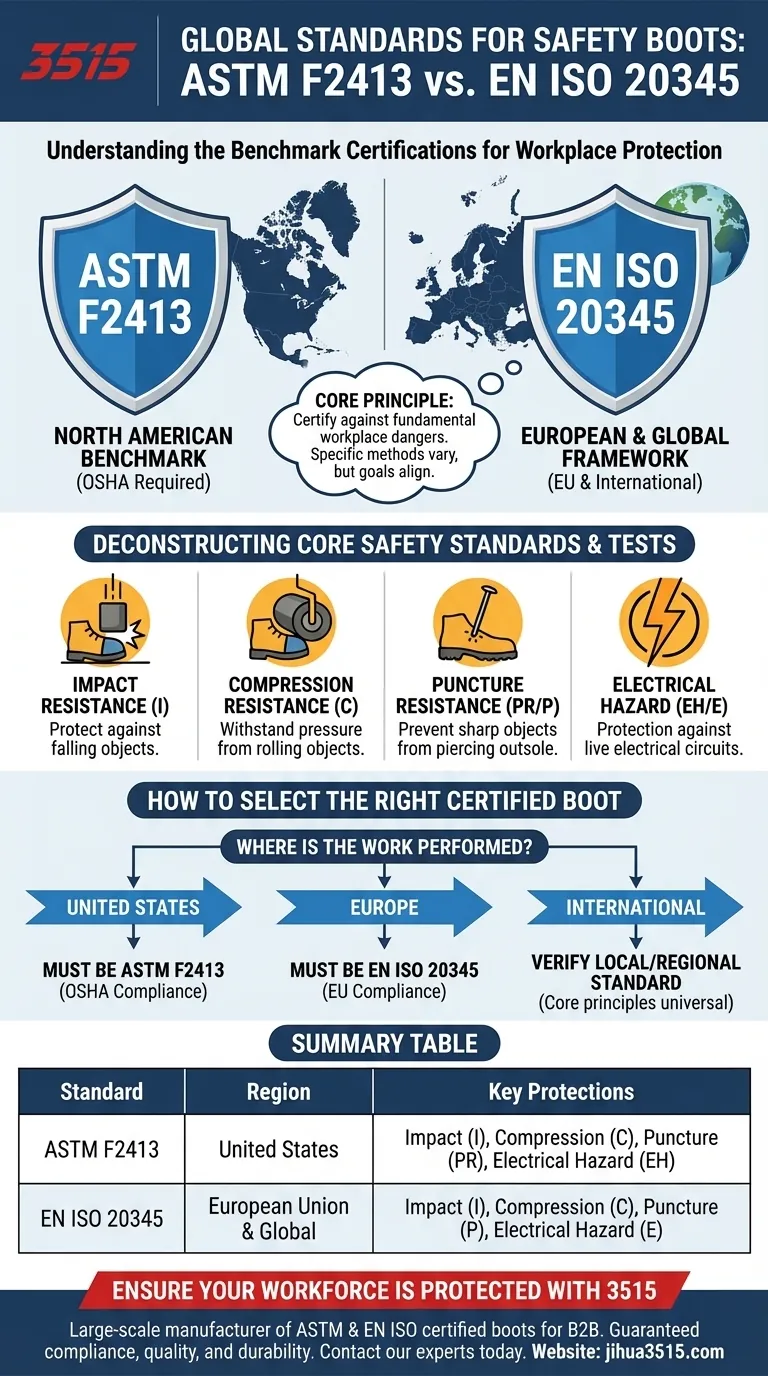
The primary global standards for safety footwear are ASTM F2413, the benchmark in the United States, and EN ISO 20345, the prevailing standard across Europe and many other parts of the world. Both frameworks establish rigorous testing requirements for critical safety features like impact and compression resistance to protect workers from job-site hazards.
The array of acronyms—ASTM, ISO, EN—can be confusing, but the core principle is simple. While specific testing methods vary, these standards all aim to certify footwear against the same fundamental workplace dangers. The most important factor is ensuring your boot's certification matches the legal requirement for your geographic region.

Deconstructing the Core Safety Standards
To ensure worker safety and regulatory compliance, several key organizations have developed comprehensive standards. These are not just suggestions; they are often legal requirements enforced by bodies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
ASTM Standards (The North American Benchmark)
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) sets the technical standards for a wide range of products, including protective footwear.
The key standard is ASTM F2413. This is the specification that OSHA requires for protective footwear in the United States. It outlines the minimum requirements for design, performance, testing, and classification.
EN ISO Standards (The European & Global Framework)
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and European Norms (EN) work together on many standards, with EN ISO 20345 being the critical one for safety footwear.
This standard is the legal requirement for safety boots sold within the European Union and is widely adopted as a benchmark for safety across the globe.
What Do These Standards Actually Test?
While the names differ, the core mission is the same: to verify protection against specific risks. A certified boot is tested for multiple performance metrics.
Key tests include:
- Impact Resistance (I): The ability of the reinforced toe cap to protect the foot from a falling object.
- Compression Resistance (C): The toe cap's ability to withstand pressure from a rolling object.
- Puncture Resistance (PR): The outsole's ability to prevent sharp objects from piercing the bottom of the boot.
- Electrical Hazard (EH): Protection against accidental contact with live electrical circuits.
Understanding the Key Differences and Overlaps
The existence of multiple standards doesn't mean one is inherently "better" than another. The primary difference lies in their regional jurisdiction and specific testing protocols.
Regional Compliance is Paramount
The most critical factor is where the work is being performed. OSHA explicitly mandates that employers provide footwear that complies with ASTM standards for work sites in the United States.
Similarly, work sites in the European Union require boots that are certified and marked according to EN ISO 20345.
Harmonization and Functional Equivalence
While testing methodologies and labeling might differ slightly, the safety goals are fundamentally aligned. A boot certified for top-tier impact and compression under ASTM provides a functionally equivalent level of protection to one certified under EN ISO 20345.
The key is not to compare the standards against each other, but to ensure the boot you choose meets the specific legal standard required for your location.
How to Select the Right Certified Boot
Choosing the right boot goes beyond comfort and durability; it's a critical decision for safety and compliance. Your selection should be based on a clear understanding of your work environment and its associated legal requirements.
- If your primary focus is working in the United States: Your footwear must be certified to the ASTM F2413 standard to comply with OSHA regulations.
- If your primary focus is working in Europe: You must select boots that are marked as compliant with the EN ISO 20345 standard.
- If your primary focus is managing international safety: Always verify the specific national or regional standard required for each work location, knowing that the core safety principles of impact and compression are universal.
Ultimately, selecting the correct certified footwear is the most direct way to ensure protection against the specific hazards of your job.
Summary Table:
| Standard | Region | Key Protections |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM F2413 | United States | Impact (I), Compression (C), Puncture (PR), Electrical Hazard (EH) |
| EN ISO 20345 | European Union & Global | Impact (I), Compression (C), Puncture (P), Electrical Hazard (E) |
Ensure your workforce is protected with the right certified safety footwear. As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of ASTM and EN ISO certified boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We guarantee compliance, quality, and durability for all your safety needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Wholesale Mesh Steel Toe Safety Shoes with Dial Closure Factory Production
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots for Wholesale
People Also Ask
- What are the primary protective functions of composite-toe boots? A Guide to Modern Safety Footwear
- What materials are used for safety toes? Choose Steel, Composite, or Aluminum for Your Work Boots
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- What type of footwear is required in meatpacking and poultry plants due to slippery conditions? Essential Safety Boots for Slippery Floors



















