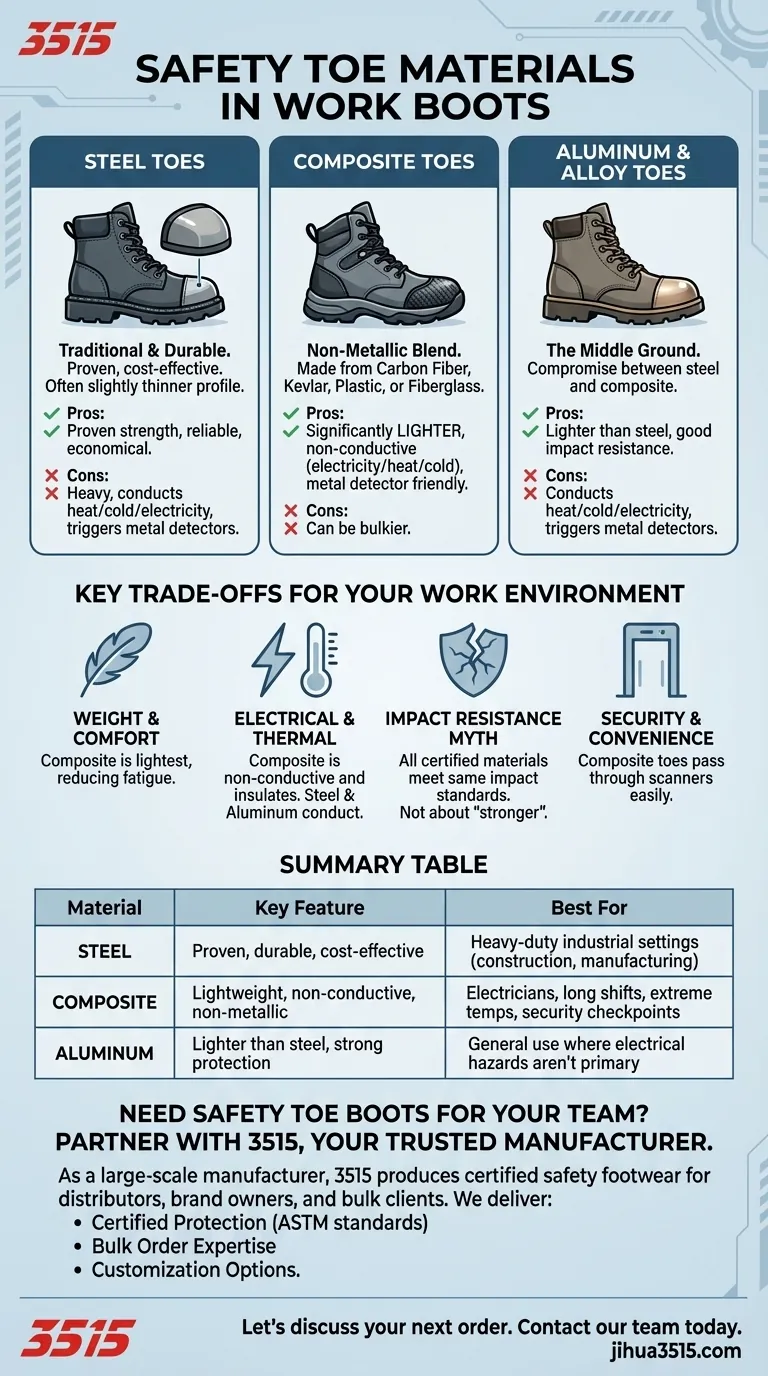
The three most common materials used for safety toes in work boots are steel, composite materials, and aluminum alloys. All are engineered to protect your feet from serious impact and compression injuries from falling or rolling objects. The primary differences between them lie in their weight, conductivity, and specific use cases.
The decision between safety toe materials is not about which is "stronger," but which offers the right balance of properties for your specific job. While all certified safety toes meet the same impact standards, their material composition dictates their weight, thermal insulation, and electrical conductivity.

Understanding the Core Material Types
A certified safety toe, regardless of material, must meet established safety standards for impact and compression resistance. The material choice is what defines the boot's performance in different work environments.
Steel Toes: The Industry Standard
Steel is the traditional material for safety toes and remains a trusted choice for heavy-duty protection. It is a proven, reliable, and often more cost-effective option.
Because of steel's inherent strength, the toe cap can sometimes be made slightly thinner, resulting in a less bulky profile in some boot designs.
Composite Toes: The Modern Alternative
Composite is a broad term for any non-metallic safety toe. These are typically made from a blend of materials like carbon fiber, Kevlar, plastic, or fiberglass.
Their primary advantage is that they are significantly lighter than steel. They also do not conduct heat, cold, or electricity, making them essential for certain hazardous environments.
Aluminum & Alloy Toes: The Middle Ground
Aluminum or other metal alloys offer a compromise between steel and composite. They provide the necessary impact resistance while being lighter than traditional steel toes.
However, like steel, they will still conduct temperature and electricity, and they will set off metal detectors.
Key Trade-offs for Your Work Environment
Choosing the right material requires you to weigh the specific demands of your job against the properties of each toe type.
The Weight and Comfort Factor
For anyone spending long hours on their feet, boot weight is a critical factor in reducing fatigue. Composite toes offer a clear advantage here, as they are noticeably lighter than their steel counterparts.
Electrical and Thermal Hazards
This is the most important distinction. Because composite toes are non-metallic, they do not conduct electricity. This makes them the only safe choice for electricians or anyone working around live circuits.
Similarly, they do not transfer cold or heat, providing superior comfort for those working outdoors in extreme temperatures. Steel and aluminum will become very cold in winter conditions.
The Impact Resistance Myth
A common misconception is that steel is inherently "stronger" than composite. In reality, any boot meeting ASTM safety standards provides the same level of certified impact protection.
Crucially, any safety boot that has sustained a significant impact must be replaced, regardless of whether the toe is steel or composite.
Security and Convenience
For workers who frequently pass through metal detectors, such as in airports or secure facilities, composite toes are far more convenient as they will not trigger the alarm.
Making the Right Choice for Your Job
Your daily tasks and work environment should be the ultimate guide in your decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability in a heavy industrial setting like construction or manufacturing: Steel toes are a proven, reliable, and cost-effective standard.
- If you work long shifts, walk extensively, or pass through metal detectors: Lightweight composite toes will provide significant comfort and convenience without sacrificing protection.
- If you are an electrician or work in extreme hot or cold environments: Non-conductive and thermally insulating composite toes are the essential choice for your safety and comfort.
- If you want a lighter boot but don't work with electrical hazards: Aluminum alloy toes offer a good balance of protection and reduced weight compared to steel.
Ultimately, choosing the right safety toe is a critical decision that balances material science with the practical demands of your daily work.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Proven, durable, cost-effective | Heavy-duty industrial settings (construction, manufacturing) |
| Composite | Lightweight, non-conductive, non-metallic | Electricians, long shifts, extreme temperatures, security checkpoints |
| Aluminum | Lighter than steel, strong protection | General use where electrical hazards are not a primary concern |
Need Safety Toe Boots for Your Team? Partner with 3515, Your Trusted Manufacturer.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety boots and work shoes with steel, composite, and aluminum toes, ensuring the right fit for every job site requirement.
We deliver:
- Certified Protection: All our safety toes meet or exceed ASTM impact and compression standards.
- Bulk Order Expertise: Reliable supply and competitive pricing for large-volume purchases.
- Customization Options: Tailor styles, materials, and branding to your specific market needs.
Let's discuss your next order. Contact our team today for a quote and see how we can support your business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
People Also Ask
- Why are safety shoes with slip-resistant soles essential for basement construction? Prevent falls on mossy surfaces.
- What are the primary safety functions of safety boots with steel-toe designs? Essential Protection for Industry
- What specific protective functions do safety shoes offer during high-risk tasks? Master Safety on Structural Beams
- What role do high-sensitivity IoT devices play in footwear material handling? Powering Green Logistics & Efficiency
- Why is specialized personal protective equipment required for specific industries? Enhancing Safety in Heavy Industry



















