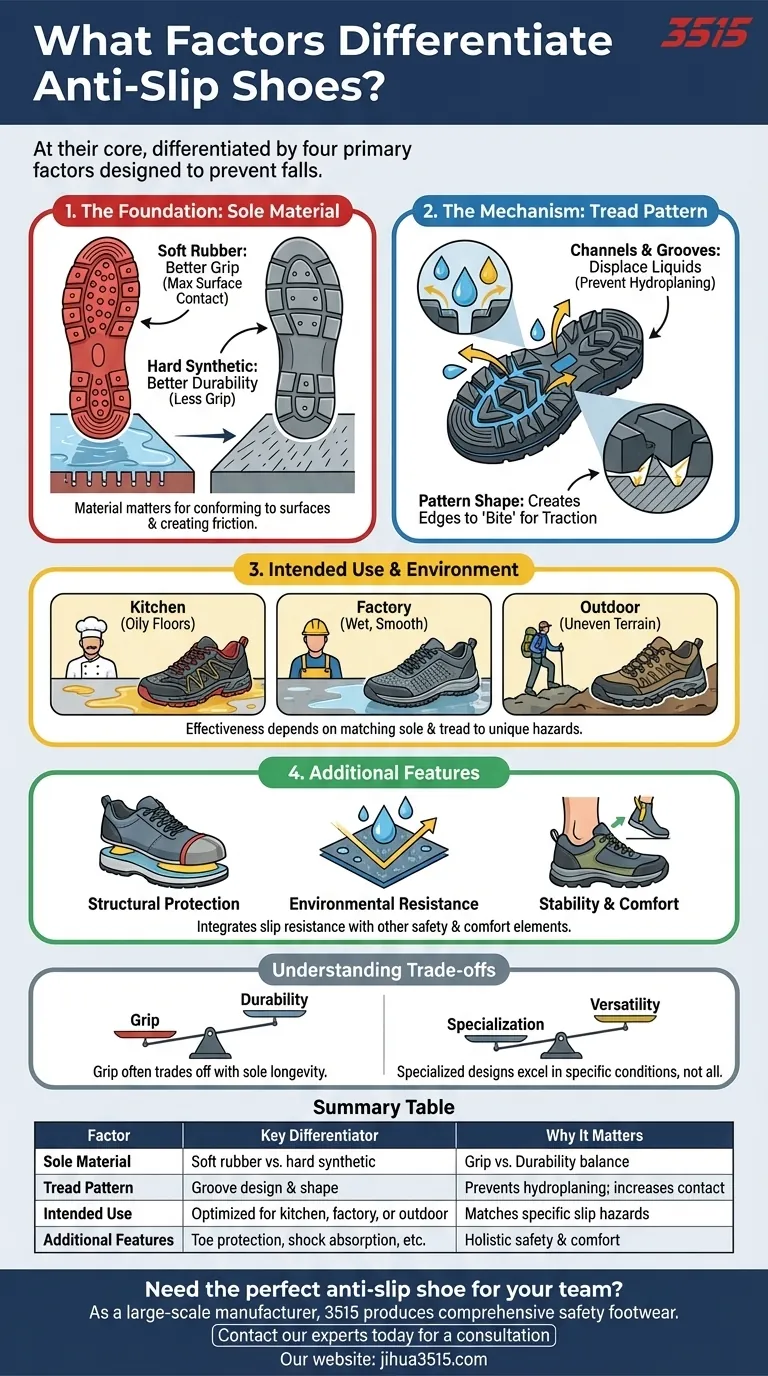
At their core, anti-slip shoes are differentiated by four primary factors: the sole material, the design of the tread pattern, their intended use or environment, and any additional safety features like toe protection or shock absorption. The interplay between the sole and tread is what generates the friction necessary to prevent falls on wet, oily, or otherwise slippery surfaces.
The most effective anti-slip shoe is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its effectiveness is determined by how well its specific sole material and tread pattern are matched to the unique hazards of your environment.
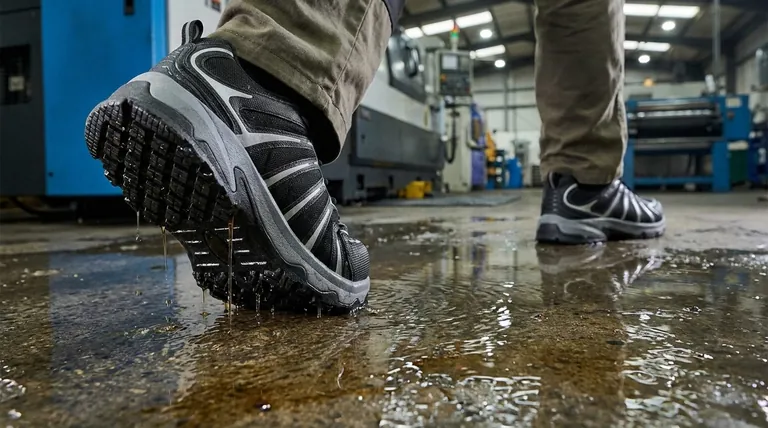

The Foundation: Sole Material
The material used for the outsole is the first point of contact with the ground and is fundamental to creating grip.
Rubber vs. Synthetic Compounds
Most slip-resistant soles are made from durable rubber or similar synthetic materials. The softness and composition of this material directly influence its ability to conform to a surface and create friction.
Why Material Matters for Grip
Softer rubber compounds generally offer better grip, especially on smooth, wet surfaces, because they maximize surface contact. Harder compounds may offer more durability but can be less effective at gripping slick floors.
The Mechanism of Grip: Tread Pattern
While material provides the potential for friction, the tread pattern is the mechanism that makes it effective in challenging conditions.
The Role of Channels and Grooves
The primary function of a tread pattern is to channel liquids—like water or oil—away from the bottom of the shoe. These small channels prevent a layer of fluid from forming between the sole and the floor, a phenomenon known as hydroplaning, which is a major cause of slips.
Pattern Shape and Surface Contact
Effective anti-slip patterns often feature many small, sharp-edged shapes. These create more edges to "bite" into the walking surface, while the deep grooves ensure that contaminants are quickly displaced to maintain direct contact between the sole and the floor.
Beyond the Sole: Additional Features
True safety footwear integrates slip resistance with other protective elements tailored to specific workplace hazards.
Structural Protection
Many work-focused anti-slip shoes include features like reinforced toe caps to protect against impacts and shock-absorbing midsoles to provide stability and reduce fatigue during long hours of standing.
Environmental Resistance
Features like water-resistant materials are crucial for keeping feet dry and comfortable, which is not just a matter of comfort but also of stability. A foot that is secure inside the shoe is less prone to slipping.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right shoe involves balancing competing priorities, as no single design excels in all conditions.
Grip vs. Durability
There is often a direct trade-off between maximum grip and sole longevity. Softer rubber compounds, which provide excellent traction, tend to wear down more quickly than harder, more durable compounds.
Specialization vs. Versatility
A shoe designed specifically for greasy kitchen floors may have a tread pattern that is less effective on rough, uneven outdoor terrain. A shoe with a very deep, rugged tread for outdoor use might feel unstable or clumsy on a smooth, flat industrial floor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
To select the most effective shoe, you must first analyze the primary hazards you face.
- If your primary focus is working in a kitchen with oily floors: Prioritize shoes with soft rubber soles and intricate, multi-directional tread patterns designed to channel away grease.
- If your primary focus is working on wet, smooth surfaces like a factory floor: Look for soles with numerous small grooves and channels that efficiently displace water to maintain contact.
- If your primary focus is working outdoors on uneven or loose terrain: Choose a shoe with a very deep, rugged tread pattern for maximum traction and durable, water-resistant upper materials.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on a clear understanding of where you'll be walking.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Differentiator | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Sole Material | Soft rubber vs. hard synthetic compounds | Softer compounds offer superior grip; harder compounds provide more durability. |
| Tread Pattern | Groove design for channeling liquids | Prevents hydroplaning by displacing water, oil, and grease from underfoot. |
| Intended Use | Kitchen, factory floor, or outdoor terrain | Specialized designs are optimized for specific slip hazards. |
| Additional Features | Toe protection, shock absorption, waterproofing | Integrates slip resistance with other essential safety and comfort elements. |
Need the perfect anti-slip shoe for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of slip-resistant shoes and boots, tailored to your specific industry hazards—from greasy kitchens to wet factory floors.
Contact our experts today for a consultation and discover how we can enhance workplace safety with high-quality, reliable footwear.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Lightweight Breathable Training Shoes for Wholesale & Custom OEM Manufacturing
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Durable & Breathable Training Shoes for Custom Brands
People Also Ask
- Why is compliance with safety standards such as PN EN ISO 20347:2012 critical? Ensure Certified Workplace Protection
- Why is it mandatory to wear safety shoes with steel toe protection during metal loading? Prevent Crushing Injuries
- What is the primary objective of utilizing dedicated safety shoes in nanomaterial work zones? Prevent Track-Out Now
- How do industrial safety shoes contribute to safety in sugar production? Ensure High-Altitude Inspection Security
- How does the shock-absorption technology in safety footwear help reduce injury? Protect Your Skeletal Health Today



















