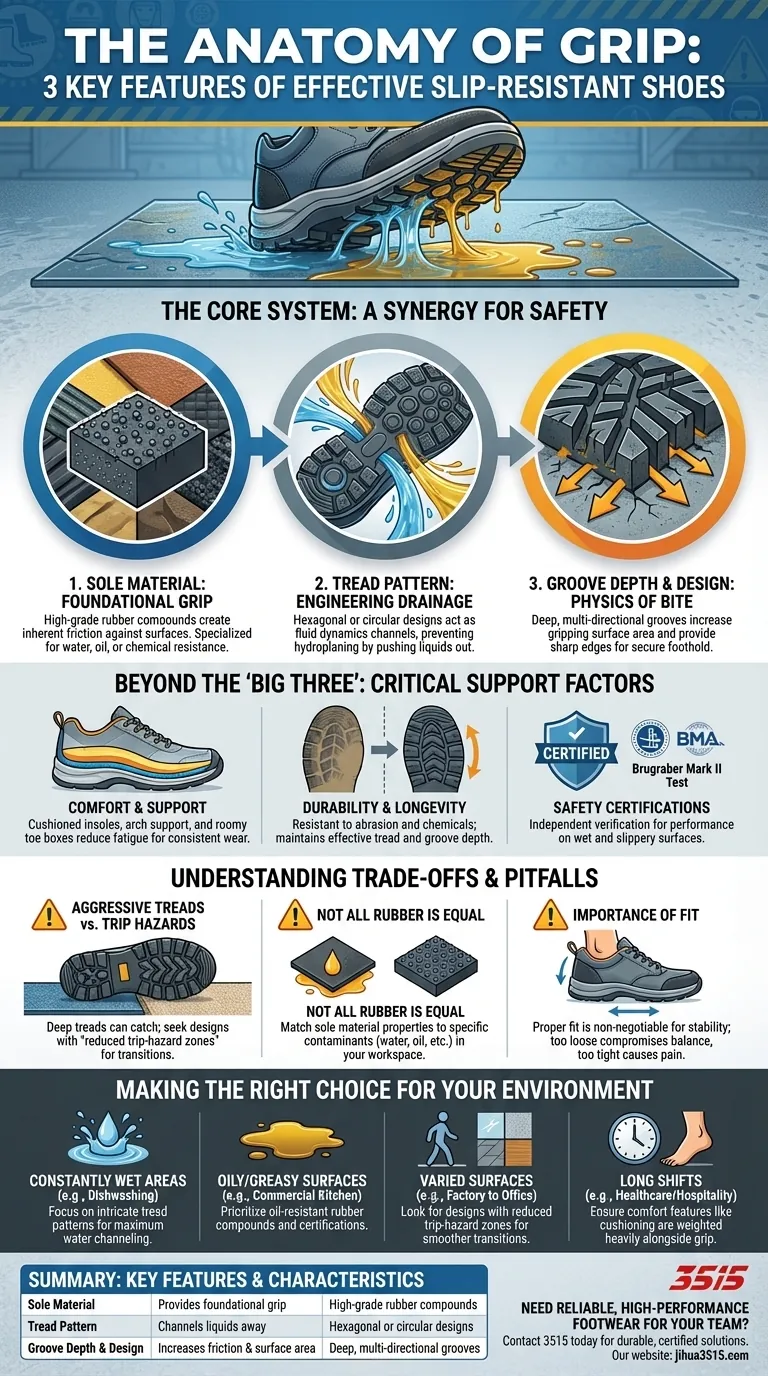
The three key design features that make slip-resistant shoes effective are the sole's material composition, the depth and design of its grooves, and the shape of its tread pattern. These elements work in concert to create superior friction and channel away liquids. High-grade rubber provides the foundational grip, deep grooves increase the gripping surface area, and specific tread patterns push water and oil out from under the foot to maintain contact with the floor.
At its core, an effective slip-resistant shoe is not about a single feature, but about a three-part system: the material provides the grip, the grooves provide the friction, and the pattern provides the drainage. This synergy is what separates true safety footwear from a standard rubber-soled shoe.
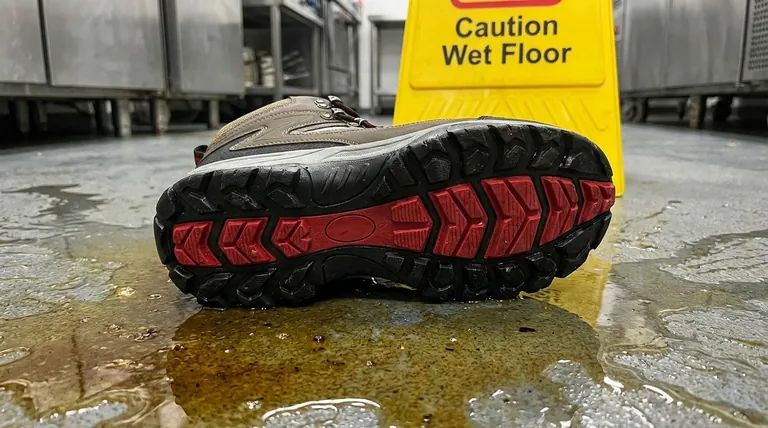

The Anatomy of Grip: How Slip-Resistant Shoes Work
To understand why these shoes are critical for safety, we must look at how each component contributes to keeping you upright in hazardous conditions. It's an engineered solution to a physics problem.
The Foundation: Sole Material
The entire system begins with the material used for the outsole. High-grade rubber is the industry standard for a reason.
This material has a naturally high coefficient of friction, meaning it inherently resists sliding when pressed against another surface. Different rubber compounds are formulated to perform best against specific contaminants like water, oil, or chemicals.
The Engineering: Tread Pattern
The specific pattern molded into the sole is not for aesthetics; it's a crucial piece of fluid dynamics.
Many high-performance designs use hexagonal or circular patterns. These shapes are highly effective at channeling water and other liquids out from under the sole, preventing a layer of fluid from forming that could cause hydroplaning.
The Physics: Groove Depth and Design
The channels and crevices in the sole are known as grooves. Their design is a key differentiator in performance.
Deeper, multi-directional grooves create more surface area and sharp edges to "bite" into the floor. This significantly increases friction and provides a more secure foothold, especially when the surface is not perfectly even.
Beyond the "Big Three": Other Critical Design Factors
While the sole is paramount, other features ensure the shoe is not only safe but also practical and consistently worn. A technically perfect shoe that stays in the locker is useless.
Comfort and Support
Safety and comfort are not mutually exclusive; they are codependent. An uncomfortable shoe can lead to fatigue, which increases the risk of accidents.
Features like cushioned insoles, proper arch support, and roomy toe boxes accommodate foot swelling during long shifts, promoting consistent wear and reducing worker distraction.
Durability and Longevity
A slip-resistant shoe is an investment in safety. Its value is measured by how long it performs its function effectively.
Look for materials resistant to abrasion and chemicals relevant to your workplace. A durable sole that doesn't wear down quickly ensures the tread pattern and groove depth remain effective.
Safety Certifications
Independent verification provides confidence in a shoe's performance claims. Certifications from recognized bodies indicate that a shoe has passed standardized tests for slip resistance.
For example, the Brugraber Mark II Test is a common industry benchmark that validates a shoe's effectiveness on wet and slippery surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Choosing the right shoe involves more than just picking the one with the most aggressive tread. The specific work environment dictates the ideal design.
Aggressive Treads vs. Trip Hazards
An extremely deep and rugged tread designed for a wet kitchen can become a liability when moving to a different surface.
The edges of these aggressive treads can catch on mats or carpeted floors, creating a trip hazard. Some advanced designs incorporate "reduced trip-hazard zones" with smoother patterns to allow for safer transitions between environments.
Not All "Rubber" Is Created Equal
The term "rubber sole" is incredibly broad. The specific compound of the rubber makes a significant difference.
A sole designed for water may not perform well on oily surfaces, and vice versa. It is critical to match the sole's material properties to the most common contaminants in your workspace.
Overlooking the Importance of Fit
A shoe that is too loose allows the foot to slide around internally, compromising balance even if the sole is gripping the floor perfectly.
Conversely, a shoe that is too tight can cause pain and fatigue, reducing focus and increasing the likelihood of a misstep. Proper fit is a non-negotiable component of safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
To select the most effective shoe, you must align its specific design features with the primary challenges of your workspace.
- If your primary environment is constantly wet (e.g., a dishwashing area): Focus on shoes with intricate tread patterns specifically designed to channel large amounts of water away from the sole.
- If you encounter oily or greasy surfaces (e.g., a commercial kitchen): Prioritize shoes with a sole material specifically compounded and certified for high oil resistance.
- If you move between varied surfaces frequently (e.g., from a factory floor to an office): Look for designs that explicitly mention reduced trip-hazard zones for smoother, safer transitions.
- If you are on your feet for long shifts (e.g., healthcare or hospitality): Ensure that comfort and support features like cushioning and a proper fit are weighted just as heavily as the sole's grip.
Ultimately, choosing the right slip-resistant shoe is an informed decision that actively protects you from one of the most common workplace injuries.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Sole Material | Provides foundational grip | High-grade rubber compounds |
| Tread Pattern | Channels liquids away | Hexagonal or circular designs |
| Groove Depth & Design | Increases friction & surface area | Deep, multi-directional grooves |
Need reliable, high-performance footwear for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety and occupational footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of slip-resistant shoes and boots, engineered with the precise material, tread, and groove combinations for your specific work environment.
Contact 3515 today to discuss your needs and get a quote for durable, certified footwear that protects your workforce.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Durable Safety Boots | Custom Steel Toe & Puncture-Resistant Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What are the primary protective functions of professional Safety Boots within the automotive maintenance process?
- How do industrial safety shoes provide protection for personnel? Safeguard Your Team from Heavy Crane Hazards
- How do professional construction boots improve operational efficiency? Boost Site Productivity with Advanced Footwear
- What core protection features do industrial-grade Safety Shoes provide? Key Safety Standards for Infrastructure Sites
- Why can metal protective toecaps become a risk factor for dorsal foot ulcers? Learn to Prevent Pressure Point Injuries



















