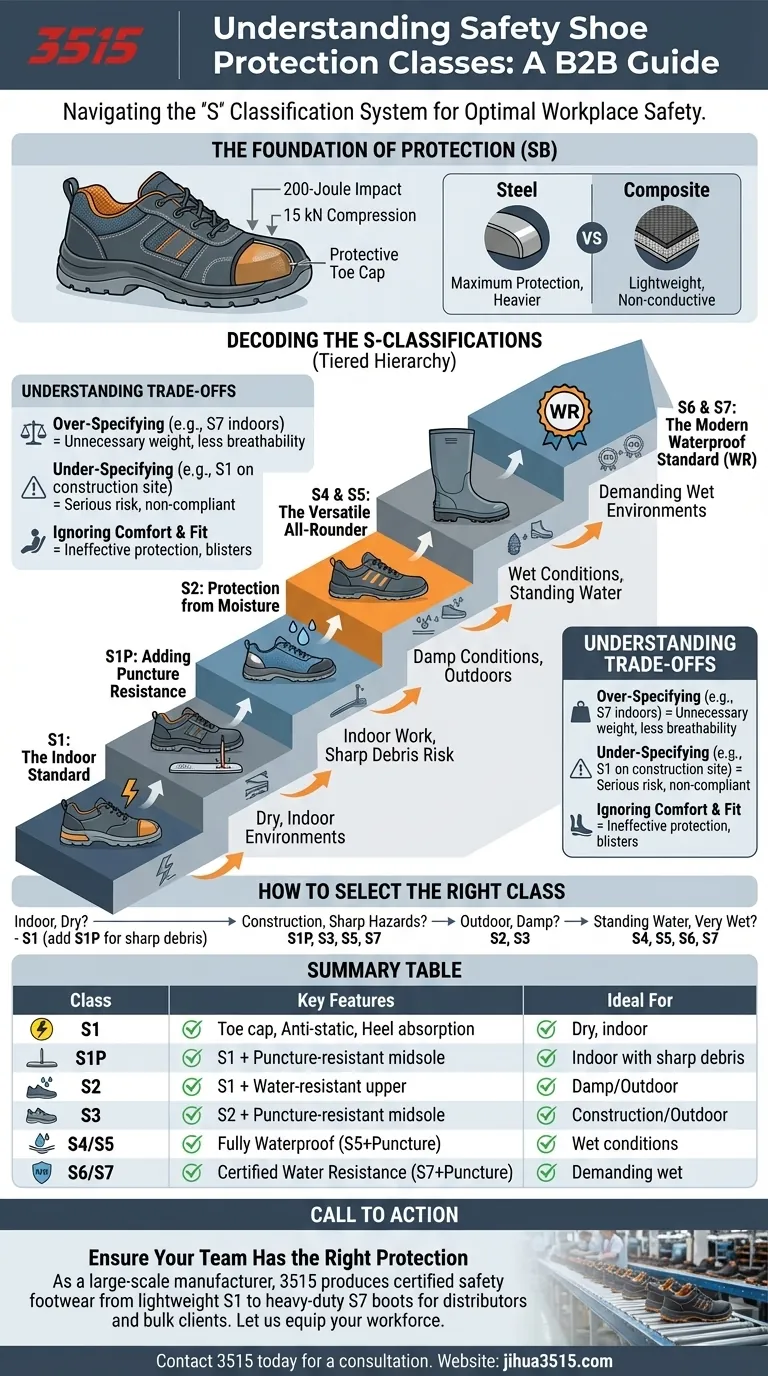
To be effective, safety shoes are categorized into standardized protection classes. These classes, primarily designated with an 'S', follow a tiered system where each subsequent level incorporates the protections of the previous one while adding new, specific safety features.
The core principle is simple: the 'S' classification system (S1, S1P, S2, S3, etc.) is a universal language for safety footwear. Understanding it allows you to precisely match the level of protection to the specific hazards of your work environment.
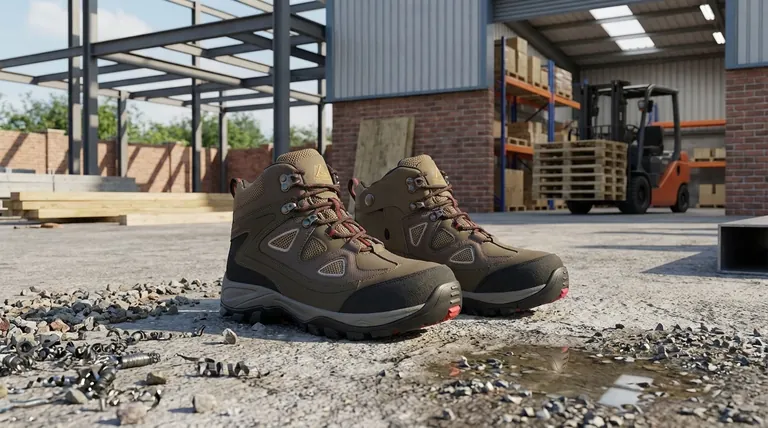

The Foundation of Protection: Core Safety Features
Before diving into the specific classes, it's essential to understand the basic requirements that all certified safety footwear must meet. This is often referred to as the SB (Safety Basic) standard.
Protective Toe Cap
Every safety shoe begins with a reinforced toe cap. This component is engineered to withstand a 200-joule impact and a 15 kilonewton (kN) compression force, protecting your feet from falling objects and crushing hazards.
Steel vs. Composite Toes
Toe caps are typically made of steel or composite materials like carbon fiber or hard plastic. Steel offers maximum protection, while composite caps are lighter and do not conduct electricity, making them ideal for certain environments.
Decoding the S-Classifications
The 'S' classes build upon the SB foundation. Each step up the hierarchy adds a new layer of defense against common workplace risks.
S1: The Indoor Standard
An S1 shoe includes all SB features plus anti-static properties, an enclosed heel for stability, and energy absorption in the heel region to reduce impact. This class is ideal for dry, indoor work environments where there is no risk of water or sharp objects underfoot.
S1P: Adding Puncture Resistance
The S1P rating includes all the features of an S1 shoe but adds a crucial element: a puncture-resistant midsole. This protective plate in the sole guards against sharp objects like nails or glass piercing the foot from below.
S2: Protection from Moisture
An S2 shoe contains all the protective features of the S1 class but adds a water-resistant upper. This does not mean it is fully waterproof, but it will prevent water penetration for a limited time, making it suitable for working in damp conditions or outdoors.
S3: The Versatile All-Rounder
S3 is one of the most common and comprehensive safety classes. It effectively combines the features of an S2 shoe (water-resistant upper) with the protection of an S1P shoe (puncture-resistant midsole). This makes it a robust choice for most outdoor and construction work.
S4 & S5: Fully Waterproof Boots
Classes S4 and S5 refer to fully molded polymer or rubber boots, like wellingtons. They are completely waterproof. An S4 boot has all the basic protections (toe cap, anti-static, heel energy absorption), while an S5 boot adds a puncture-resistant midsole and a cleated outsole for enhanced grip.
S6 & S7: The Modern Waterproof Standard
Newer standards have introduced S6 and S7. An S6 shoe has all the features of S2 but with complete, certified water resistance (WR). An S7 shoe is the top tier, combining all S3 features (including puncture resistance) with certified water resistance (WR).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right shoe isn't just about picking the highest number. Each feature comes with a trade-off in weight, breathability, and cost.
Over-Specifying Protection
Using a fully waterproof S7 boot in a dry, indoor warehouse adds unnecessary weight and significantly reduces breathability. This can lead to discomfort and foot fatigue without providing any relevant safety benefit for that environment.
Under-Specifying Protection
The opposite mistake is far more dangerous. Wearing an S1 shoe on a construction site leaves you completely vulnerable to nail punctures and wet conditions, directly violating safety requirements and putting you at serious risk.
Ignoring Comfort and Fit
A boot with the perfect safety rating is ineffective if it doesn't fit properly. Poor fit can cause blisters, reduce stability, and lead workers to modify or avoid wearing their footwear, nullifying its protective qualities.
How to Select the Right Protection Class
Your choice should be dictated entirely by a risk assessment of your specific work environment.
- If your primary focus is indoor work in dry conditions: An S1 shoe provides the necessary impact and anti-static protection. Add S1P if there's any risk of sharp floor debris.
- If your primary focus is construction, demolition, or jobs with sharp hazards: Puncture resistance is non-negotiable. Your minimum should be S1P, with S3, S5, or S7 being the most appropriate choices.
- If your primary focus is outdoor work or in consistently damp areas: Water resistance is key. Look for S2 or S3 rated footwear.
- If your primary focus is working in standing water or very wet conditions: You need a fully waterproof boot. Choose between S4, S5, S6, or S7 based on whether you also need puncture resistance.
By understanding these classifications, you can move beyond guessing and make an informed, data-driven decision to ensure your safety.
Summary Table:
| Class | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | Basic toe cap, anti-static, energy-absorbing heel | Dry, indoor environments |
| S1P | S1 features + puncture-resistant midsole | Indoor work with sharp debris risk |
| S2 | S1 features + water-resistant upper | Damp or outdoor conditions |
| S3 | S2 features + puncture-resistant midsole | Construction, most outdoor work |
| S4/S5 | Fully waterproof boot (S5 adds puncture resistance) | Wet conditions, standing water |
| S6/S7 | Modern standard with certified water resistance (S7 adds puncture resistance) | Demanding wet environments |
Ensure Your Team Has the Right Protection
Choosing the correct safety footwear is critical for compliance and worker safety. As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety shoes and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of protective footwear, from lightweight S1 shoes to heavy-duty S7 boots, ensuring you get precisely what your market needs.
Let us help you equip your workforce with optimal safety and comfort.
Contact 3515 today for a consultation to discuss your specific requirements and explore our full catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Durable Safety Boots | Custom Steel Toe & Puncture-Resistant Manufacturing
- Wholesale Customizable Safety Boots Durable & Protective Footwear Manufacturing
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
People Also Ask
- Why can metal protective toecaps become a risk factor for dorsal foot ulcers? Learn to Prevent Pressure Point Injuries
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management
- What core protection features do industrial-grade Safety Shoes provide? Key Safety Standards for Infrastructure Sites
- What are the primary protective functions of professional Safety Boots within the automotive maintenance process?
- How do industrial safety shoes provide protection for personnel? Safeguard Your Team from Heavy Crane Hazards



















