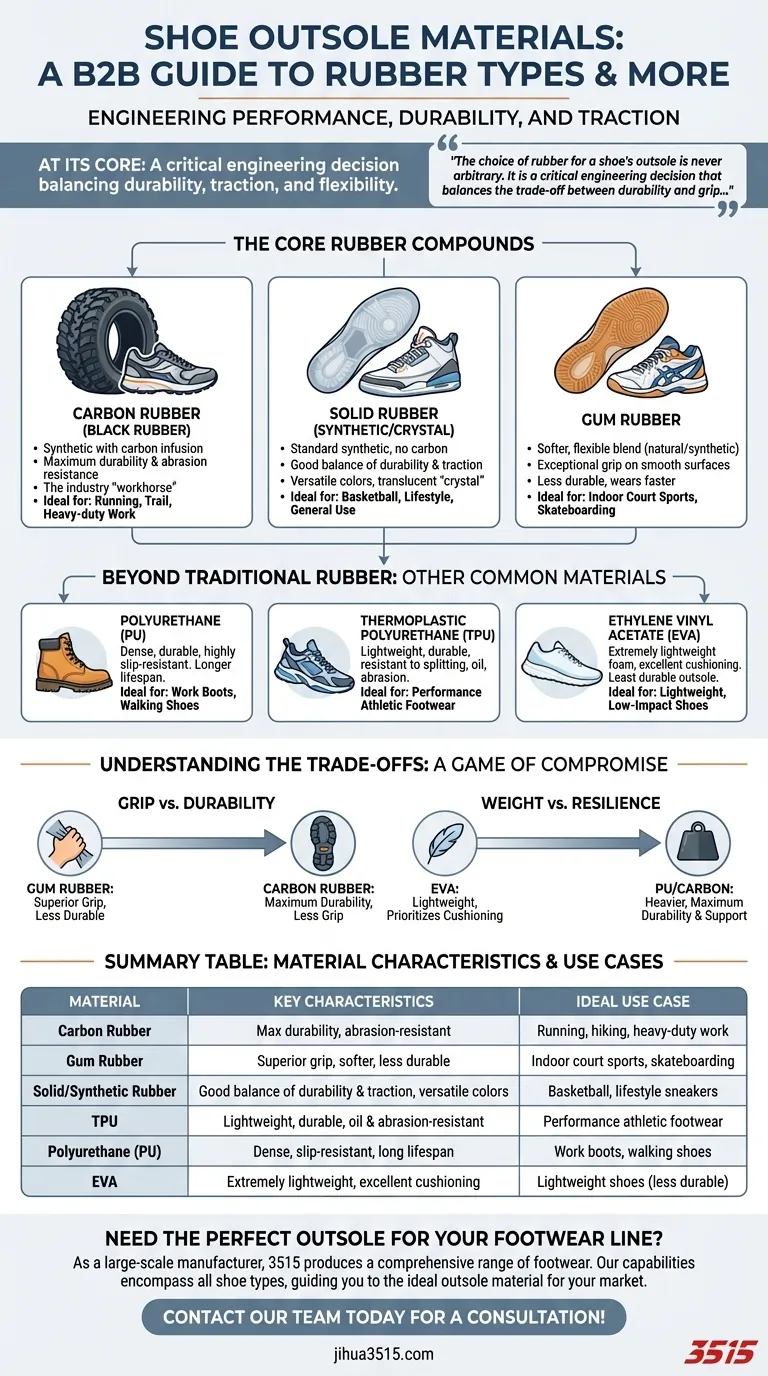
At its core, a shoe outsole is typically made from one of three primary rubber categories: carbon rubber, solid rubber (including synthetic or "crystal" rubber), and gum rubber. Each compound is engineered with a specific balance of durability, traction, and flexibility in mind, directly impacting the shoe's performance and ideal use case.
The choice of rubber for a shoe's outsole is never arbitrary. It is a critical engineering decision that balances the trade-off between durability and grip to match the footwear's intended environment and purpose.

The Core Rubber Compounds Explained
Understanding the fundamental types of rubber is the first step in decoding why a shoe performs the way it does. The composition of the rubber directly dictates its most important physical properties.
Carbon Rubber (Black Rubber)
This is a synthetic rubber compound infused with carbon. This addition dramatically increases the material's durability and abrasion resistance.
It is the workhorse of the footwear industry, especially for outsoles that must withstand significant wear and tear. You will typically find it on running shoes and trail shoes.
Solid Rubber (Synthetic/Crystal)
This refers to a standard synthetic rubber compound without the carbon additive. It offers a well-rounded blend of good durability and reliable traction.
Because it lacks carbon, it can be produced in any color, making it a versatile choice for basketball shoes and lifestyle sneakers where aesthetics are important. Translucent versions of this are often called crystal rubber.
Gum Rubber
Gum rubber is a softer, more flexible compound often made from a blend of natural and synthetic rubber. Its defining characteristic is its exceptional grip, especially on smooth, clean surfaces.
This superior traction comes at the cost of durability; gum rubber wears down much faster than carbon rubber. It is the preferred choice for indoor court shoes (like volleyball or squash) and some skate shoes.
Beyond Traditional Rubber: Other Common Materials
While not strictly "rubber," several other polymer-based materials are frequently used for outsoles and are important to understand in this context.
Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane is a dense, durable, and highly slip-resistant polymer. It offers a longer lifespan than many other materials, making it common in work boots and high-quality walking shoes.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
TPU is a specific class of polyurethane that is prized for being lightweight, durable, and highly resistant to splitting, oil, and abrasion. It provides a great balance of properties and is often used in performance athletic footwear.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
EVA is an extremely lightweight foam material known for its excellent cushioning properties. While it's most famous as a midsole material, it is sometimes used for the outsoles of very light shoes, though it offers the least durability of these options.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The selection of an outsole material is a game of compromise. Improving one characteristic often means sacrificing another.
Grip vs. Durability
This is the most critical trade-off. Softer compounds like gum rubber conform to surfaces better, providing phenomenal grip but wearing away quickly.
Harder compounds like carbon rubber can withstand immense abrasion but may feel slicker on smooth, polished surfaces.
Weight vs. Resilience
Heavier, denser materials like PU and carbon rubber provide maximum durability and support for demanding activities.
Lighter materials like EVA prioritize cushioning and reduced weight for comfort and speed, but they will break down much faster with repeated impact and friction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your activity dictates the ideal outsole material. Use this as your guide.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for running or hiking: Look for shoes with carbon rubber outsoles, which can handle the high abrasion of pavement and trails.
- If your primary focus is elite grip for indoor court sports: Choose footwear with gum rubber outsoles for the best possible traction on polished floors.
- If your primary focus is a versatile blend of style, comfort, and everyday wear: Solid synthetic rubber or TPU outsoles offer the best all-around performance and design flexibility.
Ultimately, understanding the material under your feet empowers you to select the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Characteristics | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Rubber | Maximum durability, abrasion-resistant | Running, hiking, heavy-duty work |
| Gum Rubber | Superior grip, softer, less durable | Indoor court sports, skateboarding |
| Solid/Synthetic Rubber | Good balance of durability & traction, versatile colors | Basketball, lifestyle sneakers |
| TPU | Lightweight, durable, oil & abrasion-resistant | Performance athletic footwear |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Dense, slip-resistant, long lifespan | Work boots, walking shoes |
| EVA | Extremely lightweight, excellent cushioning | Lightweight shoes (less durable) |
Need the Perfect Outsole for Your Footwear Line?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, and we can expertly guide you in selecting the ideal outsole material—whether it's durable carbon rubber for work boots or high-grip gum rubber for court shoes—to match your specific market and performance requirements.
Let's discuss your project and create high-performance footwear together. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Leather Tactical Boots Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing for Brands
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- Premium Wholesale Tactical Style Safety Shoes Boots with Quick Lacing
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Wholesale Lightweight Tactical Boots with Dial Closure OEM & Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of incorporating nano-clay or carbon nanotubes into bio-based shoe sole materials?
- What types of work environments are hiker-style rubber outsoles best for? Ideal for Outdoor & Industrial Safety
- What are the most popular materials used for making shoe soles? Choose the Right Material for Durability & Comfort
- Why is high-grade rubber used in slip-resistant shoe soles? For Superior Traction on Slippery Surfaces
- What are the pros and cons of PVC soles? Uncover the Truth About Footwear Performance
- Why is specific grade sandpaper used in rubber hysteresis testing? Ensure Accurate Data via High-Friction Anchoring
- What are the main types of shoe soles? A Guide to Choosing the Right Material
- Why is an open mill required for the secondary processing of anti-slip rubber outsoles? Master Scorch Prevention



















