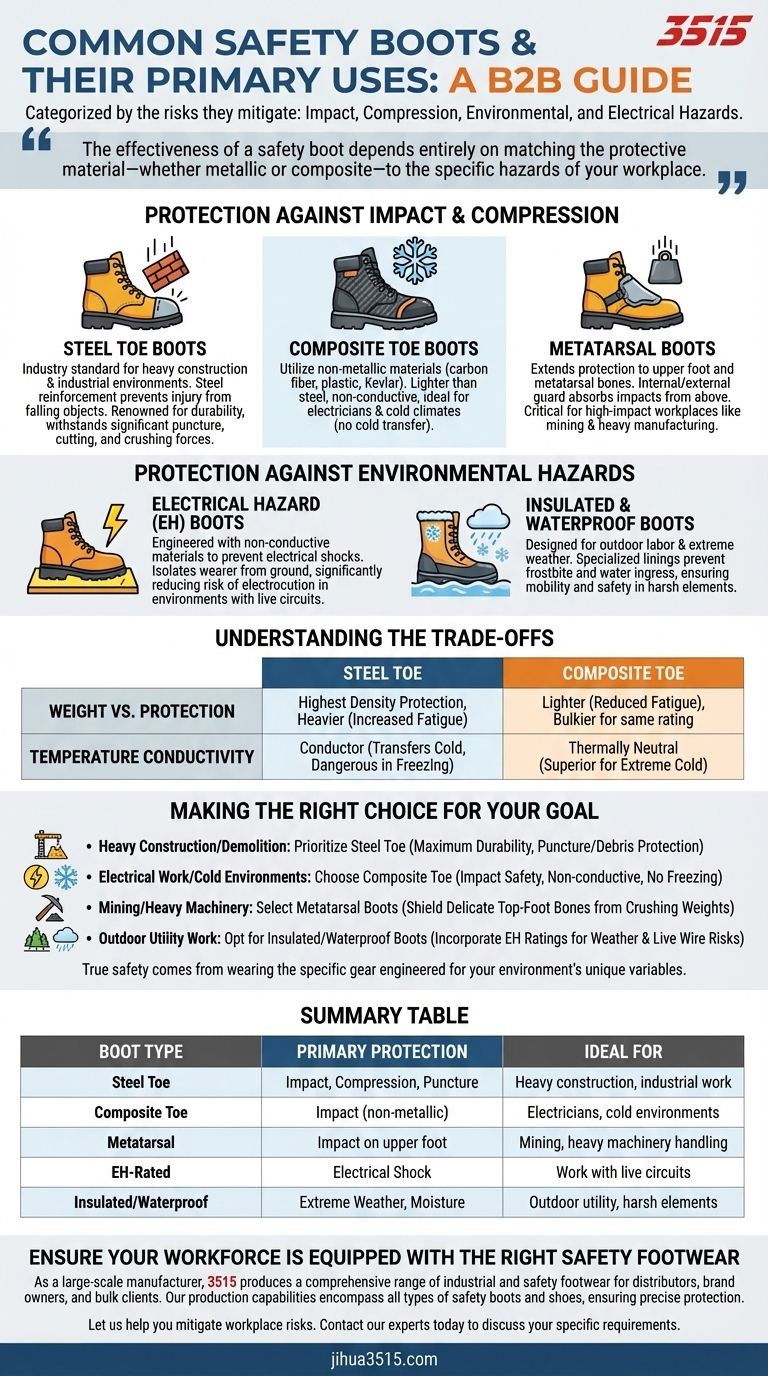
Safety boots are categorized by the specific risks they mitigate, ranging from physical impact and compression to environmental and electrical hazards. The primary types include Steel Toe and Composite Toe for structural protection, Metatarsal Boots for upper-foot safety, and specialized Electrical Hazard (EH) and Insulated/Waterproof boots for environmental defense.
The effectiveness of a safety boot depends entirely on matching the protective material—whether metallic or composite—to the specific hazards of your workplace, such as conductivity, temperature, or crush risks.

Protection Against Impact and Compression
For most industrial professionals, the primary concern is protecting the toes and feet from falling objects or heavy compression.
Steel Toe Boots
These are the industry standard for heavy construction and industrial environments. They feature a steel reinforcement plate in the toe box to prevent injury from heavy falling objects.
They are renowned for their durability and ability to withstand significant puncture, cutting, and crushing forces.
Composite Toe Boots
Composite boots utilize non-metallic materials like carbon fiber, plastic, or Kevlar to provide protection. Because they contain no metal, they are lighter than steel toe options and do not conduct electricity.
They are the ideal choice for electricians or professionals working in cold climates, as the material does not transfer ambient cold to the toes.
Metatarsal Boots
While standard boots protect the toes, Metatarsal boots extend protection to the upper foot and metatarsal bones. They feature an internal or external guard that absorbs impacts from above.
These are critical for high-impact workplaces like mining and heavy manufacturing, where the risk involves heavy loads dropping on the top of the foot.
Protection Against Environmental Hazards
Beyond physical impact, safety boots act as a barrier against the elements and invisible dangers like electricity.
Electrical Hazard (EH) Boots
EH boots are engineered specifically with non-conductive materials to prevent electrical shocks. They isolate the wearer from the ground, significantly reducing the risk of electrocution in environments with live circuits.
Insulated and Waterproof Boots
Designed for outdoor labor and extreme weather, these boots prioritize keeping the foot dry and warm. They utilize specialized linings to prevent frostbite and water ingress, ensuring mobility and safety in harsh elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the "strongest" boot is often a mistake; you must weigh the trade-offs of the materials used.
Weight vs. Protection
Steel toe boots offer the highest density of protection but are heavier, which can increase fatigue over long shifts. Composite boots are lighter and reduce fatigue, but they can be bulkier physically to achieve the same impact rating as steel.
Temperature Conductivity
Steel is a conductor. In freezing environments, a steel toe cap can transfer cold to your feet, making them uncomfortable or dangerous. Composite materials are thermally neutral, making them superior for extreme cold despite being less "traditional."
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting safety footwear is a risk-assessment exercise. Use the following guide to align your choice with your primary daily hazards.
- If your primary focus is heavy construction or demolition: Prioritize Steel Toe Boots for maximum durability and protection against punctures and heavy falling debris.
- If your primary focus is electrical work or cold environments: Choose Composite Toe Boots, which provide impact safety without conducting electricity or freezing temperatures.
- If your primary focus is mining or handling heavy machinery: Select Metatarsal Boots to ensure the delicate bones on top of your foot are shielded from crushing weights.
- If your primary focus is outdoor utility work: Opt for Insulated and Waterproof Boots that incorporate EH ratings to handle both weather and live wire risks simultaneously.
True safety comes not just from wearing protection, but from wearing the specific gear engineered for your environment's unique variables.
Summary Table:
| Boot Type | Primary Protection | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Toe | Impact, Compression, Puncture | Heavy construction, industrial work |
| Composite Toe | Impact (non-metallic) | Electricians, cold environments |
| Metatarsal | Impact on upper foot | Mining, heavy machinery handling |
| EH-Rated | Electrical Shock | Work with live circuits |
| Insulated/Waterproof | Extreme Weather, Moisture | Outdoor utility, harsh elements |
Ensure Your Workforce is Equipped with the Right Safety Footwear
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of industrial and safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety boots and shoes, ensuring you get the precise protection your team needs.
Let us help you mitigate workplace risks. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our footwear solutions can enhance your safety protocols.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
- Premium Sport Style Safety Boots for Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What are the primary hazards that firefighters' footwear must protect against? Engineered for Multi-Threat Environments
- Why are safety shoes with slip-resistant soles essential for basement construction? Prevent falls on mossy surfaces.
- What manufacturing processes are essential for Safety Shoes? Ensure Durability with Advanced Production Standards
- How do I determine the right security guard safety boot sizes? A Guide to Perfect Fit & Protection
- What is the role of an industrial friction coefficient tester? Ensuring Slip Resistance for Safety Footwear
- How do slip-resistant outsoles in safety shoes mitigate the risk of physical imbalance? Boost Grip & Prevent Falls
- How often should work shoes be replaced for those who stand all day? Protect Your Joints and Prevent Pain
- Why are specialized protective shoes or safety shoes considered essential components in standard infection prevention plans? Crucial for Healthcare Safety & Pathogen Control



















