In short, the 2010s were not defined by a single invention but by the convergence and maturation of multiple technologies. This decade saw the smartphone evolve from a novelty into the central hub of modern life, fueled by ubiquitous cloud computing, advanced AI, and breakthroughs in specialized fields like material science.
The core technological advancement of the 2010s was the creation of a deeply interconnected digital ecosystem. The smartphone, powered by the cloud and intelligent algorithms, became the primary interface through which we experienced work, commerce, and social life.

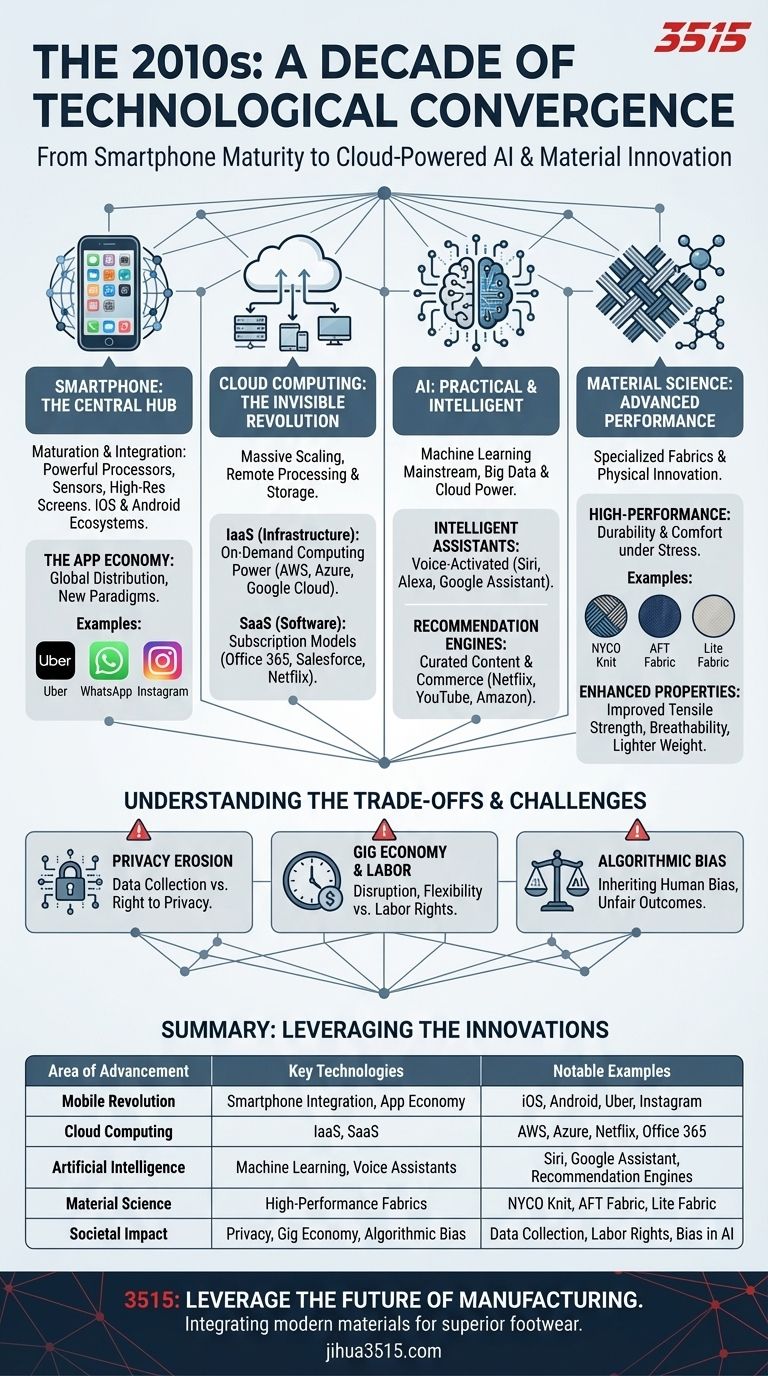
The Smartphone Becomes the Center of the Universe
The 2010s was the decade the smartphone became indispensable. While the iPhone was introduced in 2007, its societal and technological impact exploded in the following decade.
Hardware and Software Integration
The rapid iteration of mobile processors, high-resolution screens, and sensor technology made phones incredibly powerful. This hardware evolution was matched by the maturation of mobile operating systems like iOS and Android, which fostered a vibrant app ecosystem.
The App Economy
The "App Store" model created a new economic paradigm. It allowed developers to distribute software globally with minimal friction, leading to an explosion of services in communication (WhatsApp), transportation (Uber), and entertainment (Instagram).
The Cloud: An Invisible Revolution
The seamless mobile experience of the 2010s was only possible because of the massive scaling of cloud computing. The cloud moved processing power and data storage from personal devices to vast, remote data centers.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure allowed startups and enterprises to rent massive computing power on demand. This dramatically lowered the barrier to entry for creating new digital services.
The Rise of SaaS
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) became the dominant model for software delivery. Businesses and consumers shifted from buying software licenses to subscribing to services like Office 365, Salesforce, and Netflix, all powered by the cloud.
The Dawn of Practical AI
While artificial intelligence research is decades old, the 2010s saw machine learning move from the laboratory into mainstream applications. This was driven by massive datasets (big data) and the affordable computing power of the cloud.
Intelligent Assistants
Voice-activated assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa became common, embedding AI into smartphones and new "smart home" devices.
Recommendation Engines
The content we consume and the products we buy came to be curated by AI. Recommendation algorithms from Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon reshaped media and retail by personalizing user experiences at scale.
Advancements in Specialized Materials
Beyond the digital realm, innovation also occurred in physical materials. The decade saw significant progress in creating advanced fabrics with specific performance characteristics.
High-Performance Fabrics
For example, specialized industries saw the introduction of materials designed for durability and comfort under stress. These included NYCO Knit workwear fabrics and mesh knits like AFT Fabric.
Enhanced Physical Properties
The goal of these new materials was to improve key metrics like tensile strength and breathability without compromising weight. Innovations like Lite Fabric demonstrated this push toward stronger, lighter, and more resilient textiles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
These powerful advancements created a new set of complex challenges that we are still navigating today.
The Erosion of Privacy
The business models of major tech platforms were built on collecting vast amounts of user data. This created a persistent tension between personalized services and an individual's right to privacy.
The Gig Economy and Labor Disruption
Platforms like Uber and Airbnb fundamentally disrupted established industries like transportation and hospitality. This created flexible work for some but also raised critical questions about labor rights, job security, and regulation.
Algorithmic Bias
As AI systems began making decisions in finance, hiring, and even criminal justice, it became clear they could inherit and amplify human biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
How to Contextualize These Changes
The advancements of the 2010s directly set the stage for the technological landscape we inhabit today. Understanding them is key to seeing where we are headed.
- If your primary focus is business strategy: Recognize that the shift to cloud-native, mobile-first, and data-driven models is no longer optional but the baseline for competition.
- If your primary focus is software development: Mastering cloud architecture, mobile application development, and the practical application of machine learning APIs are essential skills.
- If your primary focus is societal impact: Critically evaluate the trade-offs between technological convenience and its consequences for privacy, labor, and social equity.
The 2010s democratized access to powerful technology, fundamentally reshaping how we build products, conduct business, and live our daily lives.
Summary Table:
| Area of Advancement | Key Technologies & Concepts | Notable Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Revolution | Smartphone Integration, App Economy | iOS, Android, Uber, Instagram |
| Cloud Computing | IaaS, SaaS | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Netflix, Office 365 |
| Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning, Voice Assistants | Siri, Google Assistant, Recommendation Engines |
| Material Science | High-Performance Fabrics | NYCO Knit, AFT Fabric, Lite Fabric |
| Societal Impact | Privacy, Gig Economy, Algorithmic Bias | Data Collection, Labor Rights, Bias in AI |
Leverage the Decade's Innovations for Your Business
The technological leaps of the 2010s—from powerful mobile platforms to advanced materials—created new opportunities for businesses to innovate and scale. As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 is at the forefront of applying these advancements to produce superior footwear. We offer a comprehensive range of durable, comfortable, and technologically advanced shoes and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our expertise in integrating modern materials and manufacturing techniques ensures your products meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Ready to elevate your footwear line with the manufacturing power of the future? Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how 3515 can be your trusted production partner.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Factory-Direct Wholesale Canvas Boots with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Custom Manufactured Air Cushion Leather Business Shoes for Wholesale
- Durable Leather Work Boots Wholesale Manufacturer & Custom Factory
- Custom Safety Shoe Manufacturer for Wholesale & OEM Brands
People Also Ask
- Why is professional CAD modeling software required for outsole textures? Master Parametric Design & Mold Precision
- What role does footwear performance play in dynamic balance tests? Enhance Stability and Test Accuracy
- How does shock-absorbing footwear assist in hip osteoarthritis? Protect Joints with Advanced Biomechanical Cushioning
- How can one maintain the waterproofing of leather boots? A 3-Step Guide to Lasting Protection
- Why is sole flexibility considered a core performance indicator? Enhance Natural Gait and Muscle Engagement
- What are the recommendations for head and neck protection in warmer conditions? Stay Cool & Protected
- How is an IMU motion capture system used to validate plantar pressure sensors? Mastering Kinematic Data Calibration
- How should large-scale footwear manufacturers integrate diabetic foot prevention principles? 3 Design Keys for Safety



















