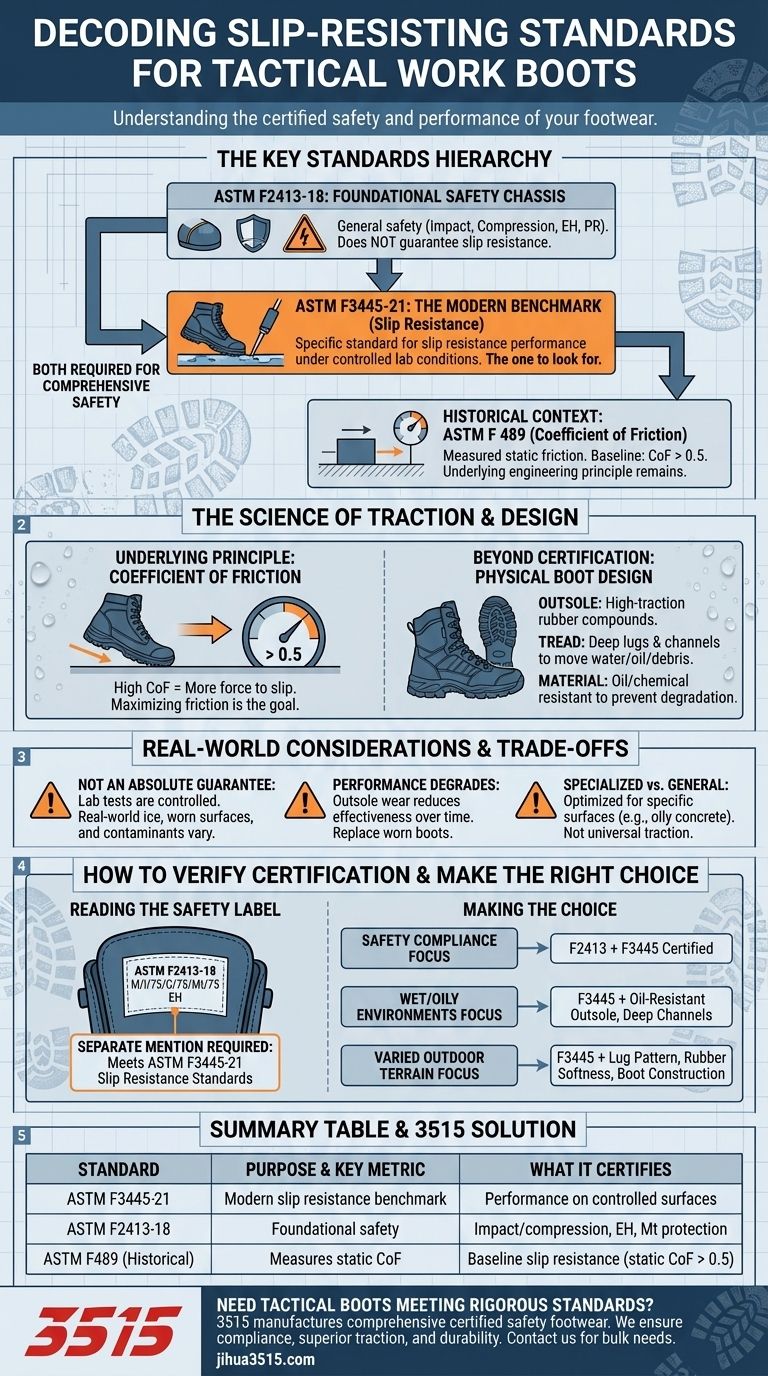
The primary standard for slip resistance in modern tactical and work footwear is ASTM F3445-21. While this is the current specification, older standards like ASTM F 489 were used to measure the static coefficient of friction, establishing a baseline where a value greater than 0.5 was considered slip-resisting. These specific ratings exist within the broader framework of general safety footwear, which is governed by ASTM F2413-18.
Your core challenge is not just finding a "slip-resistant" boot, but decoding the specific standards that prove it. The key is to understand that general boot safety (ASTM F2413) and slip resistance (ASTM F3445) are distinct certifications, and you must verify both.

Deconstructing the Key Standards
To select the right boot, you need to understand how the different ASTM standards function together. One provides the overall safety chassis for the boot, while the other is a specialized rating for a single, critical performance attribute: slip resistance.
The Modern Benchmark: ASTM F3445-21
This is the current, specific standard you should look for regarding slip resistance. It establishes performance requirements and testing methods for footwear under controlled laboratory conditions, simulating common workplace slip hazards.
A boot that is certified to ASTM F3445-21 has passed the industry's benchmark test for traction.
The Underlying Principle: Coefficient of Friction (ASTM F 489)
The fundamental goal of a slip-resistant sole is to achieve a high coefficient of friction against a walking surface. This is a measure of the force required to cause slipping.
Historically, standards like ASTM F 489 were used to test this, requiring a static coefficient of friction of more than 0.5 to qualify. While F3445 is the modern certification standard, this underlying principle of maximizing friction remains the core engineering goal.
The Foundation of Safety: ASTM F2413-18
This is the master standard for protective footwear in the United States. It does not, by itself, guarantee slip resistance.
Instead, ASTM F2413-18 certifies that a boot meets minimum requirements for things like:
- Impact and Compression Resistance for the toe cap (e.g., I/75, C/75).
- Metatarsal Protection from drop hazards (e.g., Mt/75).
- Electrical Hazard (EH) protection from live circuits.
- Puncture Resistance (PR) for the sole.
A boot must first meet these foundational requirements before adding a specialized rating for slip resistance.
Beyond the Standards: Physical Boot Design
Certification is critical, but the physical construction of the outsole is where the performance is delivered.
The Importance of the Outsole
Look for outsoles made of high-traction rubber compounds. The design of the tread is equally important.
Deep lugs and channels help move water, oil, and debris away from the contact points of the sole, allowing the rubber to make a solid connection with the surface.
Resisting Oil and Contaminants
Many slip hazards involve more than just water. True slip-resistant boots use materials that will not degrade or lose their grip when exposed to oils, greases, and other common industrial chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A certification provides a baseline for performance under specified test conditions, but it's crucial to understand its limitations in the real world.
A Rating is Not an Absolute Guarantee
An ASTM rating for slip resistance is performed on specific, clean surfaces under laboratory control. Real-world conditions involving ice, worn surfaces, or unusual contaminants can still present a significant slip hazard.
Performance Degrades Over Time
As the outsole tread wears down, its ability to channel away liquids and grip a surface diminishes. A boot that was compliant when new will lose its effectiveness over time and must be replaced.
Specialized vs. General-Purpose Use
A boot with an outsole designed for oily concrete floors in a warehouse may not provide the same level of traction on loose gravel or wet, muddy inclines. The standard certifies a specific type of slip resistance, not universal traction for all conditions.
How to Verify Certification
You must confirm the standards by checking the boot's label. This information is typically found stitched to the interior or under the tongue.
Reading the Safety Label
A compliant boot will have a label with a line of codes. It will start with the general safety standard and list its specific protections.
For example, a label might read: ASTM F2413-18 M/I/75/C/75/Mt/75 EH.
Critically, you must then look for a separate mention of the slip-resistance standard, such as "Meets ASTM F3445-21 Slip Resistance Standards" on the label, box, or official product description.
Making the Right Choice for Your Mission
Use these standards to align your purchase with your primary operational need.
- If your primary focus is meeting safety compliance: Your boot must be certified to ASTM F2413-18 for foundational protection and also explicitly state compliance with ASTM F3445-21 for slip resistance.
- If your primary focus is performance in wet or oily environments: Prioritize the ASTM F3445-21 rating and closely inspect the outsole design for deep, liquid-channeling treads made from oil-resistant rubber.
- If your primary focus is varied outdoor terrain: Use the ASTM standards as a starting point, but pay closer attention to the lug pattern, rubber softness, and boot construction designed for traction on natural, uneven surfaces.
By understanding these specific standards, you can confidently select tactical footwear that provides a certified foundation of safety and stability.
Summary Table:
| Standard | Purpose & Key Metric | What It Certifies |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM F3445-21 | Modern slip resistance benchmark | Performance on controlled surfaces (e.g., oily, wet) |
| ASTM F2413-18 | Foundational safety for protective footwear | Impact/compression resistance, electrical hazard, metatarsal protection |
| ASTM F489 (Historical) | Measures static coefficient of friction | Baseline slip resistance (static CoF > 0.5) |
Need Tactical Boots That Meet Rigorous Slip-Resistance Standards?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of tactical and work boots engineered to comply with ASTM F3445-21 for superior slip resistance and ASTM F2413-18 for foundational safety.
We ensure your footwear provides:
- Certified Compliance: Boots that meet or exceed the latest ASTM standards.
- Superior Traction: Outsoles designed with high-traction rubber and effective tread patterns.
- Durability & Performance: Built to withstand demanding environments while maintaining safety ratings.
Let us help you equip your team with reliable, standards-compliant footwear.
Contact 3515 today for a consultation to discuss your specific requirements and volume needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
People Also Ask
- What is the core function of professional safety boots within a construction Health and Safety (H&S) management system? Beyond Protection: Boost Safety & Productivity
- What are the core advantages of using impact-resistant safety shoes in dairy farm mechanical work zones?
- What are the primary protective functions of industrial-grade safety shoes during heavy machinery maintenance such as ship engine overhauls? Essential Protection for Extreme Environments.
- How do Robotic Gait Systems verify the durability and safety of mass-produced safety boots? Ensure Unrivaled Performance in Extreme Conditions
- How do industrial safety shoes provide protection for personnel? Safeguard Your Team from Heavy Crane Hazards



















