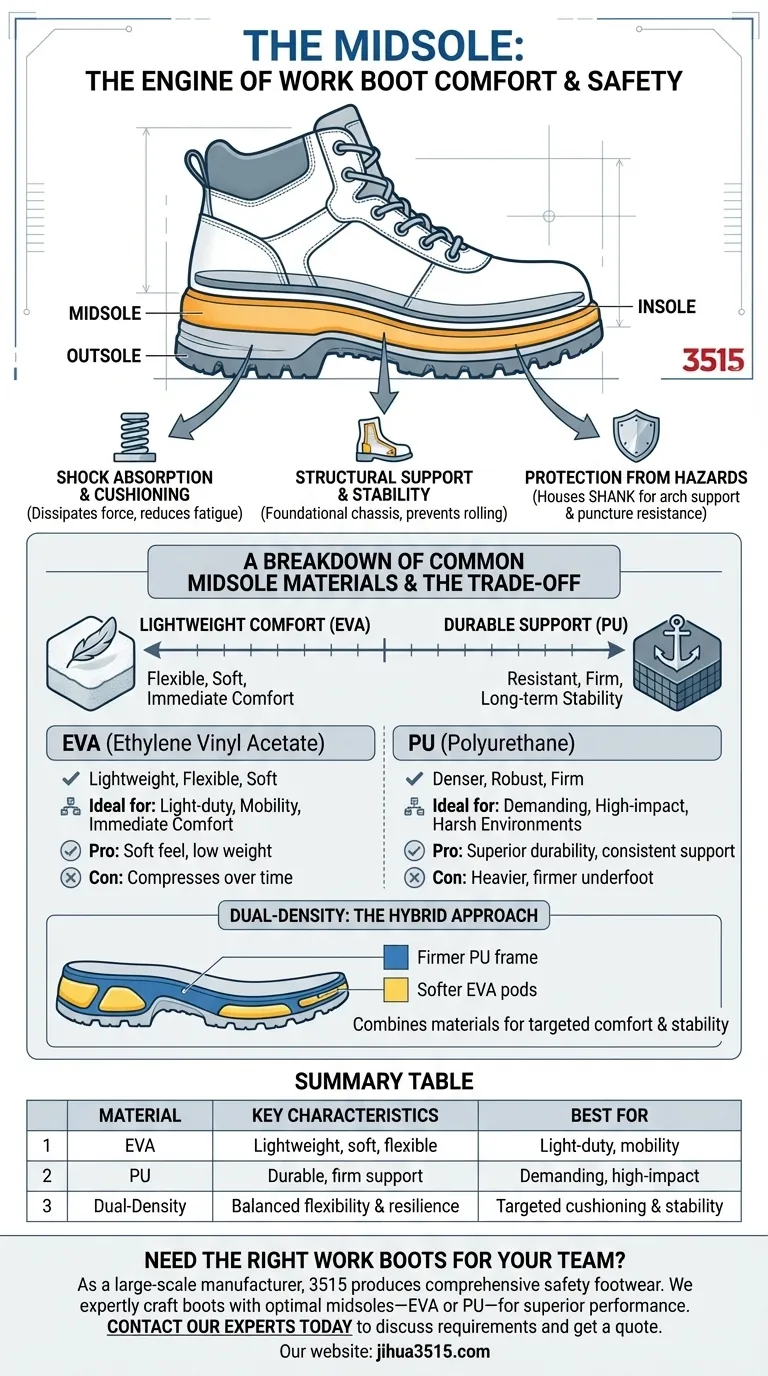
In a work boot, the midsole is the primary engine for comfort and safety. Located between the outsole that touches the ground and the insole your foot rests on, its core functions are to provide cushioning, absorb shock from hard surfaces, and offer structural support. The most common materials used for this critical component are Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) and Polyurethane (PU).
The choice of a work boot's midsole material presents a fundamental trade-off. You are essentially choosing between the lightweight, immediate comfort of EVA and the superior durability and long-term support of Polyurethane (PU).

The Midsole's Critical Functions
A work boot's performance is largely defined by this unseen layer. It dictates how the boot feels after hours of standing and how it protects your body from repetitive impact.
Shock Absorption and Cushioning
The midsole's main job is to dissipate the force generated every time your foot hits the ground. This reduces stress not just on your feet, but also on your ankles, knees, and back, preventing fatigue over a long workday.
Structural Support and Stability
This layer forms the foundational chassis of the boot. It provides the stability needed to prevent your foot from rolling and ensures the boot maintains its shape under heavy loads and on uneven terrain.
Protection from Hazards
While not the material itself, the midsole often houses a shank—a rigid piece of steel, composite, or nylon. This component adds arch support and provides crucial protection against puncture hazards from below.
A Breakdown of Common Midsole Materials
The material used in the midsole directly impacts the boot's weight, comfort, and lifespan. The two dominant choices, EVA and PU, have distinct properties.
EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate): The Lightweight Comfort Choice
EVA is a foam-like polymer known for being extremely lightweight, flexible, and soft. This makes it an excellent material for cushioning and immediate, out-of-the-box comfort.
It is often used in lighter-duty work boots or tactical boots where mobility and minimizing weight are top priorities.
Polyurethane (PU): The Durable Workhorse
PU is a denser and more robust polymer than EVA. Boots with PU midsoles are generally heavier but offer significantly better resistance to compression, impact, and chemical breakdown.
This material provides a firmer, more stable foundation that will not "pack out" or flatten as quickly as EVA, making it ideal for demanding, high-impact work environments.
Dual-Density: The Hybrid Approach
Some manufacturers combine materials to achieve specific goals. A dual-density midsole might use a firmer PU frame for stability and durability, with a softer pod of EVA placed in the heel or forefoot for targeted cushioning.
Understanding the Trade-offs: EVA vs. PU
Choosing the right boot means understanding the compromises inherent in each material. No single material is universally superior; the best choice depends entirely on your work environment and physical needs.
Comfort and Weight
EVA provides a softer, more "athletic shoe" feel and keeps the boot's overall weight down. This is an advantage for workers who cover long distances on foot.
PU feels firmer underfoot and adds weight, but its support is more consistent over the life of the boot.
Durability and Lifespan
PU is the clear winner for durability. It can withstand years of compression and abuse without degrading, making it a better long-term investment for harsh job sites.
EVA will compress and break down over time, losing its cushioning properties much faster than PU. This is the primary reason boots with EVA midsoles often feel "flat" after several months of hard use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Work
Select a midsole based on the primary demands of your job.
- If your primary focus is mobility and all-day comfort on flat surfaces: Choose an EVA midsole for its superior lightweight cushioning.
- If your primary focus is durability and support in harsh conditions: Choose a Polyurethane (PU) midsole for its long-lasting resistance to compression and impact.
- If you need a balance of targeted flexibility and rugged resilience: Look for boots with a dual-density midsole that leverages both materials.
Understanding this single component empowers you to choose a boot based on its performance core, not just its exterior.
Summary Table:
| Midsole Material | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) | Lightweight, soft cushioning, flexible | Light-duty work, mobility, immediate comfort |
| PU (Polyurethane) | Durable, firm support, long-lasting | Demanding, high-impact environments |
| Dual-Density (Hybrid) | Combines stability (PU) with targeted cushioning (EVA) | Balance of flexibility and resilience |
Need the right work boots for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We expertly craft boots with the optimal midsole—whether it's lightweight EVA for comfort or rugged PU for durability—to ensure superior performance and protection for your workforce.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
People Also Ask
- How have engineer boots influenced women's fashion? A Symbol of Rugged, Androgynous Style
- Why are shock-absorbing insoles important in firefighter boots? Enhance Safety & Reduce Fatigue
- What ergonomic features contribute to comfortable work boots? The Key to All-Day Comfort & Reduced Fatigue
- What features should work boots have for cold or hot working conditions? A Guide to Temperature-Specific Safety
- What are the benefits of rubber boots for farm work? Unbeatable Protection in Wet & Muddy Conditions
- Why are composite toe work boots better for extreme weather? Insulate Against Heat and Cold
- How can you freshen smelly work boots? A Permanent Guide to Eliminating Odor
- How do work boots help prevent slips, trips, and falls? Engineered Outsoles for Maximum Grip



















