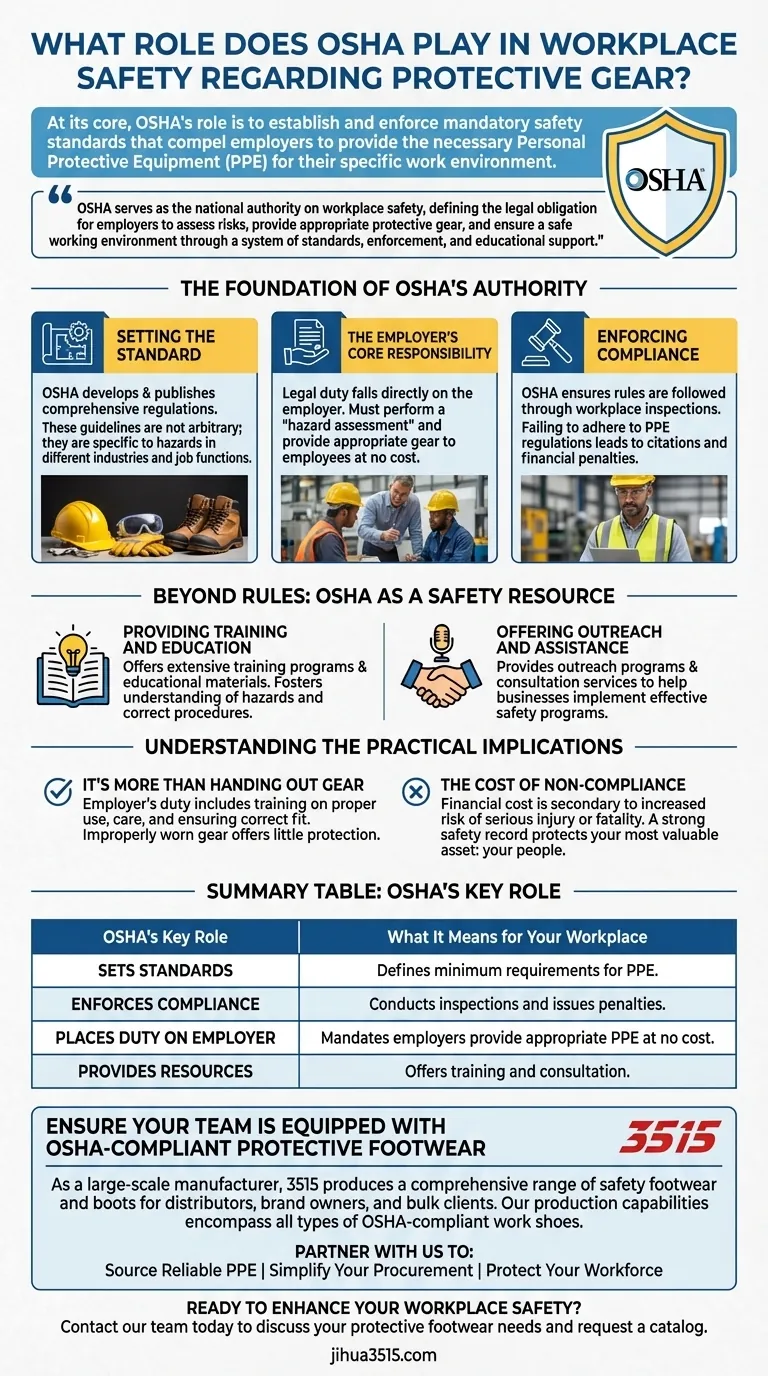
At its core, OSHA's role is to establish and enforce mandatory safety standards that compel employers to provide the necessary Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for their specific work environment. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets these baseline requirements to ensure every worker is protected from identifiable workplace hazards.
OSHA serves as the national authority on workplace safety, defining the legal obligation for employers to assess risks, provide appropriate protective gear, and ensure a safe working environment through a system of standards, enforcement, and educational support.

The Foundation of OSHA's Authority
OSHA's influence on protective gear is built on three key pillars: setting standards, enforcing them, and placing the primary responsibility on the employer. This framework is designed to move safety from a suggestion to a non-negotiable requirement.
Setting the Standard
OSHA develops and publishes comprehensive regulations that detail the minimum requirements for PPE. These standards cover a wide range of equipment, from safety footwear and hard hats to respirators and eye protection.
These guidelines are not arbitrary; they are specific to the hazards present in different industries and job functions.
The Employer's Core Responsibility
Under OSHA regulations, the legal duty to provide a safe workplace falls directly on the employer. This includes performing a "hazard assessment" to identify the specific risks that require PPE.
Once hazards are identified, the employer must select and provide the appropriate gear to employees at no cost to them.
Enforcing Compliance
OSHA ensures these rules are followed through workplace inspections. If an employer fails to adhere to PPE regulations, OSHA has the authority to issue citations and financial penalties.
This enforcement power gives weight to the standards, creating a strong incentive for companies to prioritize safety and compliance.
Beyond Rules: OSHA as a Safety Resource
While known for enforcement, a significant part of OSHA's mission is to proactively help workplaces become safer. The agency is not solely punitive; it also serves as a vital educational partner.
Providing Training and Education
OSHA offers extensive training programs and educational materials. These resources help both employers and employees understand specific hazards and the correct procedures for using protective gear.
This focus on education empowers workers to take an active role in their own safety.
Offering Outreach and Assistance
The agency provides outreach programs and consultation services, often for free, to help businesses—especially small businesses—understand their obligations and implement effective safety programs.
This assistance helps companies comply with the law before an accident or inspection occurs.
Understanding the Practical Implications
Simply knowing OSHA sets rules is not enough. Understanding the implications of their role is critical for creating a truly safe culture.
It's More Than Handing Out Gear
An employer's duty does not end with distributing equipment. They must also train employees on how to properly use and care for their PPE and ensure it fits correctly.
Protective gear that is worn improperly offers little to no protection and can create a false sense of security.
The Cost of Non-Compliance
Failing to follow OSHA standards can lead to significant penalties, but the financial cost is often secondary. The true cost of non-compliance is the increased risk of serious injury or fatality in the workplace.
A strong safety record is not just about avoiding fines; it is about protecting your most valuable asset: your people.
How This Applies to Your Workplace
Understanding OSHA's role allows you to take clear, decisive action, whether you are managing a team or working on the front lines.
- If you are an employer: Your responsibility is to actively assess workplace hazards, provide the correct and compliant PPE, and train your team on its proper use.
- If you are an employee: You have the right to receive appropriate protective gear and the necessary training, and you have a responsibility to use it correctly as instructed.
Ultimately, OSHA provides the essential framework that holds employers accountable for creating a fundamentally safe work environment.
Summary Table:
| OSHA's Key Role | What It Means for Your Workplace |
|---|---|
| Sets Standards | Defines the minimum requirements for PPE like safety footwear and hard hats. |
| Enforces Compliance | Conducts inspections and issues penalties for non-compliance. |
| Places Duty on Employer | Mandates employers provide appropriate PPE at no cost to employees. |
| Provides Resources | Offers training and consultation to help businesses implement safety programs. |
Ensure Your Team is Equipped with OSHA-Compliant Protective Footwear
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of OSHA-compliant work shoes, ensuring your workforce is protected from identified hazards.
Partner with us to:
- Source Reliable PPE: Access a wide range of durable, compliant safety footwear.
- Simplify Your Procurement: Streamline your supply chain with a trusted manufacturer.
- Protect Your Workforce: Equip your team with gear that meets OSHA standards.
Ready to enhance your workplace safety? Contact our team today to discuss your protective footwear needs and request a catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Wholesale Durable Breathable Safety Boots Custom OEM Manufacturer
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- How do industrial safety shoes provide protection for personnel? Safeguard Your Team from Heavy Crane Hazards
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture
- What are the primary protective functions of professional Safety Boots within the automotive maintenance process?
- How do professional construction boots improve operational efficiency? Boost Site Productivity with Advanced Footwear



















