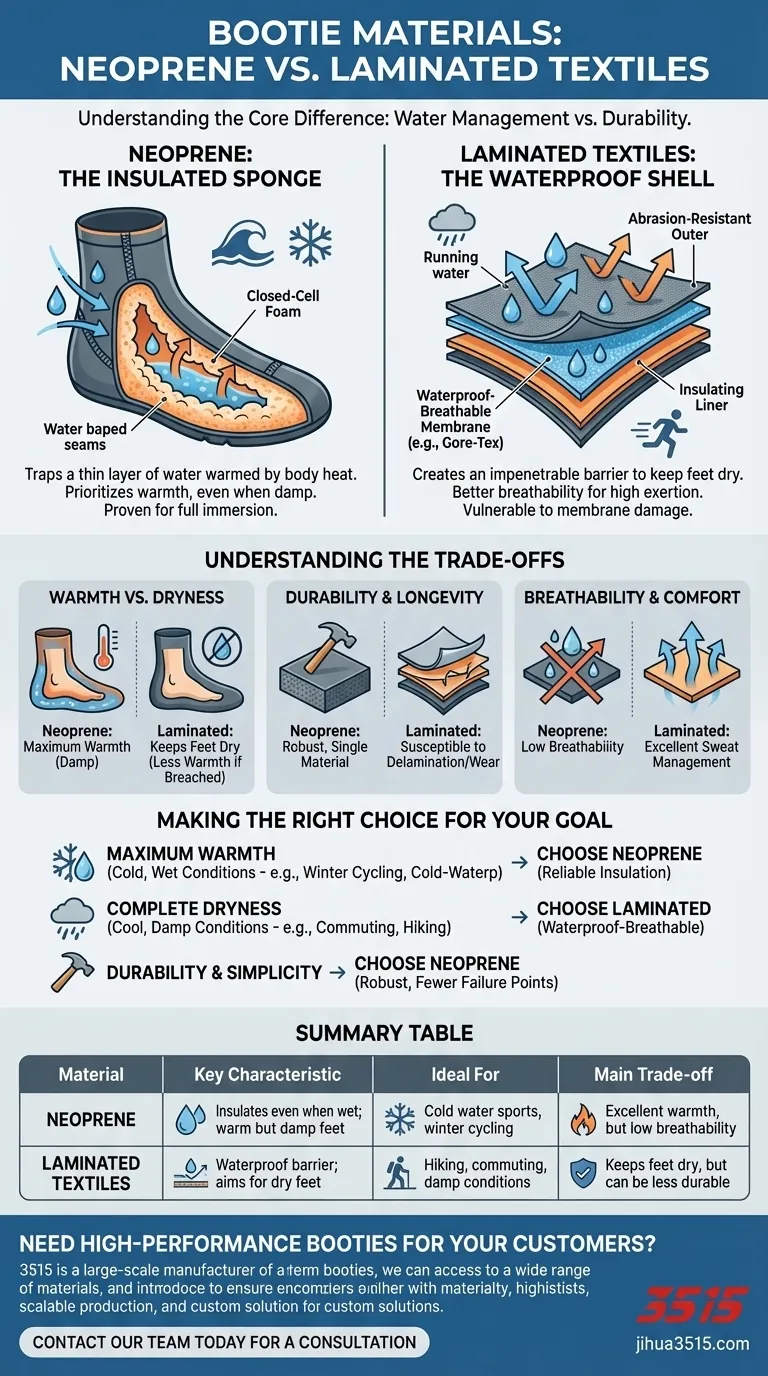
At their core, booties are typically constructed from either neoprene or laminated textiles. Neoprene is a synthetic rubber known for absorbing some water but retaining excellent insulation, making it ideal for wet and cold conditions. Laminated materials, in contrast, feature a waterproof outer layer bonded to an insulating inner layer, designed to keep water out entirely.
The choice between bootie materials is a direct trade-off between water management and durability. Neoprene excels at providing warmth even when wet, while laminated materials aim for complete water repellency, often at the cost of long-term wear resistance.

The Two Primary Material Philosophies
The fundamental difference in bootie construction comes down to how each material handles water. This choice dictates the bootie's performance, feel, and ideal use case.
Neoprene: The Insulated Sponge
Neoprene is a closed-cell foam that traps nitrogen gas bubbles, providing exceptional insulation. It functions like a wetsuit for your feet.
While it is technically waterproof, water inevitably enters at the seams and openings. The material then traps a thin layer of this water, which your body heat warms up, creating an effective thermal barrier.
This approach means your feet will get damp, but they will stay warm. It's a proven, reliable material, especially for activities involving full immersion.
Laminated Textiles: The Waterproof Shell
Laminated materials work by bonding multiple layers together. This typically includes a tough, abrasion-resistant outer fabric, a waterproof-breathable membrane like Gore-Tex or OutDry, and a soft, insulating inner liner.
The goal is to create an impenetrable barrier that stops external water from ever reaching your foot, keeping it completely dry.
These materials often offer better breathability than thick neoprene, allowing sweat vapor to escape. This can be a significant advantage for comfort during high-exertion activities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither material is universally superior. The right choice depends entirely on your activity, the conditions you face, and your personal priorities.
Warmth vs. Dryness
Neoprene prioritizes warmth above all else, even if it means your feet get damp. It is exceptionally reliable in very cold water.
Laminated textiles prioritize keeping your feet dry. While the inner insulation provides warmth, a breach in the waterproof membrane can lead to cold, wet feet much faster than with neoprene.
Durability and Longevity
Neoprene is a single, robust material that is generally very durable and resistant to abrasion. It can withstand significant abuse.
Laminated materials, with their multiple bonded layers, can be more susceptible to delamination or wear over time, especially at flex points. The waterproof membrane can also be punctured, compromising its primary function.
Breathability and Comfort
High-end laminated materials with breathable membranes (like Gore-Tex) offer a significant advantage in managing sweat. This makes them more comfortable for long-duration or high-intensity activities where your feet might sweat regardless of external conditions.
Neoprene offers very little breathability. It is designed for insulation in wet environments, not for wicking internal moisture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your intended activity is the most important factor when selecting a bootie material.
- If your primary focus is maximum warmth in very cold, wet conditions (e.g., winter cycling, cold-water paddling): Choose neoprene for its reliable insulation, even when your feet are damp.
- If your primary focus is staying completely dry in cool, damp, or rainy conditions (e.g., commuting, hiking): Opt for a high-quality laminated material with a waterproof-breathable membrane.
- If your primary focus is durability and simplicity: Neoprene is often the more robust and straightforward choice with fewer points of failure.
Ultimately, understanding how each material manages water and heat is the key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Characteristic | Ideal For | Main Trade-off |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neoprene | Insulates even when wet; warm but damp feet | Cold water sports, winter cycling | Excellent warmth, but low breathability |
| Laminated Textiles | Waterproof barrier; aims for dry feet | Hiking, commuting, damp conditions | Keeps feet dry, but can be less durable |
Need High-Performance Booties for Your Customers?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether your market demands the reliable warmth of neoprene or the advanced dryness of laminated textiles, our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots.
Partner with us to:
- Access a wide range of materials and construction techniques.
- Benefit from scalable production to meet your volume needs.
- Develop custom solutions tailored to your specific market.
Let's discuss your next bootie line. Contact our team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Breathable Training Shoes Custom Athletic Footwear Manufacturer
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Durable & Breathable Training Shoes for Custom Brands
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of breathable mesh in shoe design? Enhance Comfort and Performance
- Does more ground contact area mean better support? Unlock the Secrets of Stable Footwear
- How do athletic shoes with non-slip features differ from regular ones? Discover the Grip Advantage
- What are the features of cross training shoes? Master Versatile Performance for Your Workouts
- What materials are best for athletic activities in warm climates? Stay Cool with Moisture-Wicking Fabrics



















