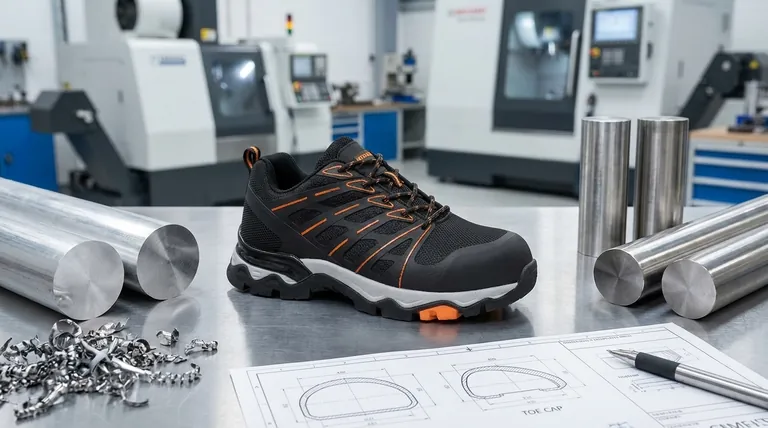
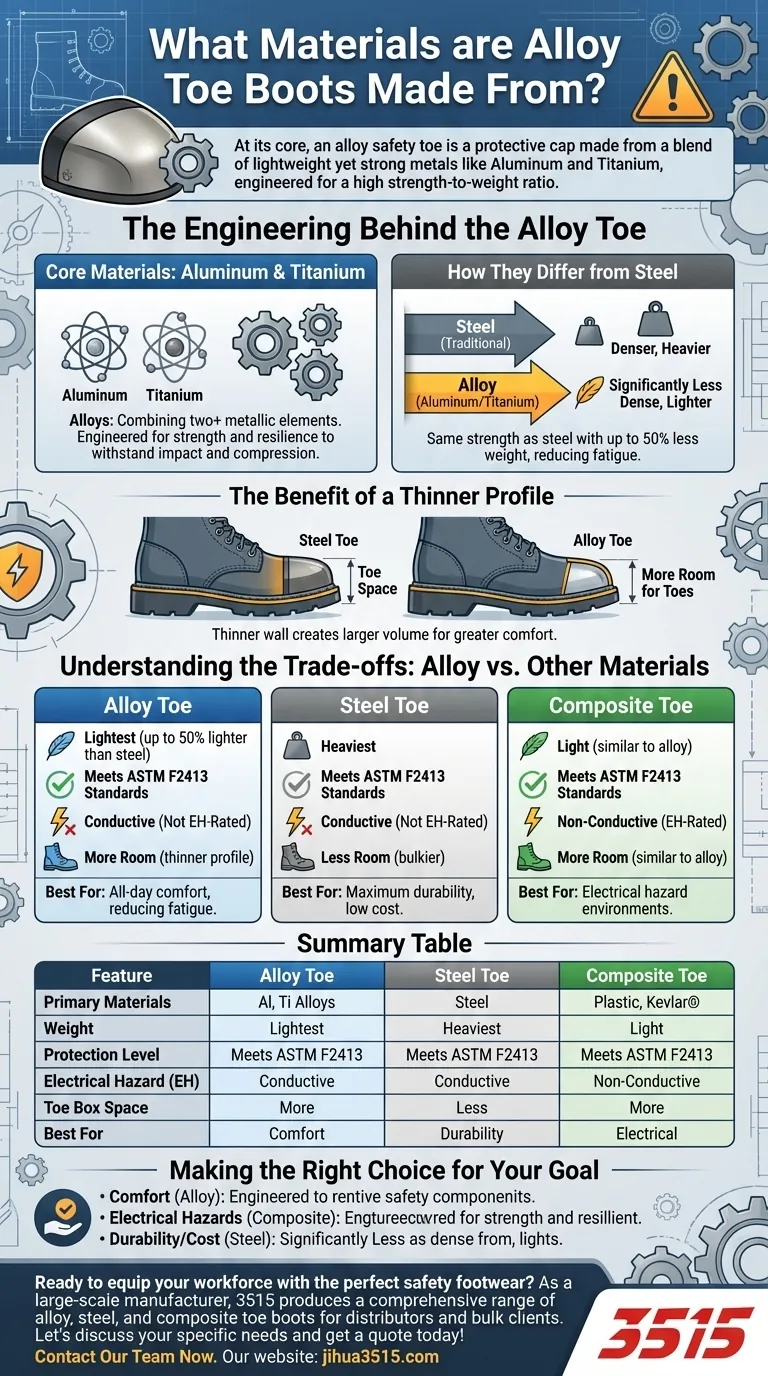
At its core, an alloy safety toe is a protective cap made from a blend of lightweight yet strong metals. The most common materials used are aluminum and titanium, which are specifically chosen for their high strength-to-weight ratio compared to traditional steel.
While often compared to steel, the true value of an alloy toe lies in its ability to meet the same rigorous safety standards with less material and less weight, directly translating to more room for your toes and greater comfort throughout the workday.

The Engineering Behind the Alloy Toe
To understand why alloy toes are a popular choice, it's essential to look at the specific materials used and how they compare to the traditional alternative: steel.
Core Materials: Aluminum & Titanium
The term "alloy" simply means a metal made by combining two or more metallic elements. In safety footwear, this almost always refers to alloys based on aluminum or titanium.
These metals are engineered to be exceptionally strong and resilient, allowing them to withstand significant impacts and compression forces.
How They Differ from Steel
The primary difference is density. Both aluminum and titanium are significantly less dense than steel.
This means a protective cap made from an alloy can be just as strong as a steel cap but will be noticeably lighter. This reduction in weight at the very end of your foot reduces fatigue over long shifts.
The Benefit of a Thinner Profile
Because these alloys are so strong, the protective cap can be manufactured with a thinner wall than an equivalent steel toe cap.
This seemingly small difference creates a larger volume inside the toe box, providing more room for your toes to rest comfortably without sacrificing certified protection.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Alloy vs. Other Materials
The alloy toe cap is only one component of a work boot, but its material directly impacts your safety and comfort. Choosing the right one depends on balancing key factors.
Weight and All-Day Comfort
This is the alloy toe's greatest advantage. Being up to 50% lighter than steel, alloy toes significantly reduce the boot's overall weight.
This leads to less strain on your legs and feet, which is a critical factor for anyone who is on their feet for extended periods. Composite toes are also extremely lightweight.
Certified Protection Level
Both alloy toe and steel toe boots must meet the same ASTM F2413 safety standards for impact and compression resistance.
While steel is denser and may have a higher ultimate breaking point in extreme scenarios, for all certified purposes, an alloy toe provides an equivalent and approved level of protection for your toes.
Electrical Hazard (EH) Concerns
This is a crucial distinction. As metals, both steel and alloy toes are conductive.
If your work involves a risk of contact with live electrical circuits, you should always choose a boot with a composite toe, which is non-metallic and non-conductive, and carries a specific Electrical Hazard (EH) rating.
Toe Box Volume and Fit
The thinner profile of alloy toes provides a more spacious and comfortable fit compared to the bulkier nature of steel toes.
For individuals with wider feet, this extra room can be the deciding factor in preventing rubbing and discomfort.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right safety toe is a functional decision based entirely on your work environment and comfort needs.
- If your primary focus is comfort and reducing fatigue: An alloy toe boot is an excellent choice due to its significantly lower weight.
- If your primary focus is safety around electrical hazards: You must choose a non-metallic composite toe boot that is explicitly EH-rated.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability at the lowest cost: Steel toe remains the traditional, time-tested, and often most budget-friendly option.
Ultimately, understanding the material science behind your safety toe empowers you to choose the boot that best serves your protection and comfort.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Alloy Toe | Steel Toe | Composite Toe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Materials | Aluminum, Titanium Alloys | Steel | Plastic, Kevlar®, Carbon Fiber |
| Weight | Lightest (up to 50% lighter than steel) | Heaviest | Light (similar to alloy) |
| Protection Level | Meets ASTM F2413 Standards | Meets ASTM F2413 Standards | Meets ASTM F2413 Standards |
| Electrical Hazard (EH) | Conductive (Not EH-Rated) | Conductive (Not EH-Rated) | Non-Conductive (EH-Rated) |
| Toe Box Space | More room (thinner profile) | Less room (bulkier) | More room (similar to alloy) |
| Best For | All-day comfort, reducing fatigue | Maximum durability, low cost | Electrical hazard environments |
Ready to equip your workforce with the perfect safety footwear?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of alloy toe, steel toe, and composite toe boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities ensure you get the ideal combination of certified safety, superior comfort, and competitive pricing.
Let's discuss your specific needs and get a quote today!
Contact Our Team Now to find the right safety solution for your customers.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Wholesale Anti-Smash & Puncture-Proof Safety Shoes Custom Manufacturing for Brands
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
People Also Ask
- How does the structural design of industrial-grade safety shoes provide protection? Engineering Foot Health at Work
- Why can metal protective toecaps become a risk factor for dorsal foot ulcers? Learn to Prevent Pressure Point Injuries
- What protective functions do safety shoes provide in construction safety? Maximize Site Safety and Reduce Downtime
- What are the requirements for a protective toe cap? Meet ASTM F2413 Standards for Maximum Safety
- What role do steel-toe safety shoes play in high-rise construction? Essential PPE for Vertical Build Security



















