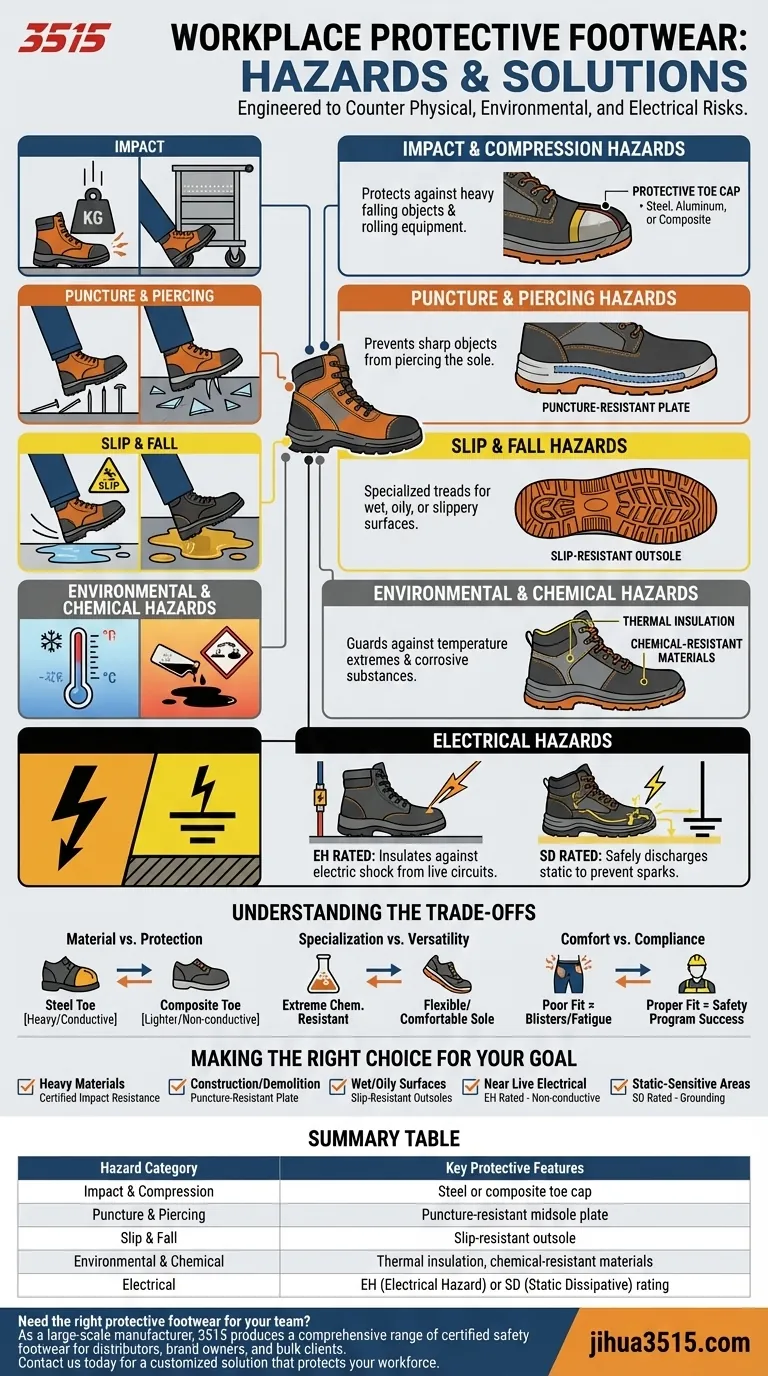
Workplace protective footwear is engineered to counter a precise set of physical, environmental, and electrical hazards. This essential equipment serves as a critical barrier, protecting workers from common dangers such as falling or rolling objects, sharp items that can pierce the sole, and wet or slippery surfaces. Specialized designs also guard against temperature extremes, corrosive chemicals, and distinct electrical risks like static discharge or electric shock.
Effective foot protection is not about a single "steel-toed boot." It requires a deliberate risk assessment to match the footwear's specific design features—such as impact ratings, puncture resistance, and electrical properties—to the actual hazards of a job.

The Core Categories of Foot Protection
To select the right footwear, you must first understand the specific dangers it is designed to mitigate. Each feature corresponds to a distinct category of workplace risk.
Impact and Compression Hazards
This is the most widely recognized function of safety footwear. It protects against injuries from heavy falling objects or from feet being caught under rolling equipment like carts or vehicles.
Footwear designed for this features a protective toe cap, which can be made from steel, aluminum, or non-metallic composite materials.
Puncture and Piercing Hazards
Work environments often have sharp objects on the floor, such as nails, screws, scrap metal, or glass.
To counter this, many safety boots include a puncture-resistant plate positioned in the midsole to prevent sharp objects from piercing the bottom of the foot.
Slip and Fall Hazards
Slips are one of the most common causes of workplace injury. They are frequently caused by water, oil, spills, or other liquids on walking surfaces.
Protective footwear addresses this with specialized slip-resistant outsoles. The tread pattern and rubber compound are engineered to channel fluids away and maintain a strong grip on the floor.
Environmental and Chemical Hazards
Some jobs expose workers to extreme temperatures or corrosive substances that can cause burns or tissue damage.
Footwear for these conditions may include thermal insulation for heat or cold, or be constructed from materials specifically chosen for their resistance to certain corrosive chemicals.
Electrical Hazards
This is a critical and often misunderstood category. The risk is not singular, and the protective footwear is highly specialized for two distinct scenarios.
First, Electrical Hazard (EH) rated footwear is made with non-conductive materials. Its purpose is to protect the wearer from electric shock if they step on a live circuit.
Second, Static Dissipative (SD) footwear is designed to safely discharge the body's static electricity into a grounded floor. This prevents a sudden spark that could damage sensitive electronics or ignite flammable materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single piece of footwear is perfect for every situation. Choosing the right protection involves understanding the inherent trade-offs between different features and materials.
Material vs. Protection
A traditional steel toe offers maximum impact protection but is heavy and conducts temperature. A composite toe is lighter, doesn't conduct heat or electricity, but may be bulkier to achieve the same safety rating.
Specialization vs. Versatility
A boot designed for extreme chemical resistance may not have the most flexible or comfortable sole for an employee who walks several miles a day. Over-specifying features can lead to unnecessary cost and discomfort.
Comfort vs. Compliance
If protective footwear is uncomfortable, workers are less likely to wear it correctly, or at all. Poor fit can cause blisters and fatigue, creating a new hazard and undermining the safety program. Proper fit is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection process must be driven by a clear assessment of the primary risks in your specific work environment.
- If your primary focus is heavy materials or machinery: Prioritize footwear with certified impact and compression resistance (e.g., steel or composite toes).
- If your primary focus is construction or demolition sites: Mandate footwear with built-in, puncture-resistant sole plates to protect against sharp debris.
- If your primary focus is wet or oily surfaces: Select boots specifically tested and rated for their high-traction, slip-resistant outsoles.
- If your primary focus is work near live electrical circuits: You must use non-conductive, Electrical Hazard (EH) rated footwear to insulate against shock.
- If your primary focus is preventing static sparks in sensitive areas: You must use Static Dissipative (SD) footwear to safely ground the wearer.
By methodically matching the footwear's capabilities to your environment's hazards, you ensure true safety and compliance.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Protective Features |
|---|---|
| Impact & Compression | Steel or composite toe cap |
| Puncture & Piercing | Puncture-resistant midsole plate |
| Slip & Fall | Slip-resistant outsole |
| Environmental & Chemical | Thermal insulation, chemical-resistant materials |
| Electrical | EH (Electrical Hazard) or SD (Static Dissipative) rating |
Need the right protective footwear for your team? As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots tailored to your specific hazard requirements—ensuring compliance, comfort, and durability. Contact us today for a customized solution that protects your workforce.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Premium Waterproof High-Cut Industrial Safety Boots for Wholesale and Bulk Orders
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
People Also Ask
- What are the primary protective functions of composite-toe boots? A Guide to Modern Safety Footwear
- Are employers required to provide steel-toe rubber boots at no cost to employees? Yes, under OSHA rules.
- What materials are used for safety toes? Choose Steel, Composite, or Aluminum for Your Work Boots
- What type of footwear is required in meatpacking and poultry plants due to slippery conditions? Essential Safety Boots for Slippery Floors
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management



















