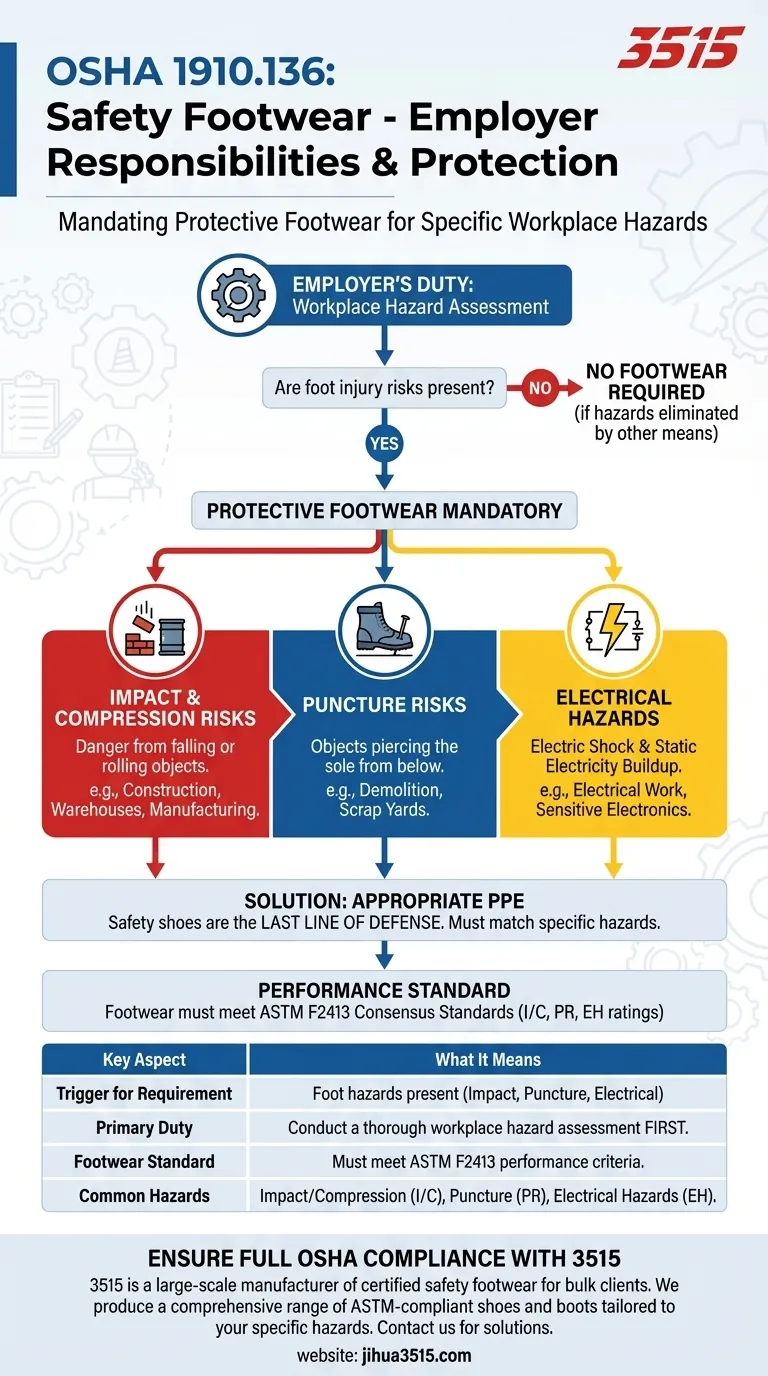
At its core, OSHA's Code of Federal Regulations 1910.136 mandates that employers require employees to wear protective footwear when their work exposes them to specific dangers. The regulation is triggered by the presence of foot injury risks from falling or rolling objects, objects that could pierce the sole of a shoe, or from identified electrical hazards.
The true purpose of OSHA 1910.136 is not simply to require safety shoes, but to compel employers to first conduct a thorough hazard assessment and then provide footwear that specifically protects against the identified risks of the job.

The Core Mandate: When is Protective Footwear Required?
OSHA 1910.136 is a performance-based standard, meaning it activates based on the conditions of the workplace. The responsibility begins with the employer's duty to analyze the work environment.
The Hazard Assessment Imperative
The regulation is not a blanket requirement for all workers. It requires the employer to first assess the workplace to determine if hazards to the feet are present.
Protective footwear is only mandated when these hazards cannot be eliminated through other means, such as engineering or administrative controls. PPE, including safety shoes, is considered the last line of defense.
Impact and Compression Risks
This is the most common trigger for the standard. It refers to any situation where there is a danger of foot injuries from falling or rolling objects.
This includes environments like construction sites, warehouses, loading docks, and manufacturing facilities where heavy materials or equipment are handled.
Puncture Risks
The standard also covers the danger of objects piercing the sole of the shoe from below.
This is a critical consideration in workplaces like demolition sites, scrap yards, or construction zones where nails, sharp metal, or other debris could be stepped on.
Electrical Hazards
Finally, the regulation requires protection when employees face electrical dangers. This is a nuanced category that covers two distinct risks.
It includes protection from open circuits (electric shock) as well as the control of static electricity buildup that could damage sensitive electronics or ignite flammable materials.
Understanding the Employer's Responsibility
Complying with 1910.136 goes beyond simply buying a pair of steel-toed boots. It requires a clear understanding of what "protective footwear" actually means in the context of specific hazards.
A Performance-Based Standard
OSHA tells you what you need to protect against, but it does not list approved brands or models of footwear. The employer is responsible for selecting footwear that is appropriate for the risk.
Deferring to Consensus Standards
To meet the performance requirements, OSHA defers to established national consensus standards, primarily ASTM F2413.
This ASTM standard provides the specific testing and performance criteria for safety footwear, including ratings for impact (I), compression (C), puncture resistance (PR), and electrical hazards (EH). Choosing footwear that meets the appropriate ASTM standard is the accepted method for ensuring compliance with OSHA's rule.
Common Pitfalls and Misinterpretations
Effective implementation requires avoiding common oversights that can undermine a safety program and lead to non-compliance.
Assuming One Shoe Fits All Hazards
A common mistake is providing a single type of safety boot for all employees. A boot rated for impact (steel toe) does not automatically protect against punctures or electrical shock.
The footwear selected must match the specific hazards identified for each job function. An electrician needs EH-rated boots, while a framer needs puncture-resistant soles.
Ignoring Proper Fit and Maintenance
Footwear that is uncomfortable or fits poorly is less likely to be worn consistently by employees, defeating its purpose. Employers should ensure a proper fit.
Furthermore, safety footwear is subject to wear and tear. A boot with a cracked sole or a compressed safety toe may no longer provide adequate protection and must be replaced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Workplace
Your goal dictates your strategy. A successful foot protection program is built on a clear understanding of your environment and a documented process.
- If your primary focus is compliance: Conduct and document a thorough hazard assessment for every job role. This assessment is your justification for the specific type of footwear you require.
- If your primary focus is impact or puncture protection: Select footwear that is clearly marked as meeting ASTM F2413 standards for I/75 C/75 and PR (puncture resistance).
- If your primary focus is mitigating electrical hazards: Carefully distinguish between the need for EH (Electrical Hazard) rated boots for shock protection and SD (Static Dissipating) footwear for controlling static discharge.
Ultimately, a properly managed foot protection program is a foundational element of a safe and productive work environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect of OSHA 1910.136 | What It Means for Employers |
|---|---|
| Trigger for Requirement | Foot hazards present (falling/rolling objects, punctures, electrical risks). |
| Primary Duty | Conduct a workplace hazard assessment before selecting footwear. |
| Footwear Standard | Must meet performance criteria of consensus standards like ASTM F2413. |
| Common Hazards | Impact/Compression (I/C), Puncture (PR), Electrical Hazards (EH). |
Ensure Full OSHA Compliance with the Right Safety Footwear
Navigating OSHA 1910.136 and selecting the correct ASTM F2413-compliant footwear for your specific workplace hazards is critical for protecting your team and maintaining compliance.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots designed to meet the specific demands of various industries, ensuring your workforce has the precise protection they need.
Let us help you build a safer workplace. We can provide the right footwear solutions tailored to the hazards identified in your assessment.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and request a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Leather Safety Boots with Customizable Protective Toe
- Custom Safety Shoe Manufacturer for Wholesale & OEM Brands
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
People Also Ask
- Why are industrial-grade safety shoes mandatory in metallurgical workshops? Essential Protection for Extreme Environments
- Why does the material performance of professional slip-resistant shoes offer superior safety? Hardware vs. Behavior
- How does the shock-absorption technology in safety footwear help reduce injury? Protect Your Skeletal Health Today
- How do industrial safety shoes contribute to safety in sugar production? Ensure High-Altitude Inspection Security
- What is the purpose of requiring subjects to wear anti-slip socks and tight-fitting sportswear? Optimize Sensor Data



















