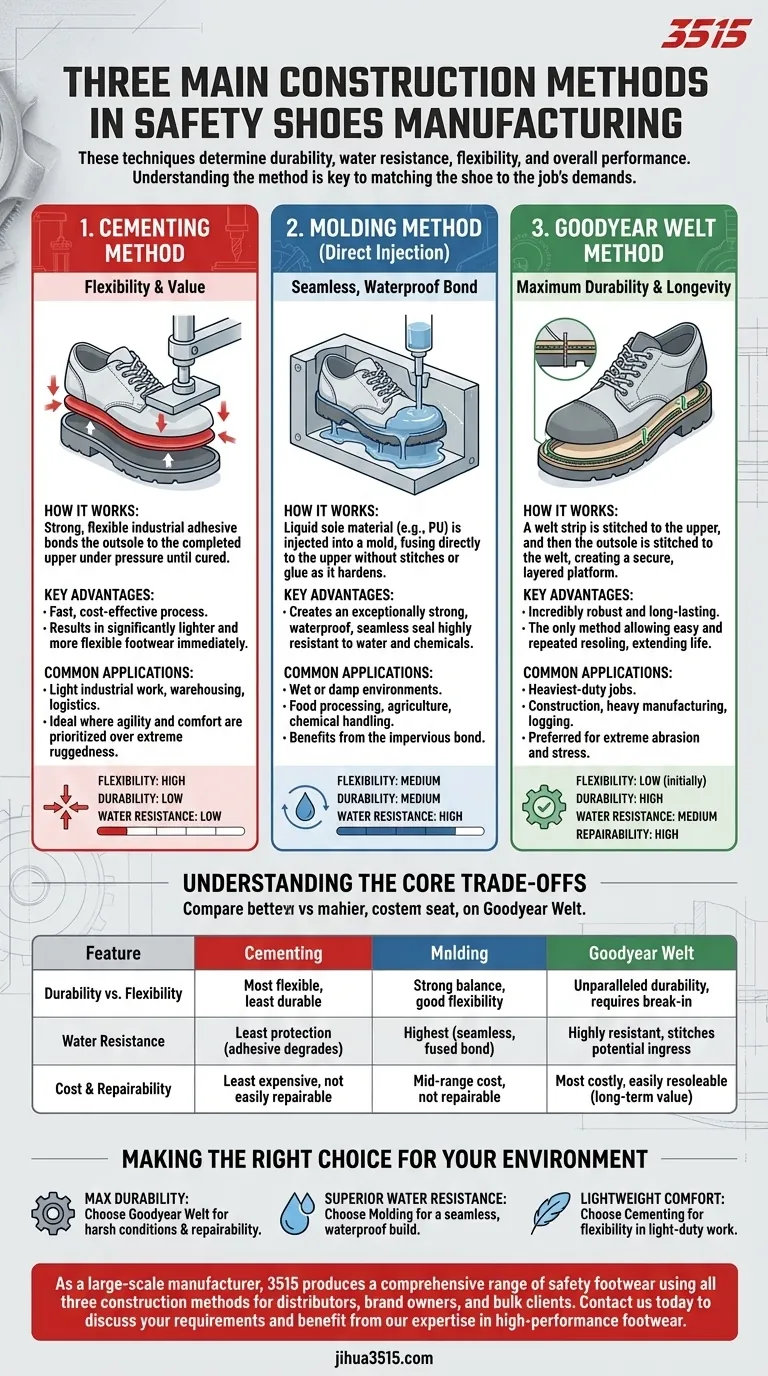
The three primary methods used to construct safety footwear are cementing, molding, and Goodyear welting. These techniques determine how the shoe's upper is attached to its sole, a critical factor that directly impacts its durability, water resistance, flexibility, and overall performance in a professional environment.
The construction method is the architectural foundation of a safety shoe. Far more than a simple manufacturing detail, it dictates the footwear's core strengths and weaknesses, making it the single most important factor to understand when matching a shoe to a specific job's demands.

The Cementing Method: Flexibility and Value
Cementing is a common and modern construction method used across many types of footwear, including safety shoes. It relies on a strong, flexible adhesive to bond the outsole to the upper.
How It Works
The outsole is prepared and a powerful, industrial-grade adhesive is applied. The sole is then pressed firmly onto the completed upper part of the shoe, where it is held under pressure until the bond is fully cured.
Key Advantages
This process is fast and cost-effective, which often translates to a more affordable shoe. Cemented construction results in footwear that is significantly lighter and more flexible right out of the box compared to other methods.
Common Applications
Cemented safety shoes are an excellent choice for light industrial work, warehousing, logistics, and any job where agility and comfort are prioritized over extreme ruggedness.
The Molding Method: A Seamless, Waterproof Bond
Molding, often referred to as direct injection, is a high-tech process that fuses the sole to the upper without the use of stitches or glue.
How It Works
The shoe's upper is placed into a specialized mold. Liquid sole material, typically Polyurethane (PU) or a similar polymer, is then injected into the mold under high pressure. This liquid flows and hardens, forming a permanent, seamless bond directly with the upper.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit is the creation of an exceptionally strong and waterproof seal. With no seams or adhesive to fail, this construction is highly resistant to water and chemical penetration at the sole line.
Common Applications
This method is ideal for wet or damp environments. Industries like food processing, agriculture, and chemical handling benefit greatly from the impervious bond created by injection molding.
The Goodyear Welt Method: Maximum Durability and Longevity
The Goodyear welt is a traditional, labor-intensive method revered for its exceptional strength and durability. It is the gold standard for heavy-duty work boots.
How It Works
A strip of leather or synthetic material, known as the "welt," is first stitched to the shoe's upper. A separate stitch is then used to attach the outsole to this welt. This double-stitching process creates a secure, layered platform.
Key Advantages
This construction is incredibly robust and long-lasting. Critically, it is the only method that allows the shoe to be easily and repeatedly resoled, vastly extending its usable life.
Common Applications
Goodyear welting is the preferred construction for the most demanding jobs. It is the hallmark of premium footwear for construction, heavy manufacturing, logging, and any field where boots face extreme abrasion and stress.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
No single construction method is universally superior; each presents a distinct balance of features. Choosing the right one depends entirely on your work environment and performance requirements.
Durability vs. Flexibility
Goodyear welting offers unparalleled durability but is often stiffer initially and requires a break-in period. Cementing provides the most flexibility and immediate comfort but is the least durable of the three. Molding strikes a strong balance, offering excellent bond strength with good flexibility.
Water Resistance
Molding provides the highest level of water resistance due to its seamless, fused bond. Goodyear welting is also highly water-resistant, though the stitches can be a potential point of ingress over time if not maintained. Cemented shoes offer the least protection, as the adhesive bond can degrade with prolonged exposure to moisture.
Cost and Repairability
Cementing is the least expensive manufacturing process. Molding sits in the mid-range. Goodyear welting is the most costly and time-consuming method, but its unique ability to be resoled can make it more cost-effective over the long term.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Your choice of construction method should be a direct reflection of your daily tasks and workplace hazards.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and longevity: Choose a Goodyear welted shoe, as it is built for repair and can withstand the harshest conditions.
- If your primary focus is superior water resistance and a seamless build: Look for injection-molded construction, which eliminates vulnerable seams and adhesives at the sole.
- If your primary focus is lightweight comfort and affordability for less intense work: A cemented construction offers the most flexibility and is ideal for indoor or light-duty environments.
Ultimately, selecting the right safety shoe begins with understanding the very foundation of its construction.
Summary Table:
| Construction Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Cementing | Lightweight & flexible | Light industrial, warehousing |
| Molding (Direct Injection) | Waterproof & seamless | Wet environments, food processing |
| Goodyear Welt | Maximum durability & resoleable | Heavy-duty construction, logging |
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear using all three construction methods for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether you need the flexibility of cementing, the waterproof seal of molding, or the unmatched durability of Goodyear welting, we have the production capabilities to meet your exact specifications.
Contact us today to discuss your safety shoe requirements and benefit from our expertise in delivering high-performance footwear for any professional environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Premium Sport Style Safety Boots for Bulk Orders
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
People Also Ask
- What are the requirements for oilfield boots? Essential Safety & Durability Features
- What are the advantages of rubber soles for work boots? Unbeatable Grip & Durability
- What is the difference between side-zip and lace-up security guard safety boots? Speed vs. Perfect Fit
- How do some boots combine materials for better performance? Achieve Superior Safety & Comfort
- What were some early hazards that safety footwear addressed? A Guide to Essential Foot Protection



















