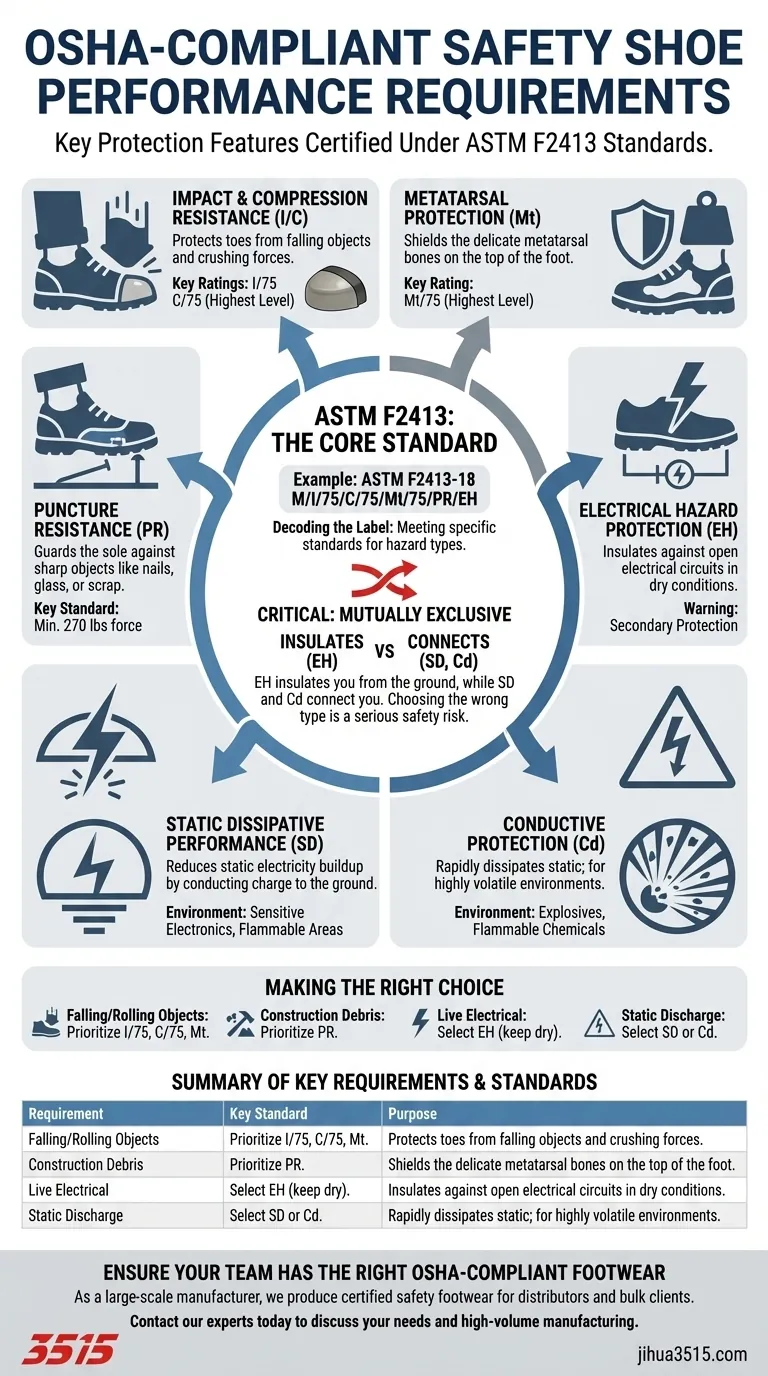
To be OSHA compliant, safety shoes must meet specific performance requirements for impact and compression resistance for the toe, metatarsal protection for the top of the foot, puncture resistance for the sole, and protection against various electrical hazards. OSHA itself does not certify footwear; instead, it requires that safety footwear meets the consensus standards set by organizations like the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM).
The core principle of OSHA compliance for safety footwear is not about a single "OSHA-approved" shoe. It's about conducting a workplace hazard assessment and selecting footwear that is certified under the ASTM F2413 standard to protect against the specific dangers identified in that environment.

Deconstructing the Core Requirements
To make an informed decision, you must understand what each performance standard actually protects against. These requirements are tested and certified by independent labs.
Impact & Compression Resistance (I/C)
This is the most fundamental feature of a safety shoe, protecting the toes from falling objects and crushing forces. The protective toe cap, which can be steel or composite, is rated for its performance.
The ratings are typically 30, 50, or 75, which corresponds to the foot-pounds of impact and pounds of compression it can withstand. A rating of "I/75 C/75" is the highest available level of protection.
Metatarsal Protection (Mt)
This standard covers protection for the top of the foot—the delicate metatarsal bones. This is crucial in environments where objects could drop or roll onto the foot.
Like toe protection, metatarsal guards are tested for their ability to withstand impact, with a rating of up to 75 foot-pounds (Mt/75).
Puncture Resistance (PR)
This feature involves a puncture-resistant plate positioned within the sole of the shoe to protect the foot from sharp objects from below, such as nails, glass, or scrap metal.
A compliant shoe must be able to withstand a minimum of 270 pounds of force to meet this standard.
Electrical Hazard Protection (EH)
EH-rated footwear is designed to insulate the wearer from the ground, reducing the potential for electric shock when stepping on live electrical circuits.
These shoes are a form of secondary protection for workers who may be exposed to open circuits under dry conditions.
Static Dissipative Performance (SD)
SD footwear is constructed to reduce the buildup of excess static electricity by conducting the body's static charge safely to the ground.
This is critical in environments with sensitive electronics or in atmospheres where a static spark could cause a fire or explosion. These shoes must perform within a specific resistance range, typically between 10 and 100 kilo-ohms.
Conductive Protection (Cd)
Conductive footwear is designed to dissipate static electricity from the body into the ground at an even faster rate than SD shoes.
This type of protection is required in highly volatile environments, such as those with explosives or flammable chemicals, where the rapid discharge of static is a primary safety concern.
Understanding the Standards and Trade-offs
Selecting the right shoe involves more than just picking features; it requires understanding how they are certified and the inherent compromises between different types of protection.
The Role of ASTM F2413
This is the dominant standard for performance requirements for protective footwear in the United States. A shoe's label will indicate which parts of the standard it complies with.
For example, a label might read: ASTM F2413-18 M/I/75/C/75/Mt/75/PR/EH. This code tells you the shoe meets the 2018 standard for a male (M), has the highest impact and compression rating, highest metatarsal protection, is puncture-resistant, and is rated for electrical hazards.
Protection Types Are Often Mutually Exclusive
A critical point is that a single shoe cannot provide protection for every type of hazard. You cannot have a shoe that is rated for both Electrical Hazard (EH) and Static Dissipative (SD) or Conductive (Cd).
The functions are opposites. EH footwear insulates you from the ground, while SD and Cd footwear connect you to it. Choosing the wrong type for your environment can create a serious safety risk.
Material Choices Matter
The choice between a steel toe and a composite toe often comes down to environmental needs and comfort. Both must meet the same ASTM impact and compression standards.
However, composite toes are lighter, do not conduct heat or cold, and will not set off metal detectors, making them preferable for certain job sites.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct OSHA-compliant shoe is always the one that matches the specific, identified hazards of your workplace.
- If your primary focus is protection from falling or rolling objects: Ensure the shoe has the highest Impact (I/75) and Compression (C/75) ratings, and consider Metatarsal (Mt) protection if warranted.
- If your primary focus is working around construction debris or scrap: Prioritize a Puncture Resistant (PR) rating to protect against nails and other sharp objects underfoot.
- If your primary focus is working near live electrical circuits: You must select a shoe with an Electrical Hazard (EH) rating and ensure it is kept dry and in good condition.
- If your primary focus is preventing static discharge around sensitive equipment or in flammable areas: A Static Dissipative (SD) or Conductive (Cd) rated shoe is required, depending on the volatility of the environment.
Ultimately, choosing the right safety shoe is a critical step in personal protective equipment, directly linking a thorough hazard assessment to proven, certified protection.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Key Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Impact & Compression (I/C) | ASTM F2413 (e.g., I/75 C/75) | Protects toes from falling/crushing objects. |
| Metatarsal Protection (Mt) | ASTM F2413 (e.g., Mt/75) | Shields the top of the foot from impact. |
| Puncture Resistance (PR) | ASTM F2413 | Guards sole against sharp objects (e.g., nails). |
| Electrical Hazard (EH) | ASTM F2413 | Provides insulation against open electrical circuits. |
| Static Dissipative (SD) | ASTM F2413 | Safely dissipates static charge in sensitive areas. |
| Conductive (Cd) | ASTM F2413 | Rapidly dissipates static in volatile environments. |
Ensure Your Team Has the Right OSHA-Compliant Safety Footwear
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots, designed to meet the exact ASTM F2413 standards your workplace requires.
We help you:
- Source the correct protection based on your hazard assessment.
- Benefit from high-volume manufacturing with consistent quality.
- Get reliable, certified footwear for your entire team.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our experts today to get a quote or learn more about our capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Wholesale Durable Safety Boots | Custom Steel Toe & Puncture-Resistant Manufacturing
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for safety toes? Choose Steel, Composite, or Aluminum for Your Work Boots
- What are the primary protective functions of composite-toe boots? A Guide to Modern Safety Footwear
- What are the differences between steel toe, composite toe, and alloy toe Wellington boots? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job
- What type of footwear is required in meatpacking and poultry plants due to slippery conditions? Essential Safety Boots for Slippery Floors
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture



















