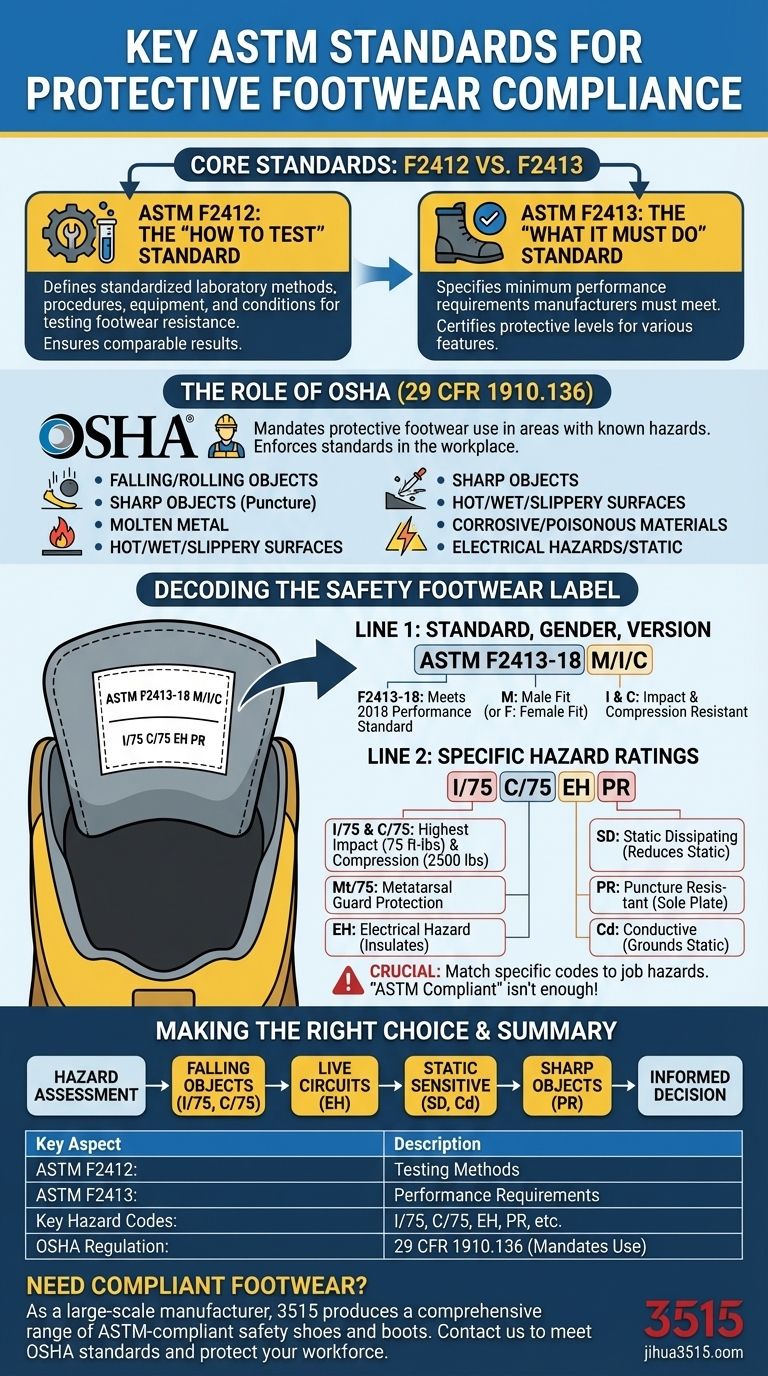
For protective footwear in the United States, the two key standards are ASTM F2412 and ASTM F2413. ASTM F2412 defines the standardized methods for testing footwear resistance to various hazards, while ASTM F2413 specifies the minimum performance requirements that the footwear must meet to be considered protective. Essentially, F2412 is the "how to test," and F2413 is the "what it must do."
True compliance isn't just about finding a boot labeled "ASTM certified." It's about understanding the specific hazard codes on that label and ensuring they directly match the specific risks present in your work environment, as mandated by OSHA.

Decoding the Core Standards: F2412 vs. F2413
Understanding the relationship between these two standards is the first step toward ensuring proper foot protection. They work together but serve distinct purposes.
ASTM F2412: The Standard for Testing
This standard is the rulebook for the laboratory. It outlines the precise procedures, equipment, and conditions required to test the protective qualities of footwear.
It ensures that when a boot is tested for impact resistance in one facility, the results are comparable to those from another. This standard focuses exclusively on the method of measurement.
ASTM F2413: The Standard for Performance
This is the specification that manufacturers build their footwear to meet. It defines the minimum performance levels for various protective features.
When a boot is labeled "ASTM F2413-18," it certifies that it has been tested according to F2412 and meets or exceeds the performance requirements outlined in the 2018 version of the F2413 standard.
The Role of OSHA in Foot Protection
While ASTM sets the standards, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) enforces their use in the workplace.
OSHA's Mandate
OSHA requires employers to ensure their employees use protective footwear when working in areas with known dangers of foot injuries.
The regulation, specifically 29 CFR 1910.136, mandates protection against hazards like falling or rolling objects, items piercing the sole, and electrical hazards.
When Protective Footwear is Required
OSHA identifies several situations where protective footwear is critical. These include work environments involving:
- Heavy objects that could fall or roll onto the foot
- Sharp objects like nails or scrap metal that could puncture the sole
- Molten metal that could splash
- Hot, wet, or slippery surfaces
- Corrosive or poisonous materials
- Live electrical circuits or risks of static discharge
How to Read a Safety Footwear Label
Compliant footwear features a specific label, typically stitched inside the tongue, that provides all the necessary information in a clear format.
The Standard Two-Line Format
The label is organized into two primary lines to quickly communicate its protective qualities.
Line 1: Standard, Gender, and Version
The first line confirms compliance with the core standard. It will read something like: ASTM F2413-18 M/I/C.
- ASTM F2413-18: Certifies the boot meets the 2018 version of the performance standard.
- M or F: Indicates whether the footwear is designed for a Male (M) or Female (F) fit.
- I and C: Confirms the presence of Impact and Compression resistant properties in the toe cap.
Line 2: Specific Hazard Ratings
The second line details the specific hazards the footwear is rated to protect against. This is the most critical information for matching a boot to a job. Key codes include:
- I/75 & C/75: Indicates the toe cap can withstand 75 foot-pounds of impact and 2,500 pounds of compression. This is the highest rating.
- Mt/75: Metatarsal protection. A guard protects the top of the foot from impacts of up to 75 foot-pounds.
- EH: Electrical Hazard. The soles provide secondary protection against accidental contact with live electrical circuits.
- SD: Static Dissipating. The footwear reduces the buildup of static electricity, crucial in sensitive electronics manufacturing or flammable environments.
- PR: Puncture Resistant. A plate is integrated into the sole to protect against sharp objects from below.
- Cd: Conductive. This footwear actively grounds the wearer to dissipate static electricity very quickly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Simply knowing the standards is not enough. Misinterpretations can lead to inadequate protection and non-compliance.
"ASTM Compliant" is Not Enough
A boot can meet the ASTM F2413 standard for impact and compression but offer zero protection against electrical hazards or punctures.
You must look beyond the general compliance statement and verify that the specific codes listed on the second line of the label match the specific hazards of the job.
EH, SD, and Cd Are Not Interchangeable
These three electrical ratings serve very different, and often opposite, purposes.
- EH footwear insulates you from the ground.
- SD and Cd footwear connect you to the ground to discharge static.
- Never wear SD or Cd footwear where EH protection is required.
The Importance of the Version Year
Standards are periodically updated to reflect new technology and safety data. The "-18" in F2413-18 refers to the year 2018.
While older versions may still be in circulation, using footwear that conforms to the latest standard is always the best practice for ensuring maximum safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final selection must be based on a thorough hazard assessment of your specific work environment.
- If your primary focus is protection from falling objects: You need footwear with an Impact (I/75) and Compression (C/75) rating.
- If your primary focus is working near live circuits: You must select footwear specifically rated for Electrical Hazard (EH).
- If your primary focus is preventing static buildup: Look for Static Dissipating (SD) footwear, or Conductive (Cd) for highly sensitive applications.
- If your primary focus is protection from sharp objects underfoot: Ensure the footwear has a Puncture Resistant (PR) designation.
By matching the detailed ASTM F2413 codes to your known risks, you can make an informed decision that ensures true safety and compliance.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM F2412 | Defines the standardized testing methods for footwear resistance to hazards. |
| ASTM F2413 | Specifies the minimum performance requirements footwear must meet. |
| Key Hazard Codes | I/75 (Impact), C/75 (Compression), EH (Electrical Hazard), PR (Puncture Resistant), etc. |
| OSHA Regulation | 29 CFR 1910.136 mandates protective footwear in hazardous work environments. |
Need compliant protective footwear tailored to your specific hazards?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of ASTM-compliant safety shoes and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of protective footwear, ensuring you get the right protection—from impact and compression to electrical hazards and puncture resistance.
Let us help you meet OSHA standards and protect your workforce. Contact our experts today for a consultation to discuss your specific needs and explore our full product catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
People Also Ask
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- Why can metal protective toecaps become a risk factor for dorsal foot ulcers? Learn to Prevent Pressure Point Injuries
- What core protection features do industrial-grade Safety Shoes provide? Key Safety Standards for Infrastructure Sites
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- How do industrial safety shoes provide protection for personnel? Safeguard Your Team from Heavy Crane Hazards



















