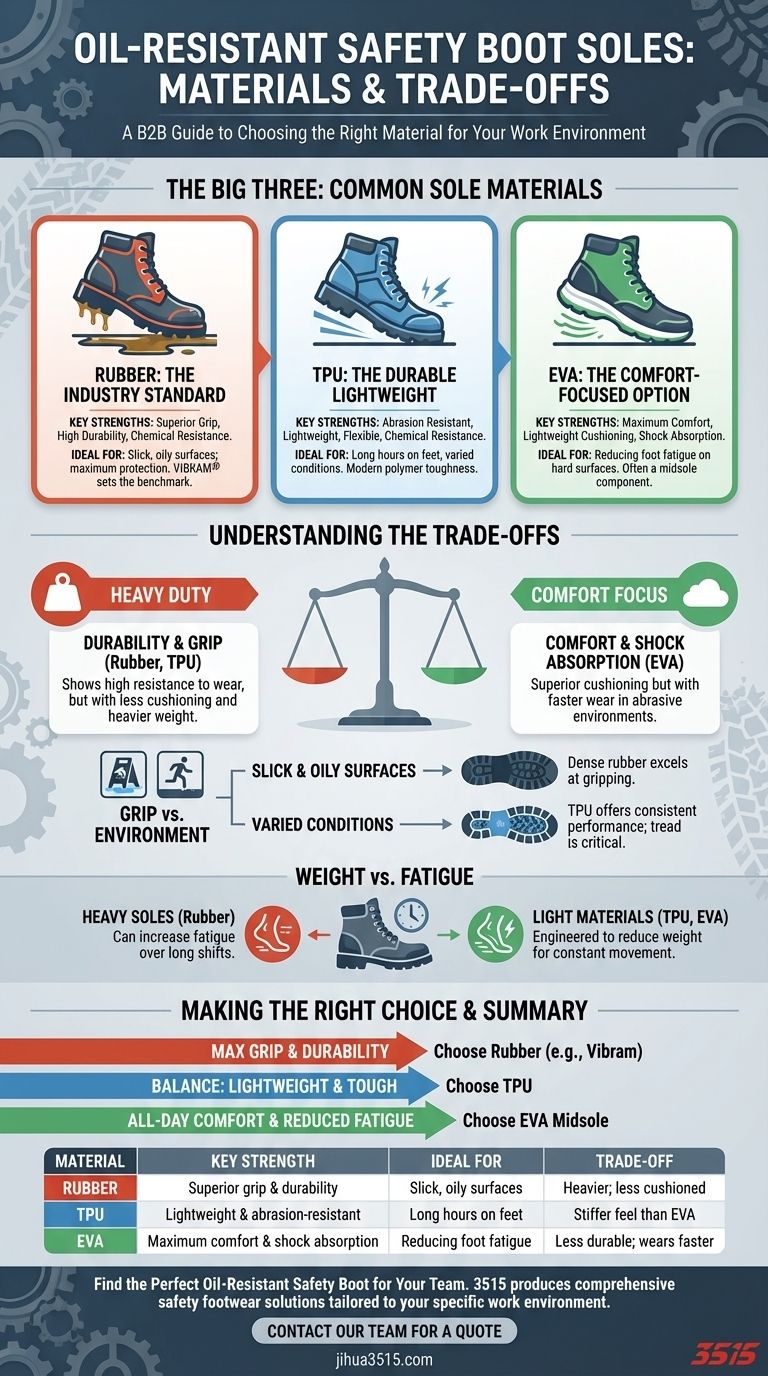
The most common sole materials for oil-resistant safety boots are Rubber, Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA). Each material provides a distinct combination of oil resistance, durability, comfort, and grip tailored for different work environments.
The challenge isn't finding a sole that is simply "oil-resistant," but understanding the trade-offs between each material. Your ideal choice depends entirely on matching the sole's specific strengths—be it rubber's grip, TPU's resilience, or EVA's comfort—to the physical demands of your workplace.

A Closer Look at Oil-Resistant Sole Materials
Each of the primary materials used for oil-resistant soles offers a unique performance profile. Understanding these differences is the key to selecting the right boot.
Rubber: The Industry Standard
Rubber is the most traditional and widely used material for safety boot outsoles. Its formulation provides excellent resistance to oils, acids, and abrasion.
High-performance brands like Vibram use proprietary vulcanized rubber compounds to deliver superior grip and exceptional durability, making them a benchmark for quality.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): The Durable Lightweight
TPU is a modern polymer known for its incredible toughness and resistance to abrasion, oils, and chemicals.
It is significantly lighter and more flexible than traditional rubber, offering a durable yet less fatiguing option for long workdays.
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA): The Comfort-Focused Option
EVA is a foam-like material prized for its lightweight cushioning and shock absorption. It is often used as a midsole component to provide stability and comfort.
While EVA offers toughness and some oil resistance, it typically serves to enhance comfort rather than as the primary outsole material due to its tendency to wear down faster than rubber or TPU.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material requires acknowledging that every benefit comes with a corresponding compromise. There is no single "best" material, only the best material for a specific application.
Durability vs. Comfort
The hardest, most durable materials like dense rubber or TPU often provide less cushioning than softer materials.
Conversely, boots with significant EVA components offer superior comfort and shock absorption but may have a shorter lifespan in highly abrasive environments.
Grip vs. Environment
All three materials are effective, but their performance varies by surface. Dense rubber compounds excel at gripping slick, oily surfaces.
TPU offers a strong, consistent performance across varied conditions, while a boot's tread pattern is just as critical as its material for ensuring stability.
Weight vs. Fatigue
Heavier, thicker rubber soles can provide maximum protection and longevity but may contribute to foot fatigue over a long shift.
Lighter materials like TPU and EVA are specifically engineered to reduce the boot's overall weight, making them ideal for jobs that require constant walking or movement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Your final decision should be guided by the most common challenges you face at work.
- If your primary focus is maximum grip and durability: Choose boots with high-quality, dense rubber outsoles, especially from reputable brands like Vibram.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort and reduced fatigue: Look for soles that incorporate an EVA midsole for superior cushioning on hard surfaces.
- If your primary focus is a balance of lightweight performance and high abrasion resistance: A TPU sole is an excellent all-around choice that won't weigh you down.
Ultimately, selecting the correct sole material is about aligning its specific advantages with the daily demands of your job.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Strength | Ideal For | Trade-off |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Superior grip & durability | Slick, oily surfaces; maximum protection | Heavier; can be less cushioned |
| TPU | Lightweight & abrasion-resistant | Jobs requiring long hours on your feet | Stiffer feel than EVA |
| EVA | Maximum comfort & shock absorption | Reducing foot fatigue on hard surfaces | Less durable; wears faster |
Find the Perfect Oil-Resistant Safety Boot for Your Team
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We have the expertise and production capabilities to deliver the right sole material—be it high-grip rubber, resilient TPU, or comfort-focused EVA—tailored to your specific work environment and safety requirements.
Contact our team today to discuss your needs and get a quote for durable, high-performance safety boots.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Wholesale Customizable Safety Boots Durable & Protective Footwear Manufacturing
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
People Also Ask
- What are the essential protective functions of Safety Shoes? Explore Core Features for High-Risk Work Environments
- What are the primary protective functions of industrial-grade safety shoes? Essential Occupational Safety Guide
- What are the key requirements for ASTM F2413 conforming safety footwear? A Guide to Selecting the Right Protection
- Do yearly updates to ASTM safety standards affect the core protection thresholds? Understanding the Stable Safety Benchmark
- What is the importance of performing failure analysis after bending tests on safety shoe toe cap composite materials? Ensure Uncompromised Safety
- Can firefighter boots be resoled? A Guide to Safe & Cost-Effective Repair
- How do the polarization and gain characteristics of industrial RFID antennas affect the identification of safety shoes?
- Why is high-specification safety footwear essential for protecting workers during waste management processes?



















