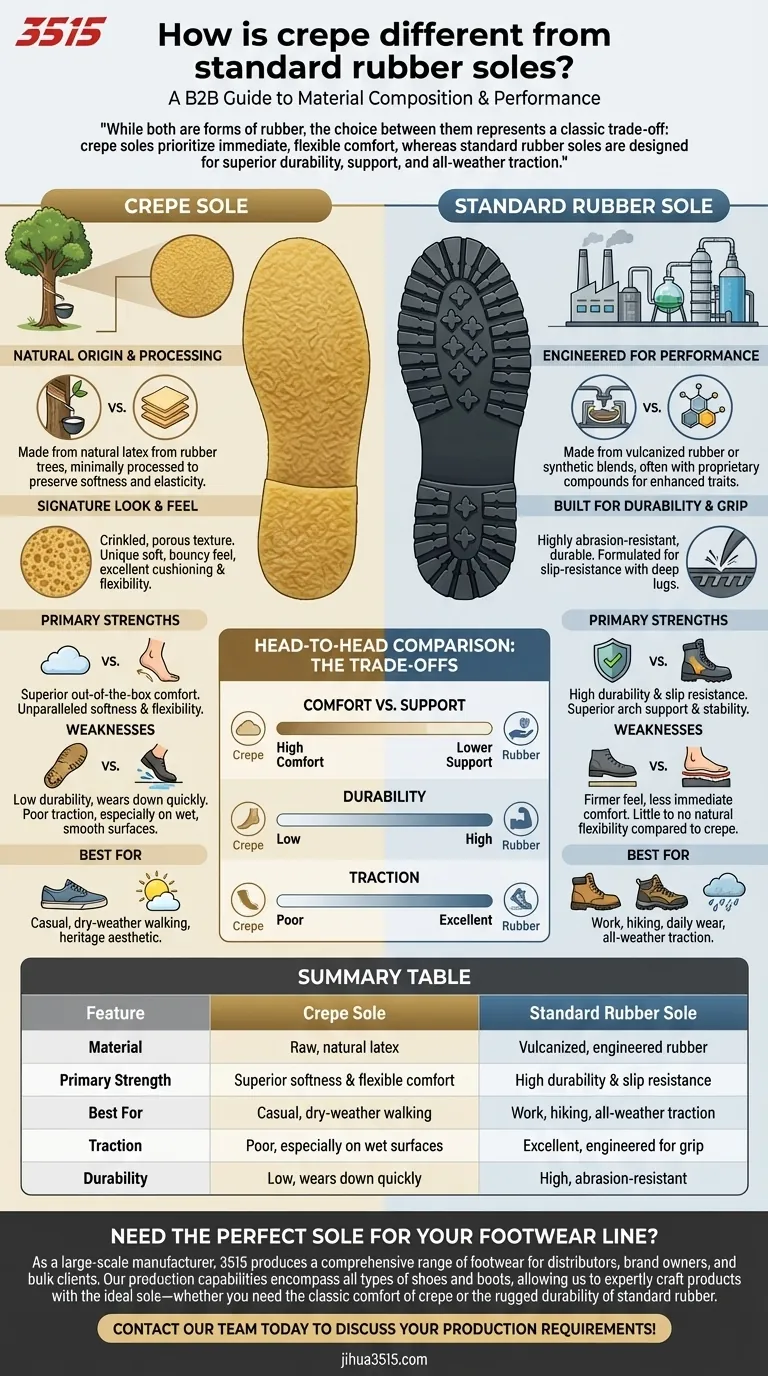
The fundamental difference between crepe and standard rubber soles lies in their material composition and processing. Crepe is a raw, natural rubber prized for its softness and flexibility, while standard rubber is a compounded material engineered for durability and grip. This core distinction dictates their performance in comfort, traction, and longevity.
While both are forms of rubber, the choice between them represents a classic trade-off: crepe soles prioritize immediate, flexible comfort, whereas standard rubber soles are designed for superior durability, support, and all-weather traction.

What Defines a Crepe Sole?
A crepe sole has a unique origin story that directly influences its distinct characteristics. It is one of the most natural forms of footwear soling material available.
A Natural Origin
A crepe sole is made from natural latex, which is tapped from rubber trees. This liquid latex is coagulated and then stretched into thin sheets, which are layered to create the final sole.
This minimal processing is key, as it preserves the rubber's natural softness and elasticity without the addition of hardening chemicals.
Signature Look and Feel
The most recognizable features of a crepe sole are its crinkled, porous texture and its typical yellow-brown, semi-translucent color.
Underfoot, it feels uniquely soft and bouncy, providing excellent cushioning and flexibility that molds to your walking motion.
What Defines a Standard Rubber Sole?
Standard rubber soles are the most common type used in footwear for a reason. They are engineered materials designed to meet specific performance demands.
Engineered for Performance
Unlike the raw nature of crepe, standard rubber soles are typically made from vulcanized rubber or proprietary synthetic blends. This process involves adding chemicals and heat to create a more stable, durable material.
Boot and shoe makers often develop their own proprietary rubber compounds to enhance specific traits like oil resistance, heat resistance, or non-marking properties.
Built for Durability and Grip
The primary benefit of this engineering is a massive increase in durability. Standard rubber is highly abrasion-resistant, meaning it can withstand rough surfaces without wearing down quickly.
It is also formulated to be slip-resistant, often molded with deep lugs and tread patterns that provide reliable traction on wet or uneven terrain.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Choosing between these two materials means understanding their opposing strengths and weaknesses. What makes one great is precisely what the other sacrifices.
Comfort vs. Support
Crepe offers superior out-of-the-box comfort due to its softness and flexibility. However, it provides very little structural or arch support.
Standard rubber is firmer and provides significantly better arch support and stability, which is crucial for long-term wear, especially in work boots or hiking shoes.
Durability
There is no contest here: standard rubber is far more durable. Crepe soles wear down much faster, especially on abrasive surfaces like concrete. They can also become sticky in high heat and tend to darken as they pick up dirt.
Traction
Standard rubber is engineered for grip. Crepe, on the other hand, is known for having poor traction, particularly on wet, smooth surfaces where it can become quite slippery.
Making the Right Choice for Your Footwear
Your decision should be guided entirely by how you intend to use the footwear.
- If your primary focus is maximum comfort for casual, dry-weather walking: Crepe is an excellent choice for its unparalleled softness and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is durability, traction, and support for daily wear or work: A standard rubber sole is the more practical and reliable option.
- If your primary focus is a specific heritage or casual aesthetic: The unique, textured look of a crepe sole is often a key part of the shoe's design.
Ultimately, understanding the core purpose of each material empowers you to select a sole that perfectly matches your needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Crepe Sole | Standard Rubber Sole |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Raw, natural latex | Vulcanized, engineered rubber |
| Primary Strength | Superior softness & flexible comfort | High durability & slip resistance |
| Best For | Casual, dry-weather walking | Work, hiking, all-weather traction |
| Traction | Poor, especially on wet surfaces | Excellent, engineered for grip |
| Durability | Low, wears down quickly | High, abrasion-resistant |
Need the perfect sole for your footwear line?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, allowing us to expertly craft products with the ideal sole—whether you need the classic comfort of crepe or the rugged durability of standard rubber.
Let us help you create footwear that perfectly matches your market's needs. Contact our team today to discuss your production requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Durable Camouflage Canvas Shoes with High-Traction Cleated Rubber Sole
- Durable Canvas Work Shoes with Rubber Lug Sole | Wholesale Manufacturer
- Wholesale Training Shoes with Dial Lacing System Custom OEM Manufacturing
- Wholesale Durable & Breathable Training Shoes for Custom Brands
- Wholesale Modern Comfort Shoes with Dial Closure for Private Label & Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- Which type of sole is better for premium sneakers and why? The Definitive Guide to Rubber Outsoles
- What are the advantages of mesh in athletic shoes? Unlock Peak Performance & Comfort
- What are the features of non-slip athletic sneakers? The Ultimate Guide to Traction & Performance
- Why should we wear rubber soled shoes? Unlock Superior Safety and Durability
- What are the properties of canvas as a shoe material? A Guide to Lightweight Comfort & Style



















