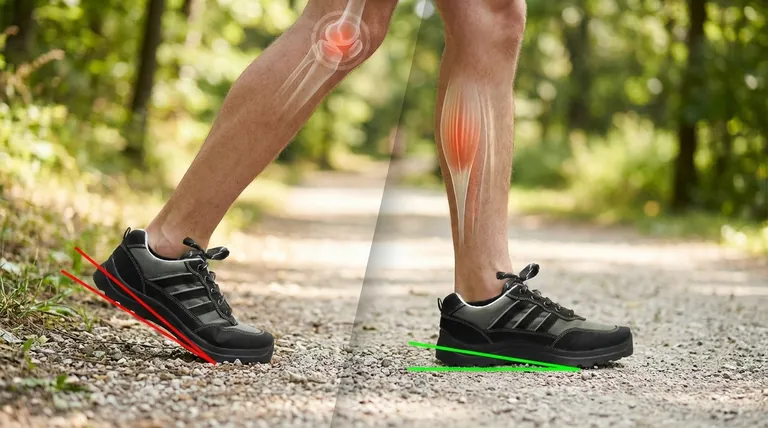
In short, heel drop changes your foot's angle, which directly impacts how force is distributed through your body as you walk. A higher drop reduces the workload on your calves and Achilles tendon by elevating your heel, but it can shift that stress to your knees and hips. A lower drop does the opposite, promoting a more natural, level foot position that may ease knee strain but requires more work from your lower legs.
The central decision in choosing a heel drop is not about finding the "best" shoe, but about understanding a fundamental trade-off: Do you need to protect your calves and Achilles, or do you need to reduce pressure on your knees and promote a more natural foot motion?
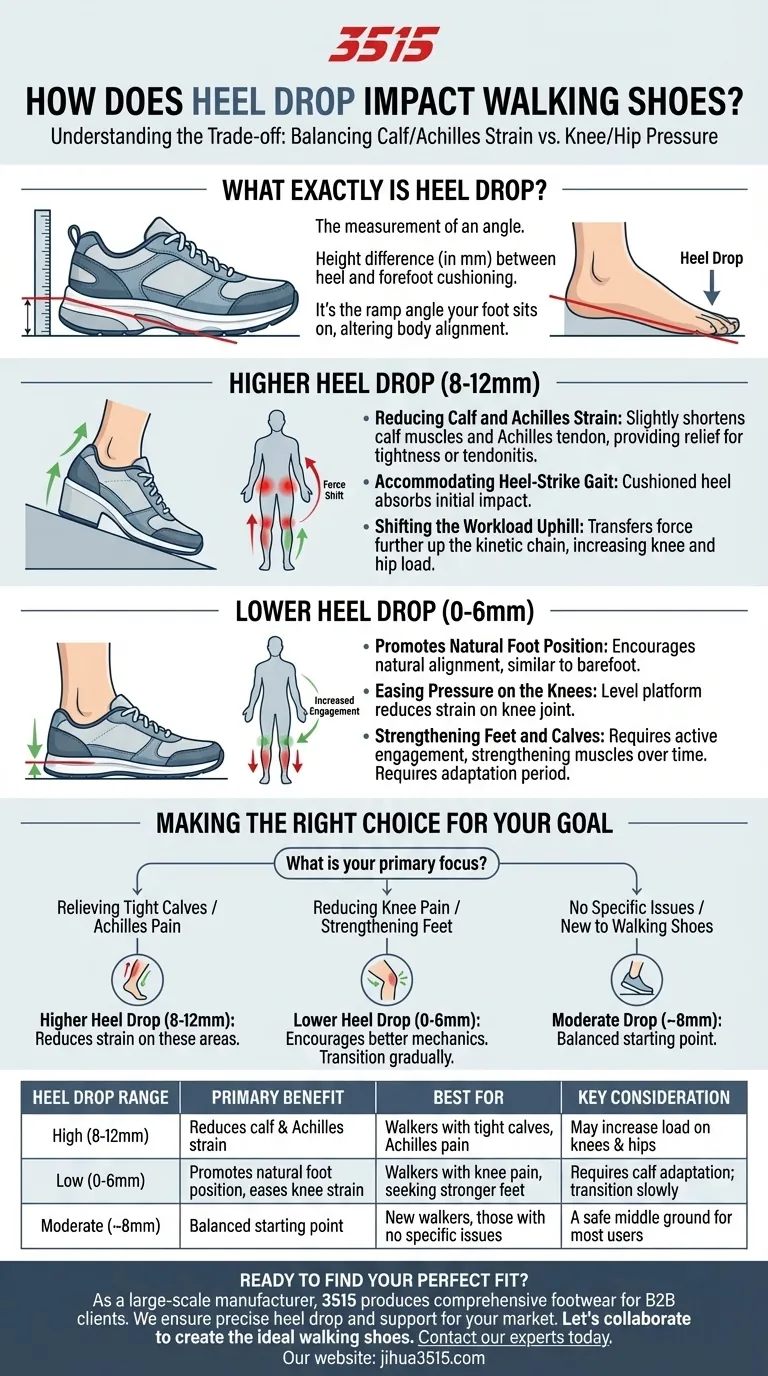
What Exactly is Heel Drop?
The Measurement of an Angle
Heel drop, also known as "offset" or "drop," is simply the height difference between the shoe's heel cushioning and its forefoot cushioning, measured in millimeters (mm).
It is not the total amount of cushioning, but rather the ramp angle your foot sits on inside the shoe.
The Impact on Body Alignment
A higher drop (e.g., 10mm) places your foot on a steeper downward slope, similar to wearing a very low-heeled shoe. A lower or zero drop (0-6mm) keeps your foot nearly parallel to the ground, mimicking your natural barefoot stance.
This seemingly small angle creates a chain reaction, altering the mechanics of your ankle, knee, and hip joints with every step you take.
The Case for Higher Heel Drop (8-12mm)
Reducing Calf and Achilles Strain
Most traditional walking shoes feature a higher drop. Elevating the heel slightly shortens the calf muscles and the Achilles tendon.
This reduced tension can provide significant relief for individuals with tight calves or a history of Achilles tendonitis.
Accommodating a Heel-Strike Gait
The typical walking gait involves landing on your heel first. A higher, more cushioned heel is designed to absorb the initial impact of this common movement pattern.
Shifting the Workload Uphill
The primary benefit of a higher drop is offloading the lower leg. However, that force doesn't disappear—it is transferred further up the kinetic chain.
This means your knees and hips must absorb more of the load, which is a critical factor to consider.
The Case for Lower Heel Drop (0-6mm)
Promoting a Natural Foot Position
A low or zero-drop shoe encourages a more natural alignment, placing your foot in a position similar to being barefoot.
This level platform allows your foot to function and flex without being forced into an artificial angle.
Easing Pressure on the Knees
By leveling the foot and promoting a more balanced posture, lower-drop shoes can help reduce the amount of strain placed directly on the knee joint during your stride.
Strengthening Your Feet and Calves
A lower drop requires more active engagement from the muscles and tendons in your feet and calves. Over time, this can help strengthen them.
However, this also means there is a necessary adaptation period. Switching too quickly can lead to strain.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Higher Drop: Protect the Calf, Pressure the Knee
A higher heel drop is a tool to reduce stress on the Achilles and calf. If you suffer from tightness or pain in those areas, it can be an effective solution.
The downside is the increased load on your knees. If you have a history of knee pain, a high-drop shoe might aggravate the issue.
Lower Drop: Engage the Foot, Demand Adaptation
A lower heel drop promotes better biomechanics and can reduce knee strain. It is excellent for strengthening your feet and achieving a more natural gait.
The risk is overloading your calves and Achilles tendon, especially if you transition from a higher-drop shoe without giving your body time to adapt.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the ideal heel drop depends entirely on your personal biomechanics and history.
- If your primary focus is relieving tight calves or Achilles pain: A higher heel drop (8-12mm) is the most direct way to reduce strain on those specific areas.
- If your primary focus is reducing knee pain or strengthening your feet: A lower heel drop (0-6mm) may provide relief and encourage better mechanics, but you must transition gradually.
- If you have no specific issues and are new to dedicated walking shoes: A moderate drop of around 8mm offers a balanced starting point between the two extremes.
Choosing the right shoe is about selecting a tool that works with your body's mechanics, not against them.
Summary Table:
| Heel Drop Range | Primary Benefit | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| High (8-12mm) | Reduces calf & Achilles strain | Walkers with tight calves, Achilles pain | May increase load on knees & hips |
| Low (0-6mm) | Promotes natural foot position, eases knee strain | Walkers with knee pain, seeking stronger feet | Requires calf adaptation; transition slowly |
| Moderate (~8mm) | Balanced starting point | New walkers, those with no specific issues | A safe middle ground for most users |
Ready to Find Your Perfect Fit?
Choosing the right walking shoe is crucial for comfort and injury prevention. As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, ensuring you get the precise heel drop and support your customers need.
Let's collaborate to create the ideal walking shoes for your market.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how we can support your business with high-quality, biomechanically sound footwear.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Breathable Training Shoes Custom Athletic Footwear Manufacturer
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Wholesale Durable & Breathable Training Shoes for Custom Brands
- Premium Lightweight Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What material is commonly used for the soles of non-slip footwear and why? Unlock the Secrets of Safe Footwear
- What were traditional shoe soles made from before rubber? The History of Leather Soles
- Which type of sole is better for hard surfaces? Rubber Soles for Superior Comfort & Durability
- What are the advantages of rubber-soled shoes? Unlock Superior Grip & All-Day Comfort
- Why might someone prefer rubber soles over leather soles? Unlock Durability & All-Weather Performance



















