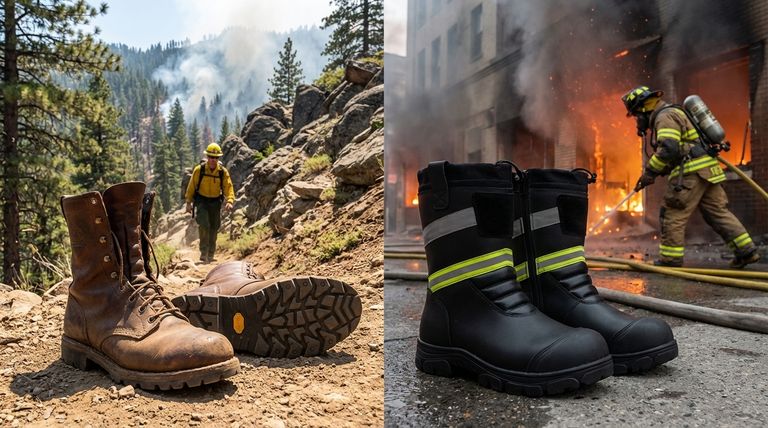
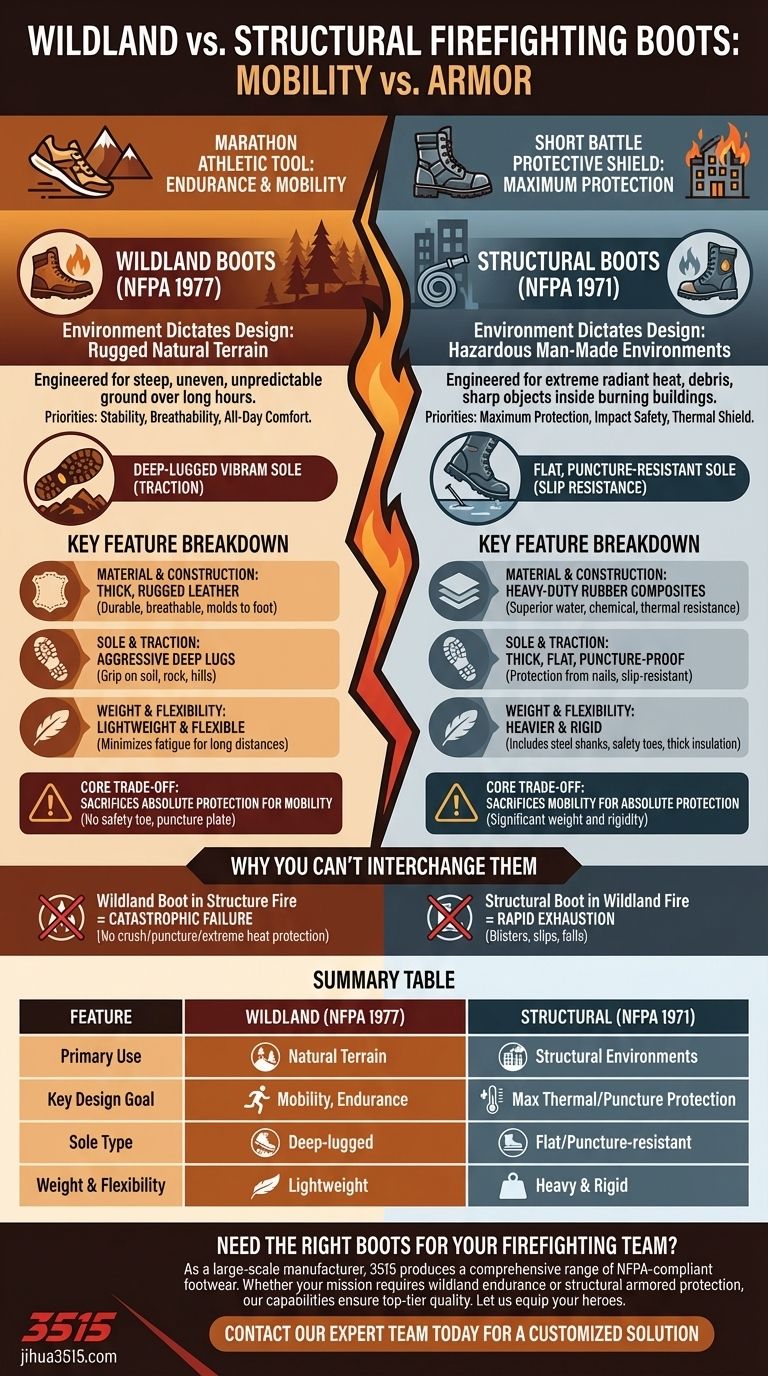
At their core, wildland firefighting boots are engineered for mobility and endurance over rugged natural terrain, while other firefighting boots, primarily structural or "bunker" boots, are built as heavy armor for protection against the intense, localized hazards of a building fire. The wildland boot is an athletic tool for a marathon; the structural boot is a protective shield for a short, intense battle.
The fundamental difference is not merely in the materials but in the philosophy of use. Wildland boots prioritize stability, flexibility, and comfort for long-duration missions on uneven ground. Structural boots sacrifice mobility for maximum thermal protection, puncture resistance, and impact safety in hazardous, man-made environments.

Environment Dictates Design
The specific dangers and physical demands of each firefighting discipline directly shape the construction and features of the footwear. A boot designed for one environment is dangerously unsuited for the other.
Wildland Firefighting: The Endurance Boot
Wildland firefighters operate on steep, uneven, and unpredictable terrain for extended periods. Their footwear must function like a high-performance hiking boot built to withstand extreme heat.
The primary goals are stability, breathability, and all-day comfort to prevent fatigue and injury over many miles and hours.
These boots are governed by the NFPA 1977 standard, which emphasizes durability, heat resistance, and performance characteristics like abrasion resistance suitable for outdoor use.
Structural Firefighting: The Armor Boot
Structural firefighters face extreme radiant heat, falling debris, sharp objects, and wet, slippery surfaces inside burning buildings. Their boots are a critical piece of personal protective equipment (PPE).
The design prioritizes maximum protection. This includes high heat resistance, puncture-proof soles, reinforced safety toes, and water resistance.
These are typically heavier, taller, and more rigid boots that meet the stringent NFPA 1971 standard for protective ensembles.
Key Feature Breakdown
The differing philosophies result in distinct features you can see and feel. Each component is optimized for a specific set of tasks and dangers.
Material and Construction
Wildland boots are almost exclusively made of thick, rugged leather. This provides durability and heat resistance while allowing the boot to mold to the foot and remain breathable during long shifts.
Structural boots can be made of either reinforced leather or, more commonly, heavy-duty rubber composites. These materials are chosen for superior water resistance and protection against chemical and thermal exposure.
Sole and Traction
A defining feature of a wildland boot is its deep-lugged Vibram sole or a similar design. This provides aggressive traction for gripping loose soil, rock, and steep hillsides.
Structural boots have thick, relatively flat rubber soles. Their primary function is providing puncture resistance from nails and glass, as well as slip resistance on wet floors.
Weight and Flexibility
Wildland boots are engineered to be as lightweight and flexible as possible. This minimizes fatigue, allowing firefighters to move quickly and safely across miles of terrain.
In contrast, structural boots are significantly heavier and more rigid. This weight comes from protective elements like steel shanks, safety toes, and thick layers of insulation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong boot for the environment isn't a matter of discomfort—it's a critical safety failure.
Why You Can't Interchange Them
Using a heavy, rigid structural boot on a wildland fire would lead to rapid exhaustion, blisters, and an increased risk of slips and falls on uneven ground.
Wearing a flexible wildland boot to a structure fire would be catastrophic. It offers no protection from crushing impacts, nail punctures through the sole, or the extreme conductive heat found on a fire floor.
Protection vs. Mobility
The core trade-off is simple. Wildland boots sacrifice the absolute protection of a safety toe and puncture plate for the mobility, flexibility, and reduced weight needed for their mission.
Structural boots make the opposite trade, accepting significant weight and rigidity as necessary compromises for providing an armored shield for the foot.
Matching the Boot to the Mission
Your choice must be dictated entirely by the environment where you will operate.
- If your primary focus is battling fires in forests and on mountainsides: You need a lightweight, durable leather boot compliant with NFPA 1977, featuring an aggressive lug sole for traction and all-day support.
- If your primary focus is responding to incidents in buildings and urban areas: You require a heavier, armored boot meeting NFPA 1971 standards, equipped with a safety toe, puncture-resistant sole, and high thermal protection.
Ultimately, choosing the right boot is a non-negotiable decision based on the unique demands and dangers of your specific firefighting role.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Wildland Boots (NFPA 1977) | Structural Boots (NFPA 1971) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Rugged, natural terrain | Man-made structural environments |
| Key Design Goal | Mobility, endurance, stability | Maximum thermal & puncture protection |
| Typical Materials | Thick, rugged leather | Heavy-duty rubber composites |
| Sole Type | Deep-lugged (e.g., Vibram) for traction | Flat, puncture-resistant for slip resistance |
| Weight & Flexibility | Lightweight and flexible | Heavy and rigid |
| Core Trade-off | Sacrifices some protection for mobility | Sacrifices mobility for absolute protection |
Need the Right Boots for Your Firefighting Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of NFPA-compliant footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether your mission requires the endurance of a wildland boot or the armored protection of a structural boot, our production capabilities ensure top-tier quality, durability, and performance.
Let us equip your heroes with the right gear for their mission. Contact our expert team today to discuss your specific needs and receive a customized solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Wholesale Waterproof Tactical Boots Custom Suede & High-Traction Soles
- Wholesale Lightweight Tactical Boots Custom Manufacturer for Desert & Combat Use
- Wholesale Lightweight Tactical Boots with Dial Closure OEM & Bulk Orders
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
People Also Ask
- Why are professional safety shoes required during heavy-duty girder erection? Essential Protection for Infrastructure
- What physical protections are provided by the S1 standard and integrated steel toecaps in industrial safety boots? Ensure Ultimate Foot Safety & Hazard Protection
- What is the purpose of steel toe caps in firefighter boots? Maximum Impact & Crush Protection
- What safety standards should oilfield work boots meet? Ensure OSHA & ASTM F2413 Compliance
- Why is safety the top priority when selecting oilfield work boots? Essential Protection for High-Risk Environments



















