For a safety shoe to be OSHA compliant, it must meet the performance criteria outlined in the ASTM F2413 standard. This standard establishes the minimum requirements for the design, performance, testing, and classification of protective footwear, covering hazards like impact, compression, and electrical shock.
OSHA itself does not approve or certify specific shoe models. Instead, it mandates that employers ensure the provided footwear meets the technical benchmarks set by consensus standards, with ASTM F2413 being the primary one for protective footwear in the United States.
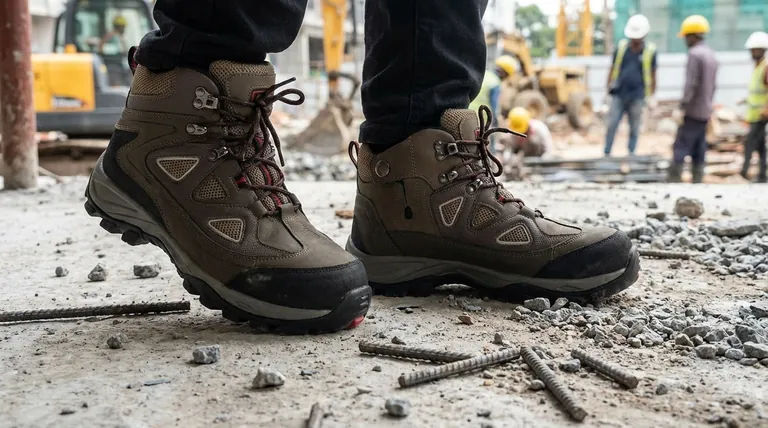

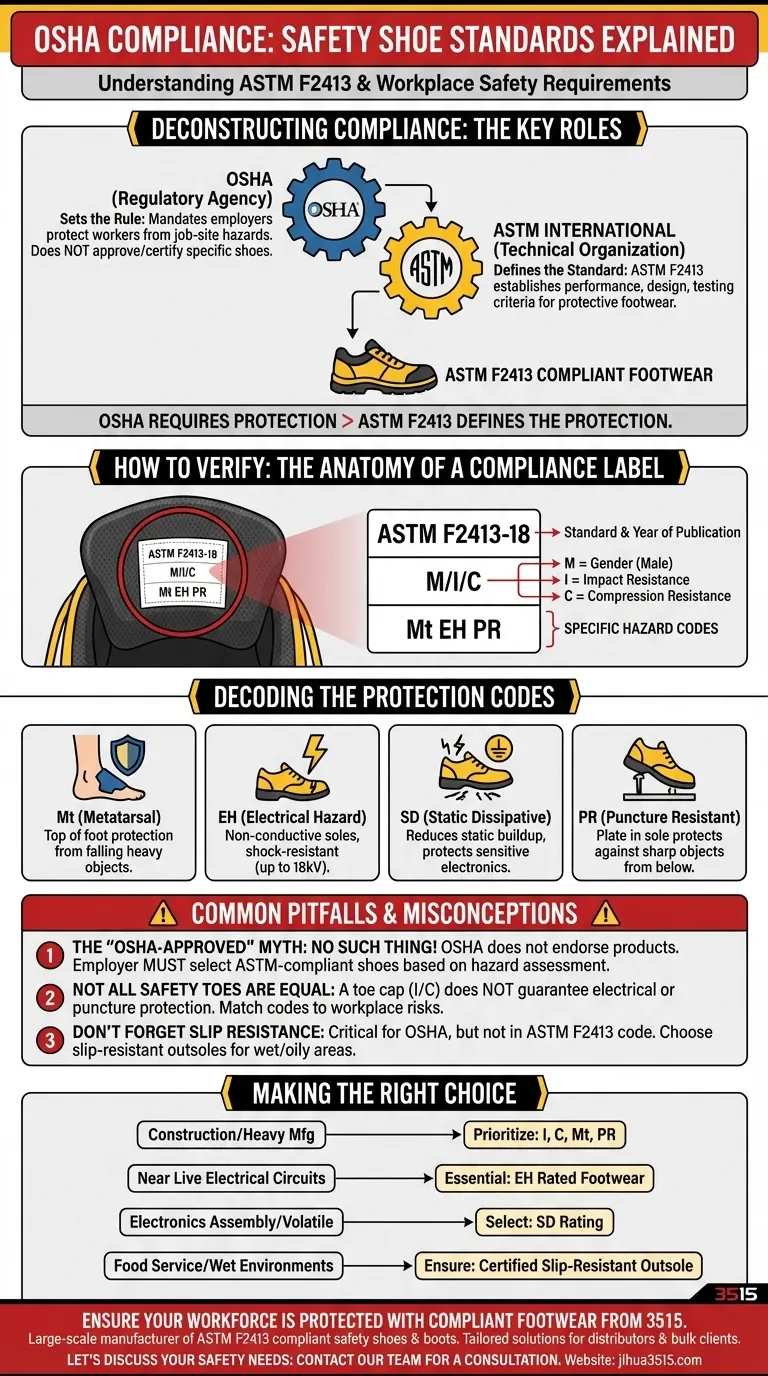
Deconstructing the Compliance Requirement
Understanding OSHA compliance means knowing the difference between the government agency that sets the rule and the technical organization that defines the standard.
OSHA's Role vs. ASTM's Role
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a regulatory agency that requires employers to protect workers from job-site hazards. For foot protection, OSHA's regulations point to the standards developed by external organizations.
ASTM International (formerly the American Society for Testing and Materials) is the organization that develops and publishes these technical standards. ASTM F2413 is the "Standard Specification for Performance Requirements for Protective (Safety) Toe Cap Footwear."
Essentially, OSHA says "you must use protective footwear," and the ASTM F2413 standard defines what "protective footwear" actually means in terms of performance.
The Key Standard: ASTM F2413
This is the current, active standard for safety footwear. It outlines specific tests for various protective features. Any safety shoe used for OSHA compliance must bear a marking inside indicating it conforms to this standard.
How to Verify Compliance on the Shoe Itself
Truly compliant footwear makes verification simple. The key is to find and understand the shoe's certification label, which is typically sewn into the tongue or collar.
The Anatomy of a Compliance Label
Every shoe that meets the ASTM F2413 standard must have an indelible marking with a specific format. This label provides a clear summary of the shoe's protective features.
A typical label will be laid out in a three or four-line format.
Line 1: ASTM F2413-18
This line identifies the standard (ASTM F2413) and the year of its publication (18 for 2018). This confirms the shoe was tested against that version of the standard.
Line 2: M/I/C
This line indicates the Gender (M for Male, F for Female) the shoe is designed for. It also specifies that it meets the Impact (I) and Compression (C) resistance requirements for the protective toe cap.
Lines 3 & 4: Specific Hazard Codes These lines list any additional hazards the shoe protects against, using specific two-letter codes.
Decoding the Protection Codes
- Mt (Metatarsal): The shoe includes extra protection for the top of the foot (the metatarsal bones).
- EH (Electrical Hazard): The footwear is made with non-conductive, shock-resistant soles and heels. It is designed to protect the wearer from open circuits of up to 18,000 volts.
- SD (Static Dissipative): The shoe is designed to reduce the buildup of static electricity by conducting it safely to the ground. This is used where static discharge could damage sensitive electronics.
- PR (Puncture Resistant): The shoe has a puncture-resistant plate built into the sole to protect against sharp objects from below.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Navigating safety standards can lead to confusion. Understanding these common points is critical for ensuring genuine workplace safety.
The "OSHA-Approved" Myth
There is no such thing as an "OSHA-approved" safety shoe. OSHA does not review, certify, or endorse specific products. An employer's responsibility is to select and provide footwear that meets the required ASTM standard based on a workplace hazard assessment.
Not All Safety Toes Are Equal
A shoe can have a protective toe cap (meeting the I/C requirements) but offer no protection against electrical hazards or punctures. You must identify the specific risks of a job and match them to the codes on the shoe's label.
Don't Forget Slip Resistance
While not part of the primary ASTM F2413 code, slip resistance is a critical factor for OSHA compliance. Slips, trips, and falls are among the most common workplace accidents. OSHA requires employers to provide footwear suitable for preventing these incidents, especially in wet or oily environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of footwear must be driven by a clear understanding of your workplace hazards. Use the label to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is construction or heavy manufacturing: Prioritize shoes rated for Impact (I), Compression (C), Metatarsal (Mt), and Puncture Resistance (PR).
- If your primary focus is working near live electrical circuits: Electrical Hazard (EH) rated footwear is essential for protecting against accidental shock.
- If your primary focus is electronics assembly or volatile environments: You must select shoes with a Static Dissipative (SD) rating to prevent static discharge.
- If your primary focus is food service or wet environments: Ensure the shoe has a certified, high-traction, slip-resistant outsole to prevent falls.
By understanding how to read the ASTM label, you can move beyond marketing claims and confidently select footwear that ensures true safety and compliance.
Summary Table:
| ASTM F2413 Code | Protection Provided | Key Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| I/C | Impact & Compression Resistance | Heavy Manufacturing, Construction |
| Mt | Metatarsal (Top of Foot) Protection | Where heavy objects could fall |
| EH | Electrical Hazard (Up to 18kV) | Working near live circuits |
| PR | Puncture Resistant Sole | Protection from sharp objects below |
| SD | Static Dissipative | Electronics, volatile environments |
Ensure your workforce is protected with compliant, high-quality safety footwear from 3515.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety shoes and boots that meet or exceed ASTM F2413 standards. We work directly with distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients to provide reliable footwear solutions tailored to your specific workplace hazards—from impact and compression to electrical hazards and puncture resistance.
Let's discuss your safety needs and how our manufacturing capabilities can support your business.
Contact our team today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Waterproof High-Cut Industrial Safety Boots for Wholesale and Bulk Orders
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Wholesale Durable Safety Boots | Custom Steel Toe & Puncture-Resistant Manufacturing
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
People Also Ask
- How does energy absorption technology in safety boots assist high foot arches? Protect Joints & Boost Stamina
- How does professional foot protection prevent fractures? Advanced Shielding and Impact Dissipation
- What is the primary function of standardized safety shoes? Essential Protection & Automated Compliance for Labs
- Why are waterproofing and breathability important in safety footwear? Essential for Worker Health & Safety
- What role do professional anti-slip safety shoes play in railway grid management? Enhance Trackside Operational Safety
- What technical standards for compression and puncture resistance must industrial safety shoes meet for railway yards?
- Why is heat resistance important in fire boots? It's the Critical Barrier Against Severe Burns
- What specific safety benefits do specialized protective shoes provide? Crucial Footwear Safety for Street Cleaners



















