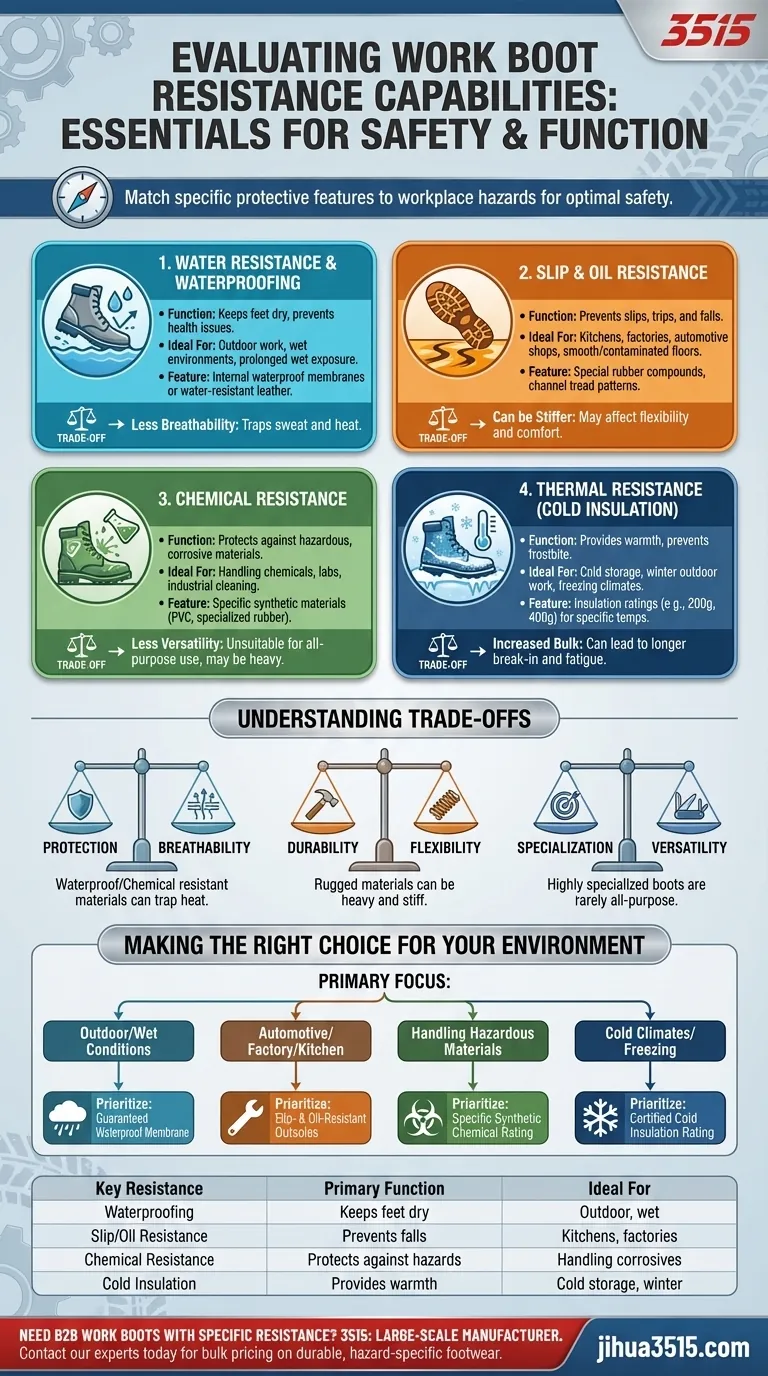
When selecting work boots, evaluating resistance capabilities is non-negotiable. The key properties to assess are resistance to water, oil, chemicals, cold temperatures, and slips. These features are not universal; the right choice depends entirely on the specific hazards present in your work environment, ensuring both safety and function.
The goal isn't to find a boot with every possible resistance. It's to match the boot's specific protective features—like waterproofing, insulation, or slip-resistant outsoles—to the daily demands and risks of your job.

Analyzing Environmental Hazards: The Core Resistance Types
The effectiveness of a work boot is measured by its ability to protect you from the specific challenges you face daily. Understanding each type of resistance allows you to accurately assess your needs.
Water Resistance and Waterproofing
Keeping your feet dry is fundamental for comfort, health, and preventing blisters or fungal infections.
Most quality leather boots offer some degree of water resistance, but for prolonged exposure to wet conditions, you need a waterproof design. This is often achieved with an internal waterproof membrane.
Slip and Oil Resistance
Slips, trips, and falls are among the most common workplace injuries. This resistance is critical for safety.
Outsoles designed for slip and oil resistance use special rubber compounds and tread patterns that channel liquids away to maintain grip on slick surfaces. This is essential for mechanics, kitchen staff, and anyone working on smooth, often-contaminated floors.
Chemical Resistance
For those who handle corrosive or hazardous materials, standard boots are insufficient and dangerous.
Chemical resistance requires boots made from specific synthetic materials, like PVC or specialized rubber, that are rated to withstand degradation from particular substances. Always match the boot's capabilities to the chemicals you use.
Thermal Resistance (Cold Insulation)
Working in cold environments without proper footwear can lead to frostbite and other serious health issues.
Insulation is the key feature for cold resistance. The level of protection is often measured in grams (e.g., 200g, 400g), with higher numbers providing more warmth for colder, less active conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a work boot is an exercise in balancing competing factors. Excelling in one area of resistance often means compromising in another.
Protection vs. Breathability
Highly waterproof and chemical-resistant boots use non-porous materials or membranes. While excellent at keeping liquids out, they also trap sweat and heat, which can be uncomfortable in warm conditions.
Durability vs. Flexibility
The most rugged and resistant materials can also be the heaviest and stiffest. This can lead to a longer break-in period and increased fatigue over a long workday.
Specialization vs. Versatility
A boot designed for maximum chemical resistance will likely be unsuitable for a job that requires climbing or walking long distances. A specialized tool is rarely a good all-purpose solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Your profession dictates your boot's requirements. Use your primary work environment as your guide to prioritize the most critical resistance features.
- If your primary focus is working outdoors or in wet conditions: Prioritize a boot with a guaranteed waterproof membrane, not just water-resistant leather.
- If your primary focus is automotive, factory, or kitchen work: Slip- and oil-resistant outsoles are your most critical safety feature.
- If your primary focus is handling hazardous materials: You must select boots made from specific synthetics rated for the exact chemicals you encounter.
- If your primary focus is working in cold climates: Look for boots with a specific insulation rating suitable for your region's temperature range.
Selecting the right resistances transforms your work boot from simple footwear into an essential piece of personal protective equipment.
Summary Table:
| Key Resistance | Primary Function | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Waterproofing | Keeps feet dry in wet conditions | Outdoor work, wet environments |
| Slip/Oil Resistance | Prevents falls on slick surfaces | Kitchens, factories, automotive shops |
| Chemical Resistance | Protects against hazardous materials | Handling corrosive substances |
| Cold Insulation | Provides warmth in freezing temperatures | Cold storage, winter outdoor work |
Need work boots with the right resistance for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of work boots and shoes, engineered with the specific resistances your workforce needs—from waterproof membranes and slip-resistant outsoles to chemical-resistant materials and certified insulation.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and get bulk pricing on durable, hazard-specific work boots that protect your workers and meet industry standards.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots for Wholesale
People Also Ask
- Why is investing in comfortable work boots important? Boost Health, Safety & Productivity
- What features should agricultural workers look for in work boots? A Guide to Safety and Durability
- Why might it be beneficial to pre-heat the boots before applying wax? Achieve Deeper, Longer-Lasting Protection
- How can you extend the lifespan of work shoes? A Systematic Guide to Doubling Your Footwear's Life
- What factors should be considered when choosing work shoes? The Ultimate Guide to Safety & Comfort
- Why are waterproof boots important for outdoor work? Protect Your Feet from Health Risks
- How do PVC, neoprene, and rubber work boots compare in weight? Choose the Right Boot for All-Day Comfort
- What is the difference between engineer boots and work boots? A Guide to Style vs. Safety



















