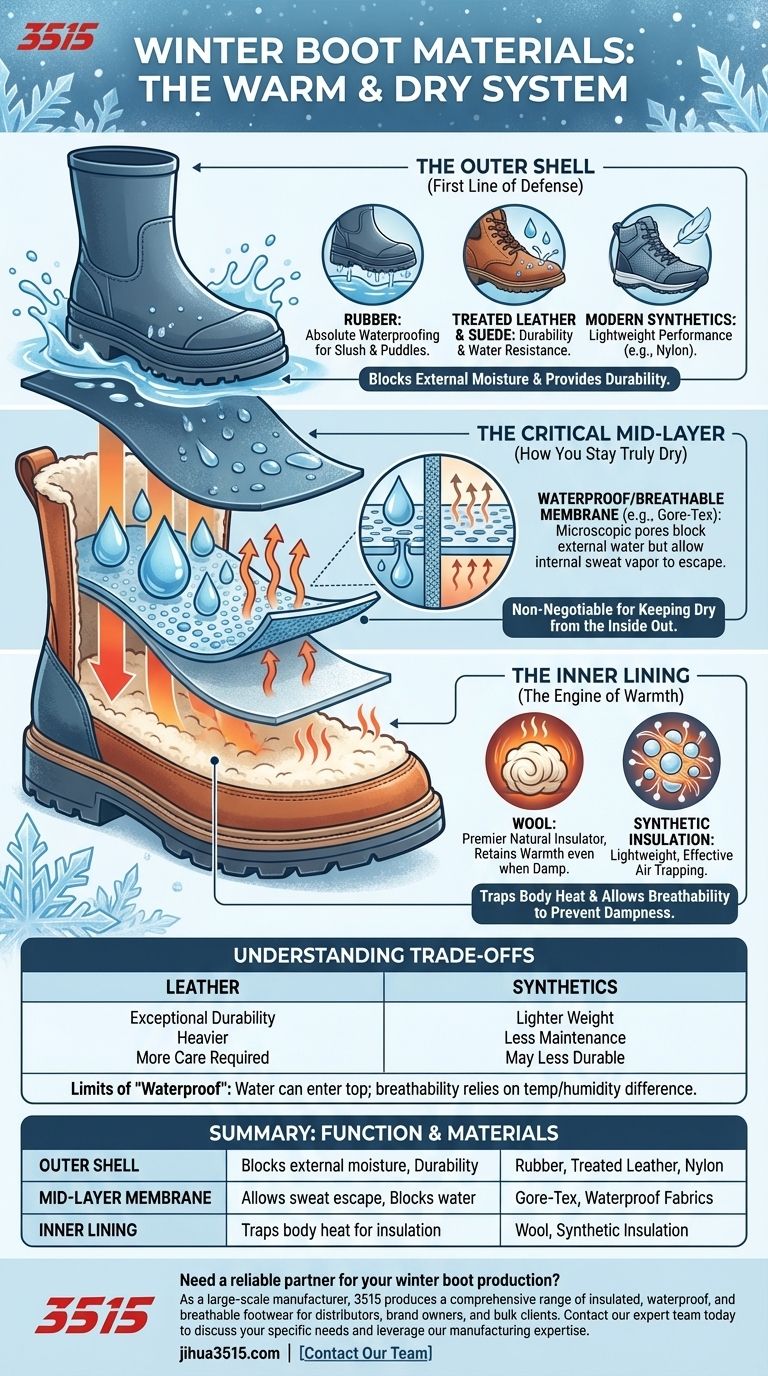
At their core, effective winter boots use a strategic system of materials to keep your feet both warm and dry. The most common materials include an outer layer of rubber, treated leather, or synthetics for waterproofing, a mid-layer waterproof and breathable membrane, and an inner lining of wool or other insulation for warmth.
The key to a high-performance winter boot isn't a single material, but a multi-layer system. The outer shell blocks external moisture, the inner lining provides insulation, and a critical membrane allows sweat to escape, ensuring your feet stay truly dry from the inside out.

The Outer Shell: Your First Line of Defense
The exterior of the boot is its armor against snow, slush, and water. The material used here dictates the boot's durability and primary level of water resistance.
Rubber for Absolute Waterproofing
Rubber is completely impermeable to water. It is the ideal material for the lower portion of a boot that will be submerged in slush or puddles.
Leather and Suede for Durability
Treated leather and suede offer excellent durability and a classic look. While not inherently waterproof, modern treatments and construction methods make them highly water-resistant and tough enough for harsh conditions.
Modern Synthetics for Lightweight Performance
Synthetic materials like nylon are often used in boot uppers because they are lightweight, durable, and can be easily treated with waterproof coatings. They are a common choice for more active or athletic winter footwear.
The Inner Lining: The Engine of Warmth
Insulation works by trapping a layer of air around your foot. Your body heat warms this trapped air, which then acts as a thermal barrier against the outside cold.
Wool for Natural Insulation
Wool is a premier natural insulator. It's highly effective at trapping air, and it has the unique ability to retain much of its insulating properties even when it gets damp from sweat.
The Role of Breathability
A boot must manage moisture from both the outside and the inside. Breathable upper layers are critical for allowing sweat to evaporate, which prevents the dampness that can lead to cold feet, blisters, and fungal infections.
The Critical Mid-Layer: How You Stay Truly Dry
Between the outer shell and the inner lining often lies the most advanced technology in the boot: the waterproof/breathable membrane.
How Membranes Work
Materials referred to as TEX membranes (like Gore-Tex) contain billions of microscopic pores per square inch. These pores are too small for external water droplets to penetrate but large enough for internal water vapor (sweat) to escape.
Why This Layer is Non-Negotiable
This technology solves the core problem of winter footwear: blocking snow and slush while preventing a build-up of sweat. Without it, your socks would become soaked from the inside, defeating the purpose of the insulation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. Choosing the right boot means understanding the inherent compromises in its design.
Leather vs. Synthetics
Leather offers exceptional durability but is often heavier and requires more care. Synthetics are lighter and require less maintenance but may not last as long under heavy use.
The Limits of "Waterproof"
Even the best waterproof boot has its limits. Water can always enter over the top of the boot. Furthermore, for a membrane to breathe effectively, there needs to be a difference in temperature and humidity between the inside and outside of the boot.
Natural vs. High-Tech
While materials like wool and leather are excellent "natural" options, high-performance features like waterproof/breathable membranes are advanced synthetic polymers. This combination of natural and synthetic materials is what creates the most effective modern winter boots.
Selecting the Right Materials for Your Needs
Focus on how the boot's material system aligns with your intended use.
- If your primary focus is daily commuting in cold, wet cities: A boot with a treated leather upper and a reliable waterproof membrane provides the best balance of protection, durability, and style.
- If your primary focus is deep snow and extreme cold: Look for a boot with a high rubber lower shell for absolute waterproofing and a thick wool or synthetic insulation lining for maximum warmth.
- If your primary focus is active winter sports like snowshoeing: Prioritize lightweight synthetic uppers with a top-tier breathable membrane to manage sweat during high-exertion activity.
Ultimately, understanding how these materials function as a system empowers you to choose the boot that will best protect your feet in any winter condition.
Summary Table:
| Layer | Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Shell | Blocks external moisture and provides durability. | Rubber, Treated Leather, Nylon |
| Mid-Layer Membrane | Allows sweat vapor to escape while blocking water. | Gore-Tex, other waterproof/breathable fabrics |
| Inner Lining | Traps body heat to provide insulation. | Wool, Synthetic Insulation (e.g., Thinsulate™) |
Need a reliable partner for your winter boot production?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of insulated, waterproof, and breathable shoes and boots, ensuring your customers stay warm and dry in any condition.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your specific needs and leverage our manufacturing expertise.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
People Also Ask
- What typically follows walking boot usage in recovery? A Guide to Safe & Effective Rehabilitation
- What defines a winter boot and what features does it have? A Guide to Warm, Dry & Stable Feet
- What are the advantages of zip-up boots for streetbike riders? Speed, Convenience & Weatherproofing
- What are the durability requirements for walking shoes? Select the Right Shoe for Long-Lasting Comfort
- What are the disadvantages of hiking boots? Key Trade-offs in Weight, Comfort & Agility
- How can you determine the right arch support for your walking shoes? Find Your Perfect Fit for Pain-Free Walking
- What are the pros and cons of leather walking boots? Weighing Durability vs. Convenience
- Should walking boots be worn while sleeping? A Guide to Protecting Your Recovery



















