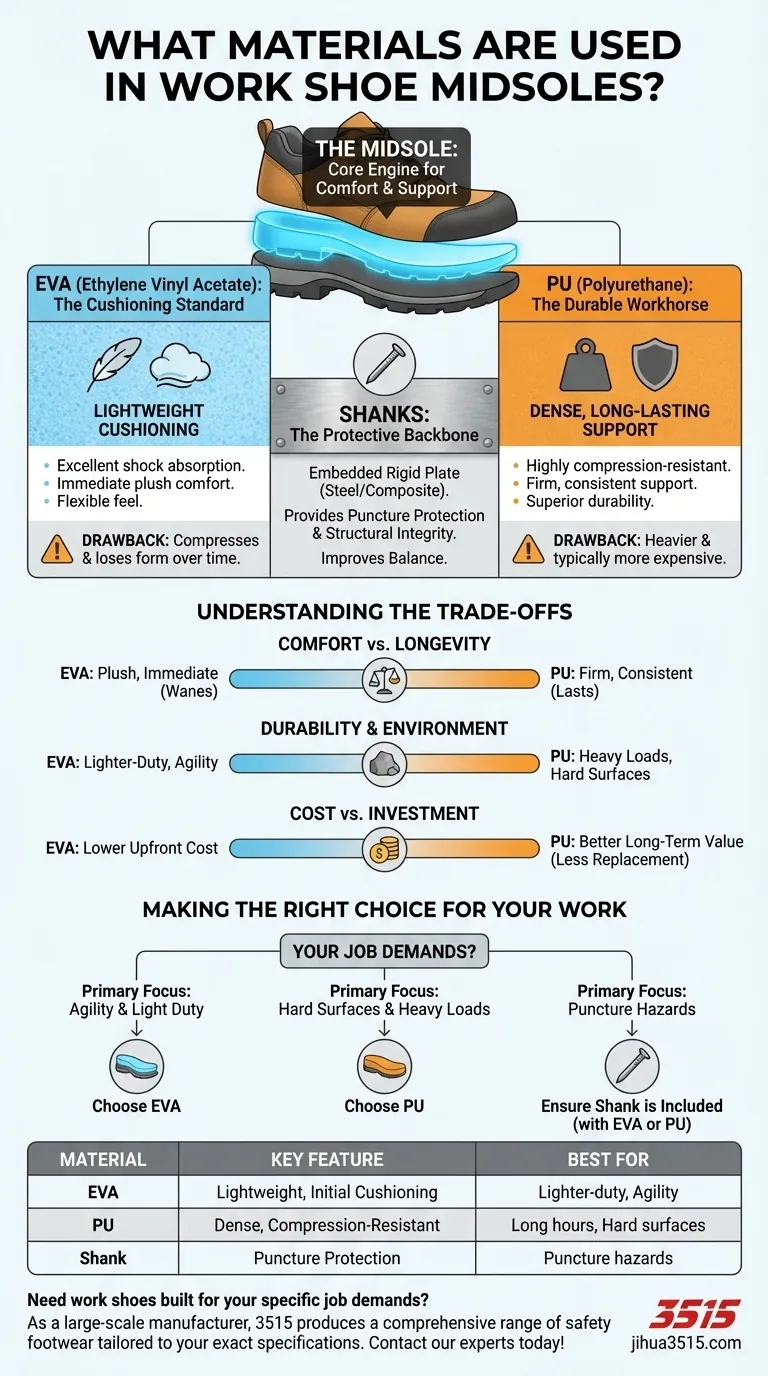
At the core of a work shoe's performance, the midsole is engineered primarily from two key materials: Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) for lightweight cushioning or Polyurethane (PU) for dense, long-lasting support. Many safety-focused designs also embed a rigid shank, often made of steel, within this layer for puncture protection and structural integrity.
The choice between midsole materials is a fundamental trade-off. You are essentially deciding between the immediate, lightweight comfort offered by EVA and the superior, long-term durability and support provided by Polyurethane.

Deconstructing the Midsole: The Core Components
The midsole is the engine of the shoe, responsible for shock absorption, support, and overall comfort. Understanding its material composition is key to selecting the right footwear for your needs.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA): The Cushioning Standard
EVA is a lightweight foam material known for providing excellent cushioning and shock absorption. Its soft, flexible nature makes for a very comfortable feel right out of the box.
However, the primary drawback of EVA is that it can compress and lose its supportive form over time, especially under heavy use.
Polyurethane (PU): The Durable Workhorse
Polyurethane is a denser polymer that offers a firmer, more resilient form of support. It is highly resistant to compression, meaning it will maintain its shape and shock-absorbing properties for much longer.
While PU is significantly more durable, it is also heavier and typically more expensive than EVA.
Shanks: The Protective Backbone
A shank is not a cushioning material but a rigid plate, often made of steel or a composite material, embedded within the midsole.
Its purpose is twofold: it protects the foot from punctures from below and provides structural support to maintain the shoe's shape and improve balance, especially when carrying heavy gear.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Comfort vs. Longevity
The material you choose directly impacts your daily experience and the shoe's lifespan. This isn't about one material being "better," but which is better for a specific job.
The Impact on All-Day Comfort
EVA provides a plush, cushioned feel that offers immediate comfort. However, as it breaks down, that comfort can wane, leading to reduced support.
PU delivers a firm, consistent level of support that won't degrade quickly. This makes it a superior choice for long hours spent standing on hard surfaces like concrete.
The Factor of Durability and Environment
For demanding jobs that involve heavy loads or rough terrain, the compression resistance of PU makes it the clear winner for longevity.
For lighter-duty work or roles requiring more agility and less weight, the benefits of an EVA midsole are often sufficient.
Cost vs. Long-Term Investment
Work shoes with EVA midsoles are generally less expensive upfront.
While PU-based shoes command a higher price, their extended lifespan often makes them a more cost-effective investment in the long run, as they will not need to be replaced as frequently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Work
Your specific job requirements should be the ultimate guide in your decision.
- If your primary focus is immediate comfort and lighter-duty work: An EVA midsole offers superior lightweight cushioning that is ideal for jobs requiring agility.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability and support on hard surfaces: A Polyurethane (PU) midsole provides resilient, compression-resistant support that will last.
- If your primary focus is protection from ground punctures: Ensure the shoe explicitly includes a steel or composite shank, regardless of the primary cushioning material.
By understanding these core materials, you can select a work shoe based on its engineered performance, not just its appearance.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) | Lightweight, excellent initial cushioning | Lighter-duty work, roles requiring agility |
| PU (Polyurethane) | Dense, compression-resistant, durable | Long hours on hard surfaces, heavy loads |
| Shank (e.g., Steel) | Puncture protection, structural integrity | Environments with puncture hazards |
Need work shoes built for your specific job demands?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety and work footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether your team needs the immediate comfort of EVA or the long-term durability of PU, our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots tailored to your exact specifications.
Let us help you equip your workforce with the right foundation.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Wholesale Breathable & Cushioned Training Shoes Custom Factory Production
People Also Ask
- Why are industrial-grade safety shoes mandatory in metallurgical workshops? Essential Protection for Extreme Environments
- How do industrial safety shoes contribute to safety in sugar production? Ensure High-Altitude Inspection Security
- What is the primary objective of utilizing dedicated safety shoes in nanomaterial work zones? Prevent Track-Out Now
- Why does the material performance of professional slip-resistant shoes offer superior safety? Hardware vs. Behavior
- Why is compliance with safety standards such as PN EN ISO 20347:2012 critical? Ensure Certified Workplace Protection



















