The most durable waterproof boots are built from a strategic combination of materials, primarily treated full-grain leather, solid rubber, and advanced synthetic fabrics that house a waterproof membrane like GORE-TEX. These materials are chosen not just for their individual properties but for how they work together as a system to block external water while managing internal moisture and withstanding physical abrasion.
The key to a truly durable waterproof boot isn't a single "best" material. It's a purpose-built system combining a rugged outer material for defense, a waterproof membrane for core protection, and robust construction techniques to eliminate weak points.

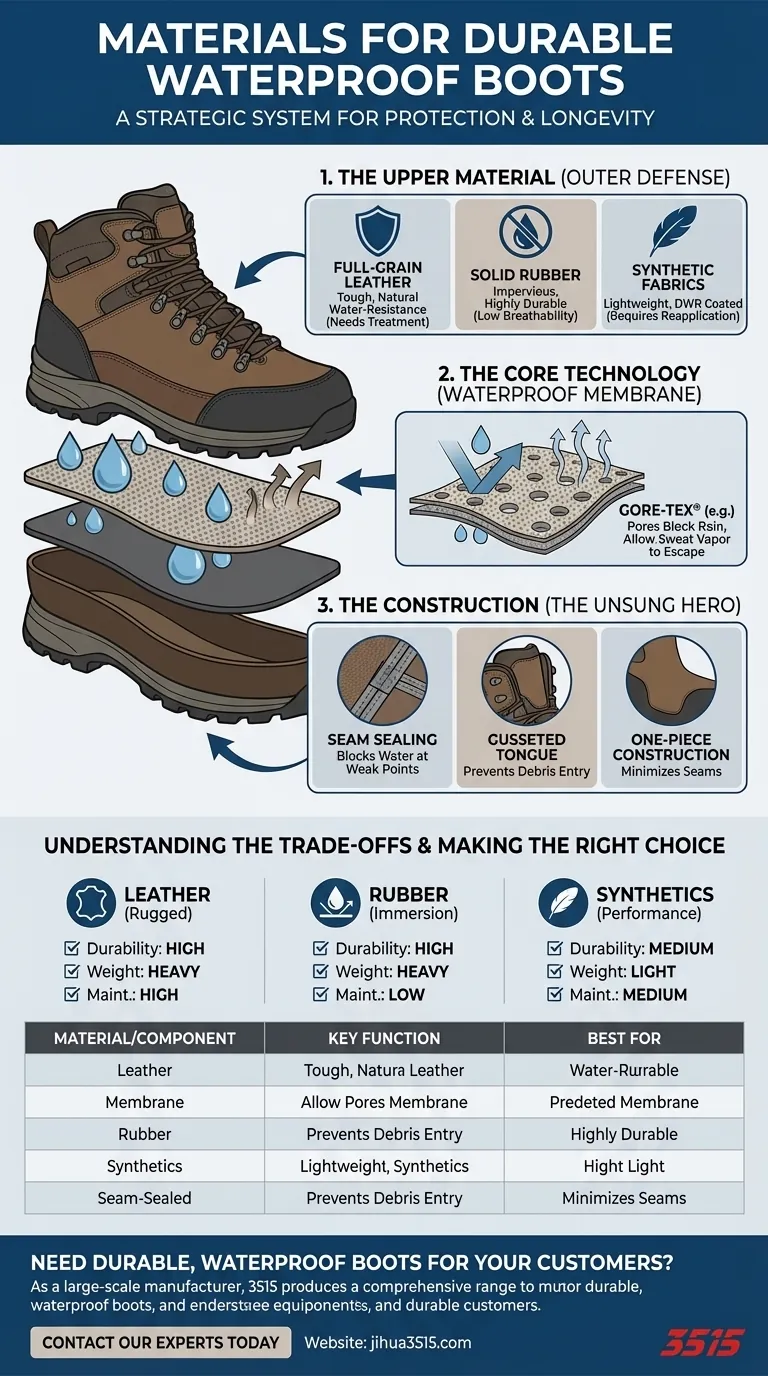
The Three Pillars of Waterproof Durability
A boot's ability to remain waterproof and durable over time depends on three interconnected elements: the upper material, the internal membrane, and the method of construction.
Pillar 1: The Upper Material (The First Line of Defense)
This is the outermost layer of the boot that faces direct contact with the elements.
- Full-Grain Leather: This is the toughest and most durable part of the animal hide. It is naturally water-resistant and highly breathable. To make it truly waterproof, it must be treated with waxes, oils, or spray-on treatments.
- Rubber: As a material, rubber is intrinsically waterproof and extremely durable against abrasion. It's the standard for outsoles and is often used for the entire boot in applications requiring total water immersion.
- Synthetic Fabrics (Nylon, Neoprene): These materials are valued for being lightweight and flexible. While not naturally waterproof, they are treated with Durable Water Repellent (DWR) coatings and serve as the protective outer shell for delicate waterproof membranes.
Pillar 2: The Core Technology (Waterproof Membranes)
Sandwiched between the upper and the inner lining, this is where the high-tech waterproofing happens.
- How Membranes Like GORE-TEX Work: These membranes are films with billions of microscopic pores per square inch. Each pore is thousands of times smaller than a water droplet, making it impossible for rain or puddle water to penetrate from the outside.
- The Breathability Factor: Crucially, these same pores are large enough for water vapor molecules (sweat) to escape from the inside. This "breathability" is essential for keeping your feet dry from the inside out.
Pillar 3: The Construction (The Unsung Hero)
Even the best materials will fail if the boot is not assembled correctly.
- Seam Sealing: Every stitch in a boot creates a tiny hole. In quality waterproof footwear, a special waterproof tape is applied over these seams from the inside to completely block this potential entry point for water.
- Gusseted Tongues: This refers to a tongue that is attached to the upper along its sides, creating a continuous, folded barrier. This simple design feature is critical for preventing water, dirt, and debris from entering through the lace area.
- One-Piece Construction: Some designs use a single piece of leather or synthetic material for the main part of the upper. This minimizes the number of seams, which are the most common points of failure for both durability and waterproofing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. Choosing the right boot means understanding the inherent compromises.
Leather: Durability vs. Maintenance
Leather offers unmatched durability and can mold to your foot over time. However, it is heavier than synthetics and requires regular cleaning and re-application of waterproofing treatments to maintain its performance.
Rubber: Absolute Waterproofing vs. Breathability
Rubber boots are completely impervious to water and easy to clean. Their major drawback is a complete lack of breathability, which can lead to very sweaty and uncomfortable feet during strenuous activity.
Synthetics with Membranes: Performance vs. Lifespan
Synthetic boots with membranes like GORE-TEX offer the best combination of low weight and breathable waterproofing. However, the membrane can be punctured, and the outer fabric's DWR coating needs to be reapplied periodically to prevent it from "wetting out" and impeding breathability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Your ideal material depends entirely on your intended use.
- If your primary focus is rugged durability for hard work or backpacking: Choose a boot made from treated full-grain leather, ideally with a waterproof membrane for added security.
- If your primary focus is complete water immersion for fishing or farming: A boot constructed entirely from rubber or neoprene is your most reliable option.
- If your primary focus is lightweight performance for hiking or trail running: Look for a boot with a synthetic upper (like nylon) that incorporates a breathable-waterproof membrane.
Ultimately, understanding how these materials and construction methods form a complete system empowers you to choose a boot that will keep you dry and protected for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Material/Component | Key Function | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Full-Grain Leather | Rugged outer defense, abrasion-resistant | Hard work, heavy-duty use |
| GORE-TEX Membrane | Blocks water, allows sweat vapor to escape | Hiking, all-weather performance |
| Solid Rubber | Total waterproofing, easy to clean | Fishing, farming, immersion |
| Synthetics (Nylon) | Lightweight, flexible with DWR coating | Trail running, lightweight hiking |
| Seam-Sealed Construction | Eliminates weak points at stitches | All applications for long-term durability |
Need durable, waterproof boots for your customers?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of durable, waterproof boots and shoes, built with the precise material systems detailed above.
We can help you source or private-label high-performance footwear that meets the specific demands of your market.
Contact our experts today to discuss your production needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
People Also Ask
- What are OSHA approved shoes? Understanding the Correct Standards for Workplace Safety
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- How long can you wear safety boots? The Lifespan is Determined by Wear, Not Time
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health



















