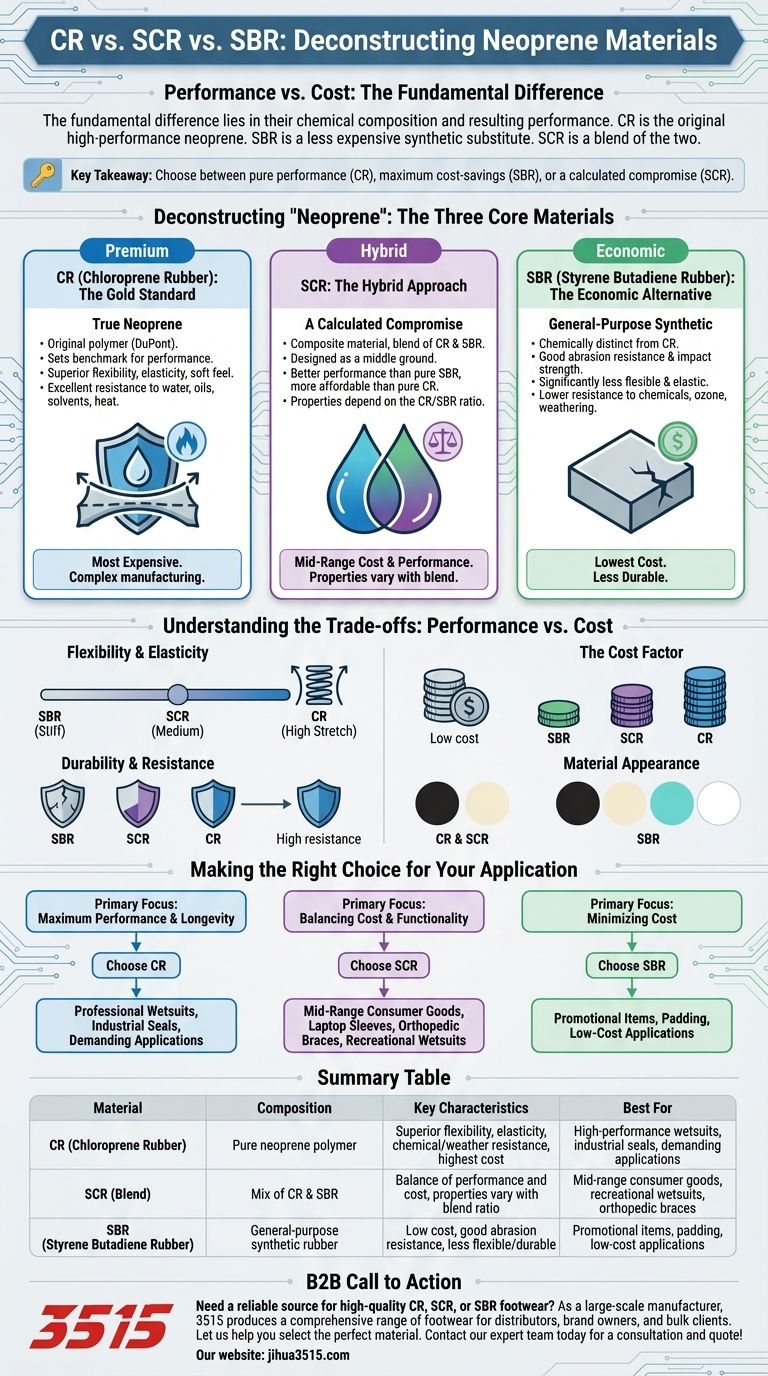
The fundamental difference lies in their chemical composition and resulting performance. CR (Chloroprene Rubber) is the original, high-performance neoprene. SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) is a less expensive synthetic rubber often substituted for neoprene, and SCR is a blend of the two materials.
The term "neoprene" is often used as a catch-all in the industry, which can be misleading. The critical takeaway is that you are choosing between pure performance (CR), maximum cost-savings (SBR), or a calculated compromise between the two (SCR).
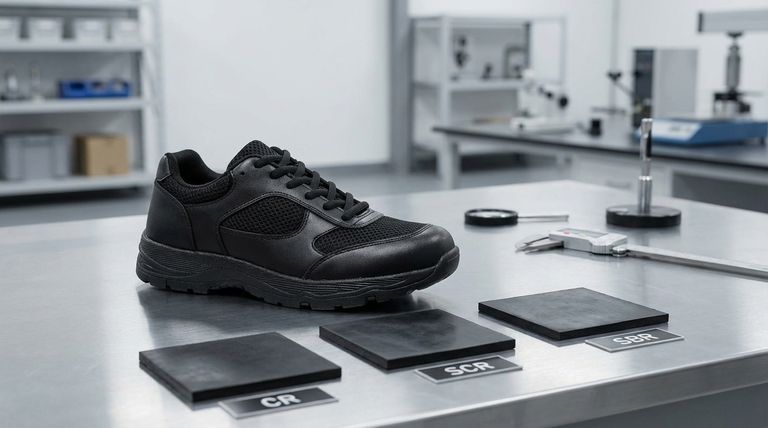

Deconstructing "Neoprene": The Three Core Materials
To select the right material, you must understand what each designation actually means for the final product's behavior and durability.
CR (Chloroprene Rubber): The Gold Standard
CR is the original polymer material developed by DuPont and marketed as Neoprene. It is "true" neoprene.
This material sets the benchmark for performance, offering superior flexibility, elasticity, and a soft feel. It provides excellent resistance to water, oils, solvents, and heat.
Because of its high performance and more complex manufacturing process, CR is the most expensive of the three options.
SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber): The Economic Alternative
SBR is a general-purpose synthetic rubber. While it is often sold under the "neoprene" umbrella, it is chemically distinct from CR.
Its primary advantage is its low cost. SBR offers good abrasion resistance and impact strength, but it is significantly less flexible and elastic than CR.
SBR also has lower resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering, making it less durable in demanding environments.
SCR: The Hybrid Approach
SCR is a composite material, a sheet sponge formed by blending CR and SBR rubber.
This material is designed to offer a middle ground. It provides better performance than pure SBR while remaining more affordable than pure CR.
The final properties of an SCR blend—such as its flexibility and durability—depend entirely on the ratio of CR to SBR used in its composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Performance vs. Cost
Your choice will almost always come down to a direct trade-off between the material's performance characteristics and its price point.
Flexibility and Elasticity
CR is the clear winner here, providing the most stretch and rebound. This is critical for applications like high-performance wetsuits or gaskets that require a perfect seal. SBR is considerably stiffer, with SCR falling somewhere in between.
Durability and Resistance
For any application exposed to chemicals, oils, or harsh weather, CR offers far superior longevity. SBR will degrade more quickly under these conditions. An SCR blend's durability is proportional to the amount of CR it contains.
The Cost Factor
This is the primary driver for the existence of SBR and SCR. SBR is the most cost-effective option, making it suitable for mass-market products where high performance is not a priority. CR is a premium material with a price to match.
Material Appearance
While properties are key, minor aesthetic differences exist. CR and SCR sponges are typically available in black and cream. SBR offers a wider range of base colors, including black, cream, aqua, and white.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires aligning its properties with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and longevity: Choose CR for applications like professional-grade wetsuits, industrial seals, and any product where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and functionality: Choose SCR for mid-range consumer goods like laptop sleeves, orthopedic braces, and recreational wetsuits where good performance is needed without a premium price.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost: Choose SBR for promotional items, padding, or products where high elasticity and chemical resistance are not required.
Understanding these distinctions allows you to select a material based on precise performance needs rather than just a marketing term.
Summary Table:
| Material | Composition | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR (Chloroprene Rubber) | Pure neoprene polymer | Superior flexibility, elasticity, chemical/weather resistance, highest cost | High-performance wetsuits, industrial seals, demanding applications |
| SCR (Blend) | Mix of CR and SBR | Balance of performance and cost, properties vary with blend ratio | Mid-range consumer goods, recreational wetsuits, orthopedic braces |
| SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) | General-purpose synthetic rubber | Low cost, good abrasion resistance, less flexible/durable | Promotional items, padding, low-cost applications |
Need a reliable source for high-quality CR, SCR, or SBR footwear?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, ensuring you get the right material and construction for your market.
Let us help you select the perfect material to balance performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness for your product line.
Contact our expert team today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Durable & Breathable Training Shoes for Custom Brands
- Durable Rubber Sole Outdoor Shoes Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Custom OEM Training Shoes Wholesale Manufacturer Durable & Breathable
- Wholesale Smart Casual Sneakers with Dial Closure | Factory Direct Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- Why is indoor custom-made footwear essential for diabetic foot prevention? Ensure 24/7 Protection and Patient Safety
- When is the best time of day to measure your feet for boot sizing? Measure in the Evening for a Perfect Fit
- How do automated gait segmentation algorithms process complex signals? Data-Driven Biomechanical Insights Explained
- What additional functionalities do protective motorcycle boots offer? Beyond Basic Footwear for Ultimate Rider Safety
- What is the function of compliant foam pads in the assessment of footwear? Master Sensory Integration & Stability
- What are the best practices for choosing socks for winter cycling? Stay Warm and Ride Comfortably
- How do ECG monitoring devices provide safety assurance during high-intensity footwear stress testing? Safeguard Athletes
- What is the difference between water-resistant and waterproof footwear? Choose the Right Protection for Your Needs



















