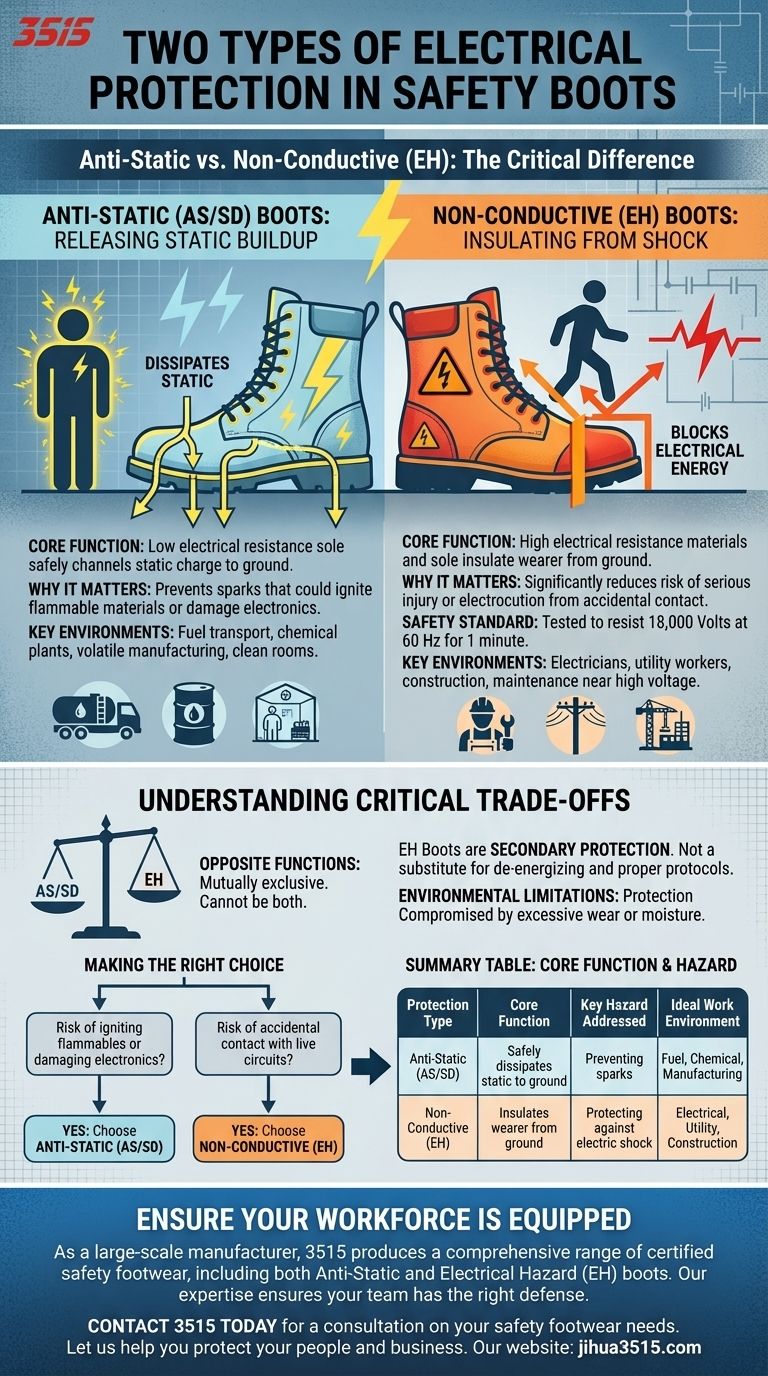
The two primary types of electrical protection offered by safety boots are Anti-Static and Non-conductive (also known as Electrical Hazard or EH). Anti-Static footwear is designed to safely dissipate static electricity from your body to the ground, while Non-conductive footwear is designed to insulate you from the ground, providing secondary protection against electrical shock from live circuits.
The core difference is simple: Anti-Static boots release electrical energy from your body to prevent sparks, whereas Non-conductive (EH) boots block electrical energy from entering your body to prevent shock. These two functions are opposites and mutually exclusive.

Anti-Static (AS/SD) Boots: Releasing Static Buildup
The Core Function
Anti-Static boots contain a sole with a specific, low electrical resistance. This allows any static charge that builds up on your body during movement to be safely channeled through the footwear and dissipated into the ground.
Why It Matters
The primary purpose is to prevent an uncontrolled electrostatic discharge—a spark. In certain environments, a tiny spark can have catastrophic consequences, such as igniting flammable liquids, vapors, or dust.
Key Environments
These boots are critical for workers in industries dealing with volatile substances or sensitive electronics. This includes fuel transport, chemical plants, certain manufacturing facilities, and clean rooms where a static discharge could destroy delicate components.
Non-conductive (EH) Boots: Insulating from Shock
The Core Function
Electrical Hazard (EH) rated boots are manufactured with non-conductive materials and a sole designed to have a very high electrical resistance. This design essentially insulates the wearer from the ground.
Why It Matters
If you accidentally step on a live electrical wire or make contact with an energized circuit, EH boots can help block the current from completing its path through your body to the ground. This significantly reduces the risk of serious injury or electrocution.
The Safety Standard
EH-rated footwear is tested to resist the application of 18,000 volts at 60 Hz for one minute with no current flow or leakage current in excess of one milliampere under dry conditions.
Key Environments
These boots are essential for anyone working near live electrical circuits. This includes electricians, utility workers, construction trades, and maintenance personnel who face the risk of accidental contact with high-voltage sources.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Opposite Functions
A boot cannot be both Anti-Static and EH-rated. One is designed to be conductive enough to dissipate static, while the other is designed to be non-conductive to insulate. Choosing the wrong one for your environment creates a significant safety hazard.
EH Boots are Secondary Protection
It is crucial to understand that EH boots are a secondary source of protection. They are not a substitute for primary safety protocols like de-energizing circuits, lockout/tagout procedures, and using properly insulated tools.
Environmental Limitations
The protective qualities of EH footwear can be compromised by excessive wear or exposure to moisture. If the sole is punctured or the boot becomes wet, its ability to insulate you from an electrical charge is severely reduced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Hazard
Choosing the correct boot is a critical safety decision based entirely on the specific hazards of your workplace.
- If your primary risk is igniting flammable materials or damaging sensitive electronics: You need Anti-Static (AS/SD) boots to safely dissipate static charge from your body.
- If your primary risk is accidental contact with live electrical circuits: You need Non-conductive (EH) boots to help insulate you from electrical shock.
Always select your protective footwear based on a thorough risk assessment of your specific job and environment.
Summary Table:
| Protection Type | Core Function | Key Hazard Addressed | Ideal Work Environment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Static (AS/SD) | Safely dissipates static electricity from the body to the ground. | Preventing sparks that could ignite flammable materials or damage electronics. | Fuel transport, chemical plants, manufacturing with volatile substances, clean rooms. |
| Non-Conductive (EH) | Insulates the wearer from the ground to block electrical current. | Protecting against electric shock from accidental contact with live circuits. | Electrical work, utilities, construction, maintenance near high-voltage sources. |
Ensure your workforce is equipped with the correct electrical protection.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear, including both Anti-Static and Electrical Hazard (EH) boots, for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our expertise ensures your team has the right defense against specific workplace dangers.
Contact 3515 today for a consultation on your safety footwear needs. Let us help you make the critical choice that protects your people and your business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Customizable Safety Boots Durable & Protective Footwear Manufacturing
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
- Premium Sport Style Safety Boots for Bulk Orders
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What are the safety benefits of integrating industrial-grade GPS modules into smart protective footwear? Enhancing Site Visibility
- What chemical protection features do safety shoes offer? A Guide to Hazard-Resistant Footwear
- How do Toe Cap Safety Shoes contribute to risk control during high-altitude construction? Elevate Worker Safety
- What role do industrial safety shoes play in feed production? Protect Your Workforce from Mechanical Hazards
- Can moc toe boots be safety boots? Blending Classic Style with Certified Protection
- How do chemical-resistant safety boots reduce health risks from VOCs? Prevent Dermal Absorption and Systemic Damage
- What are the technical benefits of a stable shoe model design in high-intensity medical environments? Boost Safety
- Why do my feet hurt when I wear safety shoes? Solve Toe Pain, Blisters & Fatigue



















