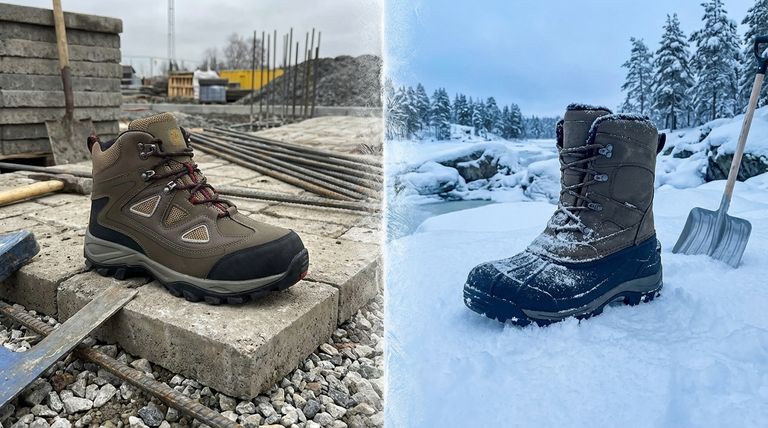
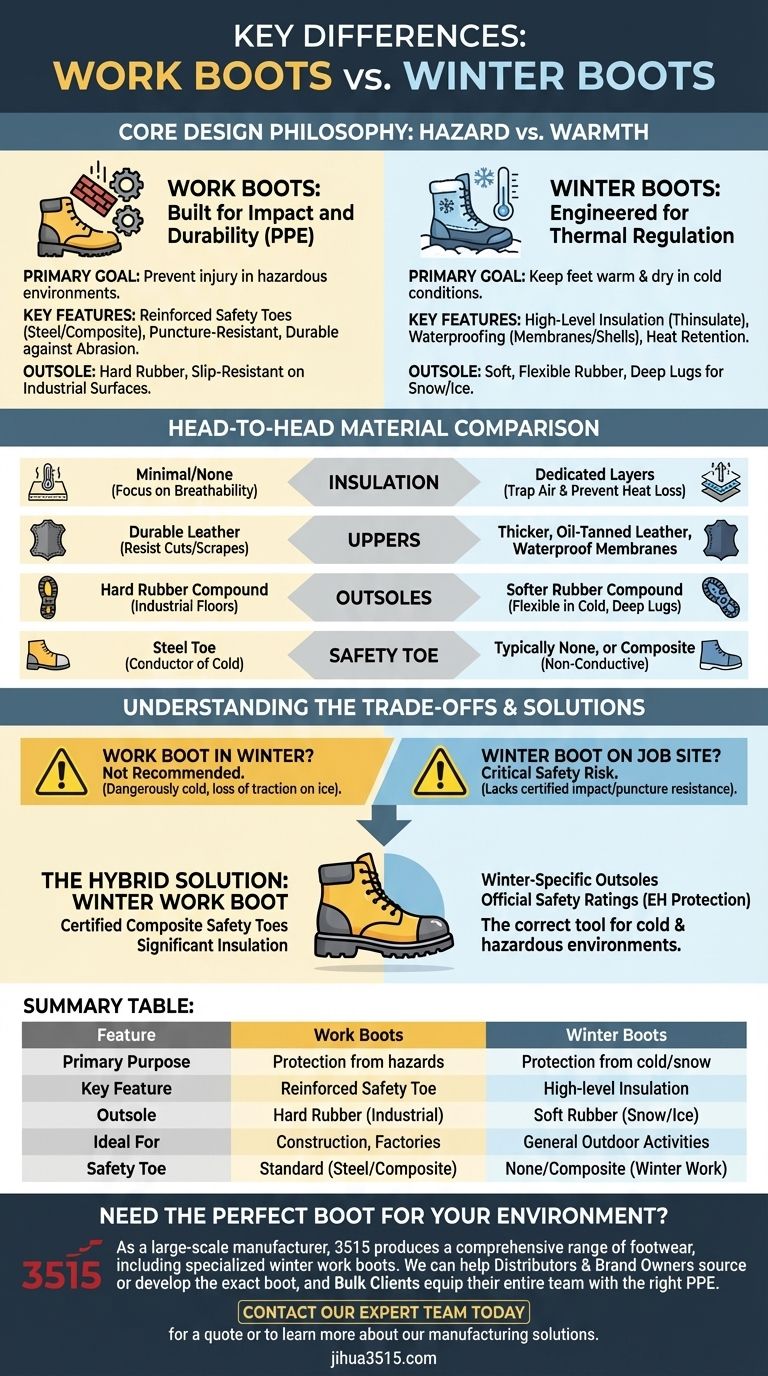
The fundamental difference between winter boots and normal work boots lies in their primary design purpose. A work boot is engineered to provide physical protection from workplace hazards like impact and punctures, while a winter boot is engineered to provide thermal protection from cold, snow, and ice. This core distinction dictates every aspect of their design, from materials to safety features.
Choosing between these boots is not a matter of which is "better," but of aligning the boot's specialized features with your environment. A work boot protects you from what you might drop or step on; a winter boot protects you from the temperature and precipitation around you.

The Core Design Philosophy: Hazard vs. Warmth
The construction of any boot begins with its intended function. For work and winter boots, these functions are fundamentally opposed, leading to two very different products.
Work Boots: Built for Impact and Durability
A standard work boot is a piece of personal protective equipment (PPE). Its main goal is to prevent injury in a hazardous environment.
This is achieved through features like reinforced safety toes (steel or composite), puncture-resistant midsoles, and outsoles designed for slip-resistance on industrial surfaces like concrete or oily floors. Durability against abrasion and chemical spills is paramount.
Winter Boots: Engineered for Thermal Regulation
A winter boot's primary goal is to keep your feet warm and dry in cold conditions. This is a battle against the elements, not physical objects.
Its design centers on insulation (materials like Thinsulate or Primaloft), waterproofing (using membranes like Gore-Tex or rubber shells), and materials that retain heat. Every component is chosen to seal out cold and moisture.
A Head-to-Head Material Comparison
The opposing design philosophies are most evident when comparing the materials and construction of each boot type.
Insulation: The Defining Feature
Work boots typically have minimal to no insulation. Their focus is on breathability and durability, not warmth.
Winter boots are defined by their insulation. They contain dedicated layers of synthetic or natural material (like wool) designed specifically to trap air and prevent heat loss. Many also feature removable liners for faster drying.
Uppers and Materials
Winter boots often use thicker, oil-tanned leather (up to 8oz), which is more resistant to moisture and cold wind. They frequently incorporate waterproof membranes and nylon panels to reduce weight and improve flexibility in the cold.
Work boots use durable leather focused on resisting cuts and scrapes. While often water-resistant, they typically lack the comprehensive waterproofing and thermal properties of a dedicated winter boot.
Outsoles and Traction
While both boot types prioritize grip, they are designed for different surfaces. A work boot's outsole is made of a hard rubber compound that resists wear and provides traction on flat, often slippery, industrial floors.
A winter boot's outsole uses a softer rubber compound that stays flexible in freezing temperatures, preventing it from becoming hard and slick. It features deep, aggressive lugs designed to bite into snow and ice.
The Safety Toe Dilemma
The safety toe is the clearest point of divergence. A steel toe, the hallmark of many work boots, is an excellent conductor of cold. In a winter boot, it would act as a thermal bridge, rapidly drawing heat away from your foot and causing discomfort or even frostbite.
Because of this, most consumer winter boots lack a safety toe entirely. Specialized winter work boots solve this by using composite safety toes, which provide certified impact protection without the thermal conductivity of steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using the wrong boot for the environment introduces significant risks to both your safety and your comfort.
Can a Work Boot Be Used in Winter?
It is not recommended for prolonged exposure. A standard work boot lacks insulation, leading to dangerously cold feet. Furthermore, its hard rubber outsole can become rigid and lose significant traction on icy surfaces.
Can a Winter Boot Be Used on a Job Site?
This is a critical safety risk. A typical winter boot lacks the certified impact and puncture resistance required for most job sites. Using one in a hazardous environment would be a direct violation of safety protocols.
The Hybrid Solution: The Winter Work Boot
For professionals who need both, a specific category exists: the winter work boot. These boots combine the essential features of both types.
They offer certified composite safety toes, puncture resistance, and official safety ratings (like Electrical Hazard protection) alongside significant insulation and winter-specific outsoles. They are the correct tool for cold and hazardous environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Your selection must be based on the primary risks you face in your daily environment.
- If your primary focus is safety on a construction site or in a factory: You must wear a certified work boot. For cold conditions, invest in a dedicated "winter work boot" that has both insulation and a composite safety toe.
- If your primary focus is warmth during general outdoor activity or low-hazard work: A dedicated winter boot is the superior choice for comfort, traction on ice, and preventing cold-related injury.
- If your primary focus is navigating deep snow and extreme wet conditions: You may need a specialized snow boot, which typically offers more height and superior waterproofing compared to a standard winter boot.
Selecting the right footwear is a crucial decision for your safety and well-being; choose the tool engineered for the specific challenges you face.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Work Boots | Winter Boots |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Protection from workplace hazards (impact, punctures) | Protection from cold, snow, and ice |
| Key Feature | Reinforced safety toe (steel/composite) | High-level insulation (Thinsulate, etc.) |
| Outsole | Hard rubber for slip-resistance on industrial surfaces | Soft, flexible rubber with deep lugs for snow/ice |
| Ideal For | Construction sites, factories, warehouses | General outdoor activities in cold weather |
| Safety Toe | Standard (steel or composite) | Typically none, or composite in winter work boots |
Need the Perfect Boot for Your Environment?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, including specialized winter work boots that combine certified safety features with essential warmth.
We can help you:
- Distributors & Brand Owners: Source or develop the exact boot your market needs, from heavy-duty work boots to insulated winter models.
- Bulk Clients: Equip your entire team with the right PPE for any season, ensuring both safety and comfort.
Let's discuss your specific requirements. Contact our expert team today to get a quote or learn more about our manufacturing solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Premium Insulated Safety Boots and Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
People Also Ask
- How do industrial safety shoes provide protection for personnel? Safeguard Your Team from Heavy Crane Hazards
- What are the primary protective functions of professional Safety Boots within the automotive maintenance process?
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management



















