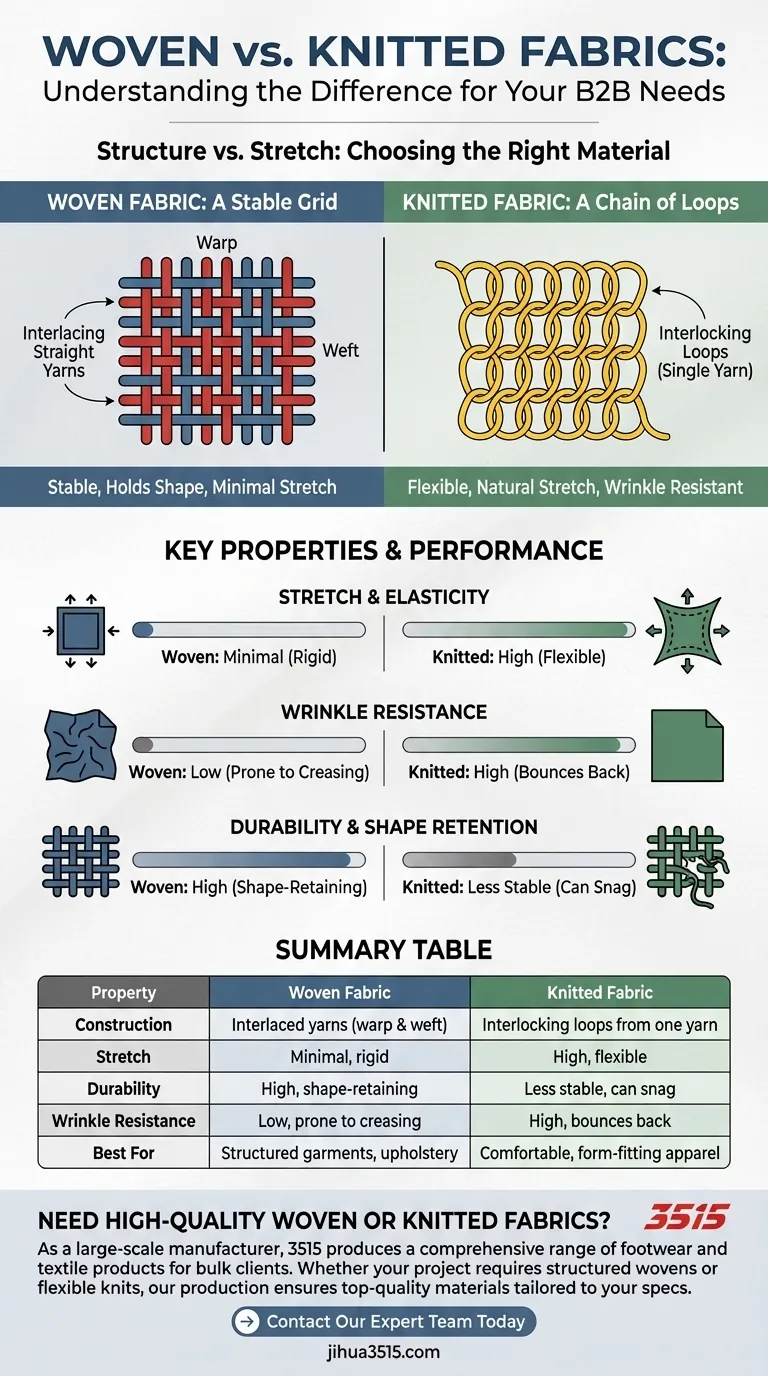
The fundamental difference between woven and knitted fabrics lies in their construction. Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two or more sets of yarns at right angles, creating a stable, grid-like structure. Knitted fabrics, in contrast, are formed by interlocking a series of loops from a single continuous yarn, which gives them inherent flexibility.
Choosing between woven and knitted fabric is a decision between structure and stretch. Woven fabrics offer stability and durability, while knitted fabrics provide flexibility and comfort, each suited for entirely different applications.

The Core Construction Difference
The method used to create a fabric is the primary determinant of its behavior, appearance, and ideal use case.
Woven Fabric: A Stable Grid
Woven fabrics are constructed by interlacing straight yarns. The lengthwise yarns are called the warp, and the crosswise yarns are the weft.
This process, similar to weaving a basket, results in a fabric that is generally very stable and holds its shape well. Common weave patterns include plain, twill (like in denim), and satin.
Knitted Fabric: A Chain of Loops
Knitted fabrics are made from a single yarn that is looped continuously. This structure is more like a series of interconnected knots or a chain-link fence.
This looped structure gives knits their signature characteristic: stretch. Even without elastic fibers, the loops can flatten and extend, allowing the fabric to move with the body.
How Construction Impacts Fabric Properties
The grid-like structure of wovens and the looped structure of knits create a distinct set of performance characteristics.
Stretch and Elasticity
Knits possess significant natural stretch in all directions due to their looped construction. This makes them ideal for comfortable, form-fitting garments like t-shirts and activewear.
Wovens have minimal stretch, typically only a small amount on the diagonal (the "bias"). This rigidity provides structure for items like tailored suits and button-down shirts.
Wrinkle Resistance
The flexible loops in knitted fabrics allow them to resist wrinkling easily. They tend to bounce back to their original shape after being compressed.
Woven fabrics, being more rigid, are more prone to creasing. A crisp linen shirt will wrinkle far more easily than a cotton jersey t-shirt.
Durability and Shape Retention
The tight, interlaced structure of woven fabrics makes them very durable and resistant to distortion. They hold a crisp shape and are excellent for applications requiring strength, such as upholstery or bags.
Knits are less dimensionally stable and can be prone to snagging if a loop is caught. Over time, they may also stretch out of shape if not cared for properly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither fabric type is universally superior; the "better" choice is always dependent on the goal. Understanding their limitations is key to a successful outcome.
The Challenge of Knits: Snagging and Curling
The primary weakness of knits is their susceptibility to snagging. A pulled yarn can create a "run" or ladder in the fabric. Additionally, the cut edges of most knit fabrics tend to curl, which can make sewing more challenging.
The Limitation of Wovens: Fraying and Rigidity
The cut edges of a woven fabric will unravel or fray if not finished properly with a seam or hem. Their lack of stretch means they cannot accommodate movement without the use of darts, gussets, or other tailoring techniques to create shape.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Use the fabric's inherent properties to your advantage by matching them to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is comfort and form-fitting garments: Choose a knitted fabric like jersey or rib knit for its natural stretch and wrinkle resistance.
- If your primary focus is structure and long-term durability: Opt for a woven fabric like twill, canvas, or poplin for items that need to hold a crisp shape.
- If your primary focus is breathability in warm weather: Select a lightweight, loosely woven fabric like linen or chambray that allows air to pass through easily.
Understanding the simple distinction between an interlocked loop and an interlaced grid empowers you to select the perfect fabric for any purpose.
Summary Table:
| Property | Woven Fabric | Knitted Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Interlaced yarns (warp & weft) | Interlocking loops from one yarn |
| Stretch | Minimal, rigid | High, flexible |
| Durability | High, shape-retaining | Less stable, can snag |
| Wrinkle Resistance | Low, prone to creasing | High, bounces back |
| Best For | Structured garments, upholstery | Comfortable, form-fitting apparel |
Need High-Quality Woven or Knitted Fabrics for Your Brand?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear and textile products for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether your project requires the structured durability of wovens or the flexible comfort of knits, our production capabilities ensure top-quality materials tailored to your specifications.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your fabric needs and discover how we can bring value to your supply chain.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Moc Toe Wedge Sole Work Boots for Wholesale and Private Label
- Wholesale Leather Work Boots with Customizable Wedge Sole for Brands
- Wholesale Durable Leather Work Boots | 8-Inch Goodyear Welt Manufacturer
- Durable Leather Work Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Durable High-Traction Canvas Sneakers Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What is the primary role of anti-slip safety shoes in palm oil mill boiler stations? Ensure Worker Safety & Stability
- How do wedge sole work boots prevent slips and falls? Maximize Grip on Concrete & Hard Floors
- Why is it important to take care of your feet? Secure Your Mobility and Overall Health
- Why are slip-on moc toe shoes a practical choice for formal events? Unlock Effortless Style & Comfort
- What are the important characteristics for work boot soles? Match the Sole to Your Job for Safety & Comfort



















