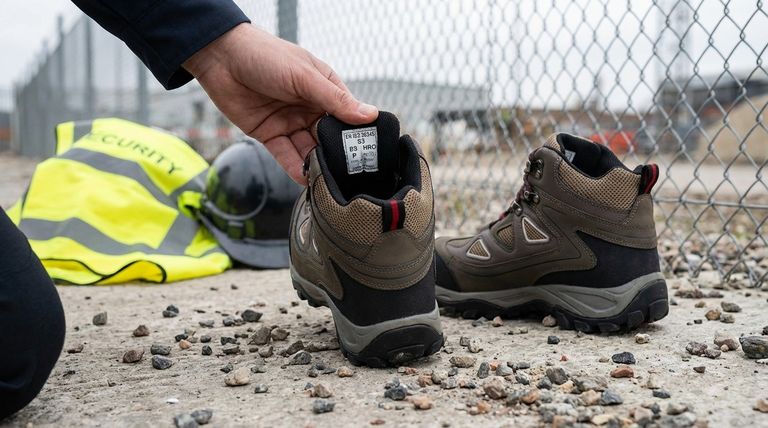
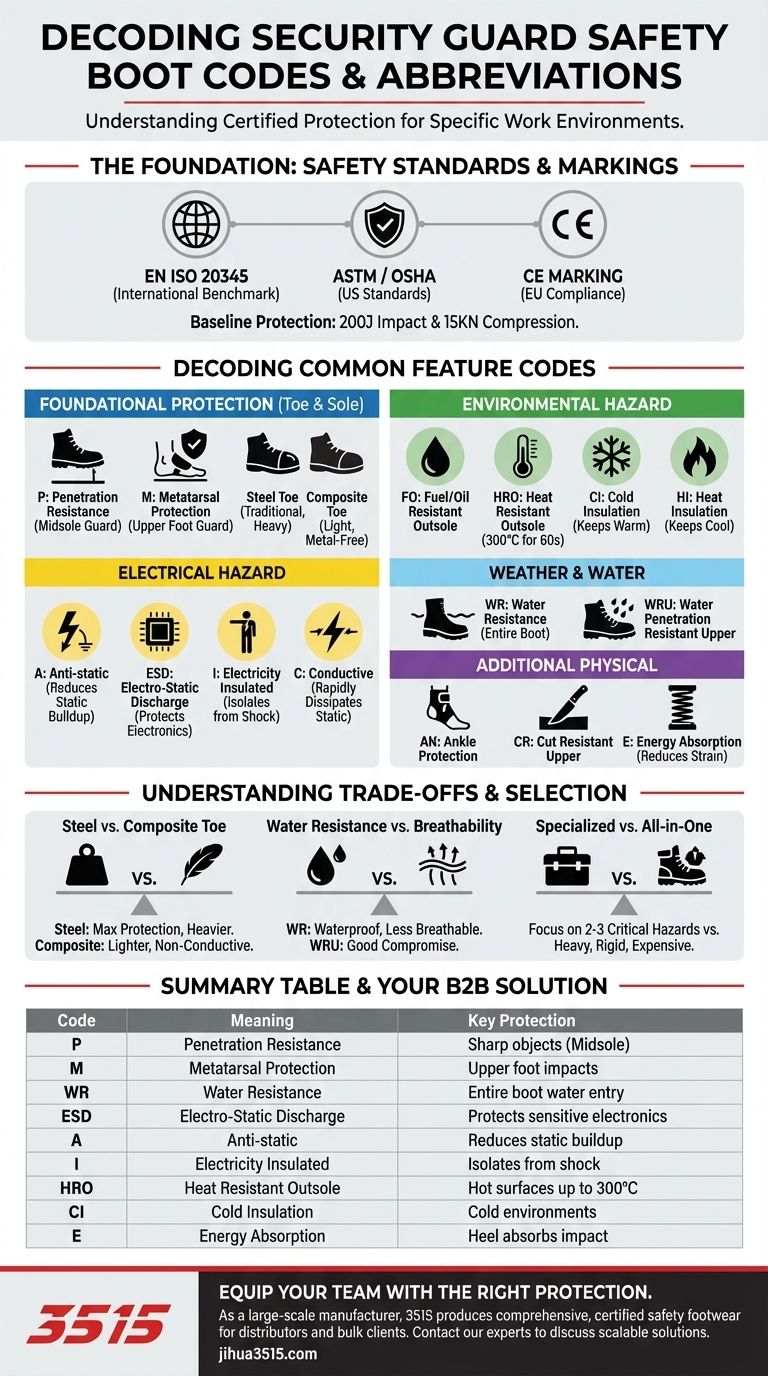
At its core, understanding the codes on security safety boots is about translating a series of letters into a clear picture of the protection they offer. These abbreviations are a universal language governed by safety standards, indicating specific resistances to hazards like impact, penetration, water, and electrical shock.
Choosing the right safety boot isn't about finding one with the most features. It's about accurately matching the boot's certified protections, indicated by its codes, to the specific and predictable hazards of your work environment.

Beyond the Codes: Understanding Safety Standards
Before decoding the individual abbreviations, it's crucial to recognize the governing standards. These frameworks ensure that when a boot is marked with a code, it has passed a specific, measurable test.
The Role of EN ISO Standards
The most common international standard is EN ISO 20345. This is the benchmark for what is legally considered "safety footwear."
Its primary requirement is that the boot must include a toe cap that protects against a 200-joule impact and a 15 Kilonewton (KN) compression force.
The Role of ASTM and OSHA Standards
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets the requirements for workplace safety.
OSHA mandates that safety footwear meets standards set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). An ASTM rating ensures the boot has been certified for impact resistance, compression resistance, and other specific hazards.
The CE Marking
The CE marking found on many boots signifies that the product complies with the essential health and safety requirements of European Union (EU) personal protective equipment (PPE) regulations.
Decoding the Most Common Safety Features
These codes are typically found on the boot's tongue or lining. They allow you to verify its specific protections at a glance.
Foundational Protection (Toe & Sole)
- P: Penetration Resistance. A steel or composite midsole is included to protect against sharp objects like nails piercing the sole.
- M: Metatarsal Protection. A built-in guard shields the upper foot (metatarsal bones) from impacts.
- Toe Caps: While not a letter code, the type is critical. Steel toe is the traditional standard, while Composite toe caps are made of non-metal materials like carbon fiber or plastic, making them lighter and suitable for metal-free environments.
Environmental Hazard Protection
- FO: Fuel/Oil Resistant. The outsole will not degrade when exposed to hydrocarbons like petrol and oil.
- HRO: Heat Resistant Outsole. The sole can withstand contact with a hot surface up to 300°C for 60 seconds.
- CI: Cold Insulation. Provides insulation against cold environments, keeping your feet warm.
- HI: Heat Insulation. Provides insulation against heat from the ground up.
Electrical Hazard Protection
- A: Anti-static. Reduces the buildup of static electricity, dissipating it to the ground. This minimizes the risk of a spark.
- ESD: Electro-Static Discharge. Offers a lower electrical resistance than Anti-static boots. This is critical for environments with sensitive electronic components.
- I: Electricity Insulated. Provides the highest level of protection from electric shock by isolating the wearer from the ground.
- C: Conductive. Offers the least electrical resistance, designed to dissipate static electricity buildup as quickly as possible.
Weather and Water Resistance
- WR: Water Resistance. The entire boot is constructed to prevent water from entering for a specified duration.
- WRU: Water Penetration Resistant Upper. The upper material of the boot (leather or fabric) is treated to resist water absorption and penetration.
Additional Physical Protections
- AN: Ankle Protection. The boot includes additional reinforcement and support for the ankle area.
- CR: Cut Resistant Upper. The boot's upper material provides a degree of protection against cuts from sharp objects.
- E: Energy Absorption. The heel region is designed to absorb impact energy, reducing strain on the feet and legs during long shifts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a boot is a balancing act. More features often mean more weight and less flexibility.
Steel Toe vs. Composite Toe
Steel offers maximum protection against impact and compression but is heavier and conducts cold or heat. Composite is much lighter and doesn't conduct temperature but may be bulkier to achieve the same safety rating.
Water Resistance vs. Breathability
A fully waterproof (WR) boot is excellent for wet conditions but can limit breathability, potentially causing discomfort on long, dry shifts. A boot with a water-resistant upper (WRU) offers a good compromise for mixed conditions.
Specialized vs. All-in-One
A boot loaded with every code—P, M, WR, CI, HRO—will be heavy, rigid, and expensive. It is far better to identify the 2-3 most critical hazards of your specific role and choose a boot designed to counter them effectively.
How to Select the Right Boot for Your Patrol
Analyze your typical work environment and choose a boot with codes that directly address your risks.
- If your primary focus is an indoor corporate or retail site: Prioritize comfort (E), slip resistance, and potentially ESD if you work near sensitive electronics.
- If your primary focus is an outdoor or construction site patrol: Your non-negotiables are a protective toe cap, P for penetration resistance, and WR or WRU for water resistance.
- If your primary focus is an industrial site with electrical risks: You must critically distinguish between A, ESD, and I to match the specific electrical hazard present.
- If your primary focus is all-weather patrol in extreme temperatures: Look for CI for cold insulation or HI/HRO for heat insulation to ensure comfort and safety.
Understanding these codes transforms a simple purchase into a critical decision for your daily safety and comfort.
Summary Table:
| Code | Meaning | Key Protection |
|---|---|---|
| P | Penetration Resistance | Steel/composite midsole vs. sharp objects |
| M | Metatarsal Protection | Guard for upper foot bones from impacts |
| WR | Water Resistance | Prevents water entry into the entire boot |
| ESD | Electro-Static Discharge | Protects sensitive electronics; dissipates static |
| A | Anti-static | Reduces static electricity buildup |
| I | Electricity Insulated | Isolates wearer from ground for shock protection |
| HRO | Heat Resistant Outsole | Withstands hot surfaces up to 300°C |
| CI | Cold Insulation | Insulates against cold environments |
| E | Energy Absorption | Heel absorbs impact, reduces leg strain |
Ensure Your Team is Equipped with the Right Protection
Decoding safety boot abbreviations is the first step; equipping your security personnel with boots that precisely match their environmental hazards is the next. As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of protective shoes and boots, ensuring you get exactly the right combination of features—like metatarsal guards, puncture-resistant soles, or electrical hazard protection—without unnecessary weight or cost.
Let us help you enhance on-the-job safety and comfort. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and explore our scalable manufacturing solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture
- What are the primary protective functions of professional Safety Boots within the automotive maintenance process?
- What are the differences between steel toe, composite toe, and alloy toe Wellington boots? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job
- Why can metal protective toecaps become a risk factor for dorsal foot ulcers? Learn to Prevent Pressure Point Injuries



















