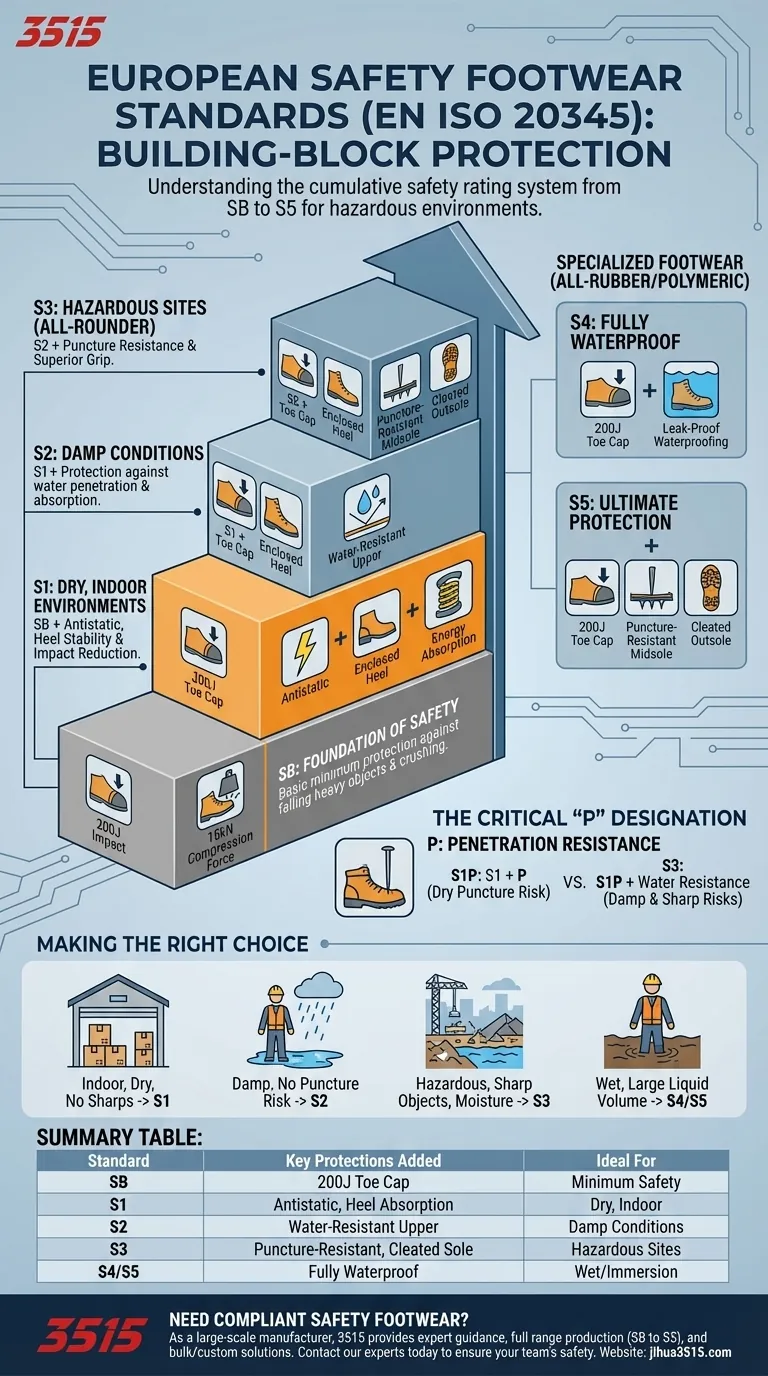
At its core, European safety footwear is categorized by a system of cumulative standards, starting with the basic SB rating and progressing up to S5. Each subsequent category incorporates all the protections of the levels below it while adding a new, specific safety feature.
The key to understanding these standards is recognizing their building-block nature. An S3 boot doesn't just have one feature; it contains all the safety elements of an S2, an S1, and the foundational SB rating, making it a comprehensive solution for hazardous environments.

The Foundation of Safety: The SB Standard
What SB Guarantees
The SB (Safety Basic) rating is the minimum standard for safety footwear.
Any boot labeled SB must have a toe cap that withstands a 200-joule impact and a 15-kilonewton compression force. This protects your toes from heavy falling objects and crushing.
Building on the Basics: The "S" Categories Explained
S1: Protection for Dry, Indoor Environments
The S1 standard includes all the features of SB and adds three more.
It requires the footwear to have antistatic properties, a fully enclosed heel for stability, and energy absorption in the heel region to reduce impact on the body. This makes it ideal for indoor work like logistics or manufacturing where there is no risk of water exposure.
S2: Adding Water Resistance for Damp Conditions
S2 footwear provides all the protection of the S1 standard but adds one critical feature.
It specifies that the upper material must be resistant to water penetration and absorption. This is designed for individuals who work outdoors or in damp conditions where protection from liquids is necessary, but full waterproofing isn't.
S3: The All-Rounder for Hazardous Sites
S3 is one of the most common and comprehensive standards for general construction and industrial work.
It combines all the features of an S2 boot—including the toe cap, antistatic properties, and water resistance—and adds a puncture-resistant midsole and a cleated outsole for superior grip.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical "P" Designation
What "P" Means: Penetration Resistance
You will often see footwear labeled with a "P" suffix, such as S1P.
This "P" indicates that the footwear has a penetration-resistant midsole added to its base standard. An S1P boot, for example, has all the features of an S1 boot plus protection against sharp objects from below.
S1P vs. S3: A Common Point of Confusion
It is crucial to understand the difference between S1P and S3.
An S1P boot protects against punctures but is not required to have the water-resistant upper of an S2 or S3 boot. An S3 boot is essentially an S1P boot that also meets the S2 water resistance requirement, making it suitable for both sharp and damp environments.
Specialized Footwear: S4 and S5 for Full Immersion
Understanding S4
S4 and S5 boots are typically all-rubber or all-polymeric footwear, like safety wellingtons.
An S4 boot is fully waterproof and leak-proof. It also includes all the standard protections of an S1 boot, such as a 200-joule toe cap and antistatic properties.
The Ultimate Protection: S5
S5 is the highest level of this standard. It has all the features of an S4 boot—complete waterproofing and S1 protection—but adds a puncture-resistant midsole and a cleated outsole, just like the S3 standard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Your work environment dictates the level of protection you need. Use your risk assessment to determine the right standard.
- If your primary focus is indoor work with no risk of water or sharp objects: S1 provides the essential baseline for professional safety and comfort.
- If your primary focus is working in damp conditions without puncture risk: S2 offers the necessary water resistance to keep you dry.
- If your primary focus is hazardous sites with risks from sharp objects and moisture: S3 is the comprehensive standard that provides all-around protection.
- If your primary focus is working with large volumes of liquid or in fully wet conditions: S4 or S5 boots are required for complete waterproof integrity.
Choosing the correct safety rating is a non-negotiable step in ensuring your personal safety on the job.
Summary Table:
| Standard | Key Protections Added | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| SB | 200J toe cap | Minimum safety requirement |
| S1 | Antistatic, heel energy absorption | Dry, indoor environments |
| S2 | Water-resistant upper | Damp conditions |
| S3 | Puncture-resistant midsole, cleated outsole | Hazardous sites (sharp objects, moisture) |
| S4/S5 | Fully waterproof (all-rubber/polymeric) | Wet conditions, liquid immersion |
Need Compliant Safety Footwear for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified work boots and shoes for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We ensure every pair meets the precise European safety standards your business requires.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Help you select the correct S-rating (S1 to S5) for your specific work environment.
- Full Range Production: Capabilities to manufacture all types of safety footwear, from basic SB to specialized S5 wellingtons.
- Bulk & Custom Solutions: Reliable supply and OEM services for large-volume orders.
Ensure your team's safety with footwear built to standard. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Premium Suede Metatarsal Guard Safety Boots Work Shoes
People Also Ask
- What are the primary protective functions of composite-toe boots? A Guide to Modern Safety Footwear
- What are the differences between steel toe, composite toe, and alloy toe Wellington boots? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job
- What materials are used for safety toes? Choose Steel, Composite, or Aluminum for Your Work Boots
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- What type of footwear is required in meatpacking and poultry plants due to slippery conditions? Essential Safety Boots for Slippery Floors



















