The most common hazards that cause workplace slips and falls are contaminants on the floor. This includes liquids like water, oil, or chemical spills, as well as loose materials such as dust, debris, or misplaced equipment.
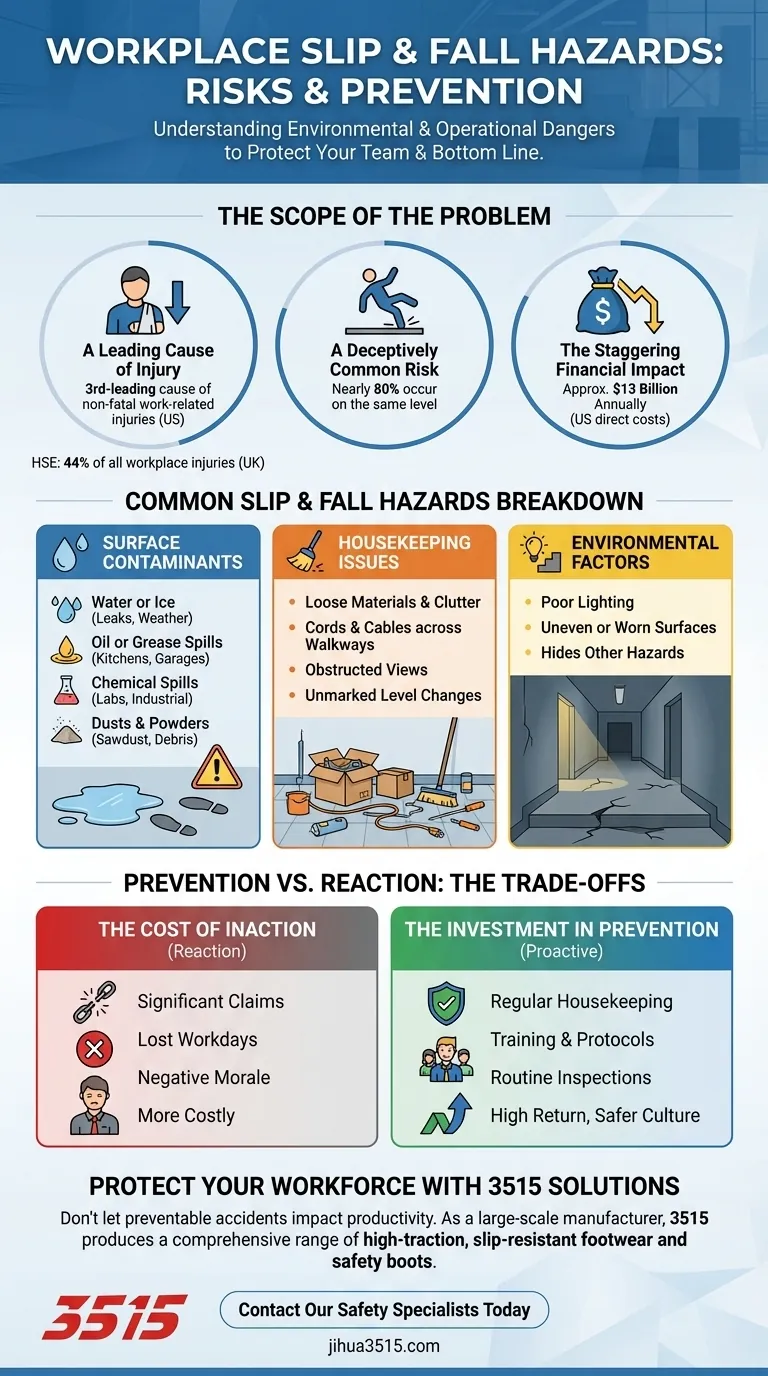
Slips, trips, and falls are not minor inconveniences; they are a leading cause of significant, non-fatal workplace injuries. Understanding the specific environmental and operational hazards is the first step toward effective prevention, protecting both your team and your bottom line.

The Scope of the Problem: Why This Matters
Before identifying specific hazards, it's crucial to understand the scale of the issue. These incidents represent a significant operational and financial risk to every organization.
A Leading Cause of Injury
Slips, trips, and falls are the third-leading cause of non-fatal work-related injuries in the U.S. across all industries.
According to the UK's Health and Safety Executive (HSE), these incidents account for an astonishing 44% of all workplace injuries, making them one of the most frequent causes of harm.
A Deceptively Common Risk
A common misconception is that falls always happen from heights. However, data shows that nearly 80% of these incidents occur on the same level, highlighting the danger of everyday walking surfaces.
The Staggering Financial Impact
The cost of these preventable injuries is immense. In the U.S. alone, they generate approximately $13 billion annually in direct workers' compensation-related costs, not including lost productivity and other indirect expenses.
A Breakdown of Common Slip & Fall Hazards
Hazards can be categorized into several key areas. Proactively identifying them is the most effective form of prevention.
Surface Contaminants
This is the most direct cause of slips. When a substance gets between a person's footwear and the walking surface, it reduces traction.
Key examples include:
- Water or ice from leaks, weather, or cleaning activities
- Oil or grease spills in kitchens, garages, or manufacturing areas
- Chemical spills in laboratories or industrial settings
- Dusts and powders like sawdust or fine debris
Environmental and Housekeeping Issues
The overall condition of the workspace plays a critical role. Poor housekeeping is a direct contributor to increased risk.
Common problems include:
- Loose materials and general clutter on floors
- Cords, cables, or hoses stretched across walkways
- Obstructed views or poor lighting that hides other hazards
- Unmarked changes in floor level or worn, uneven surfaces
Understanding the Trade-offs: Prevention vs. Reaction
Addressing slip and fall hazards requires a conscious choice between investing in prevention or paying the high cost of reaction.
The Cost of Inaction
Ignoring these risks leads to predictable and expensive consequences. A single incident can result in significant workers' compensation claims, lost workdays, and a negative impact on team morale. Reacting after an injury has already occurred is always the more costly option.
The Investment in Prevention
Proactive safety is an investment, not an expense. Implementing regular housekeeping schedules, training employees on spill cleanup, and conducting routine hazard inspections requires time and effort upfront. However, this investment yields a high return by preventing costly injuries and fostering a safer, more productive culture.
How to Apply This to Your Workplace
Use this knowledge to take targeted action based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is immediate risk reduction: Conduct a thorough "hazard hunt" walkthrough of your facility specifically looking for surface contaminants, obstructions, and poor lighting.
- If your primary focus is long-term prevention: Implement a formal housekeeping program with clear responsibilities and provide regular training on spill reporting and cleanup protocols.
- If your primary focus is building a safety culture: Empower all employees to identify and report hazards without delay, and visibly act on those reports to show that their input is valued.
By shifting from a reactive response to proactive hazard management, you can create a safer and more reliable environment for everyone.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Examples | Primary Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Contaminants | Water, oil, grease, chemical spills, dust | Reduces traction, causing immediate slips |
| Housekeeping Issues | Clutter, loose materials, cords across walkways | Creates tripping hazards and obstructs paths |
| Environmental Factors | Poor lighting, unmarked level changes, uneven floors | Hides hazards and causes missteps |
Protect your workforce and your bottom line. Slips and falls are a leading cause of workplace injury, costing businesses billions annually. Don't let a preventable accident impact your team and productivity. As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of high-traction, slip-resistant footwear and safety boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of occupational shoes and boots designed to mitigate these very risks.
Contact our safety specialists today to discuss how our durable, reliable footwear solutions can be a cornerstone of your proactive safety program.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of snake gaiters? Superior Versatility, Breathability & Cost-Effectiveness
- How does industrial-grade sewing equipment contribute to footwear integrity? High-Strength Stitching for Durable Uppers
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of a cotton/polyester blend as a liner material? A Guide to Balanced Performance
- What special types of CORDURA fabric are available? From Waterproof to Flame-Retardant
- What factors should be considered for proper boot fit? A Guide to Avoiding Pain and Blisters
- Why does the rider need new boots for their horse? For Superior Protection During Conditioning
- What are the three types of tall boots? A Guide to Choosing the Right English Riding Boot
- How do statistical and qualitative analysis software assist in interpreting biomechanical data? Elevate Health Insights



















